Windows 10 Mobile: A Retrospective On Microsoft’s Mobile Ambitions
Windows 10 Mobile: A Retrospective on Microsoft’s Mobile Ambitions
Related Articles: Windows 10 Mobile: A Retrospective on Microsoft’s Mobile Ambitions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Windows 10 Mobile: A Retrospective on Microsoft’s Mobile Ambitions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 Mobile: A Retrospective on Microsoft’s Mobile Ambitions

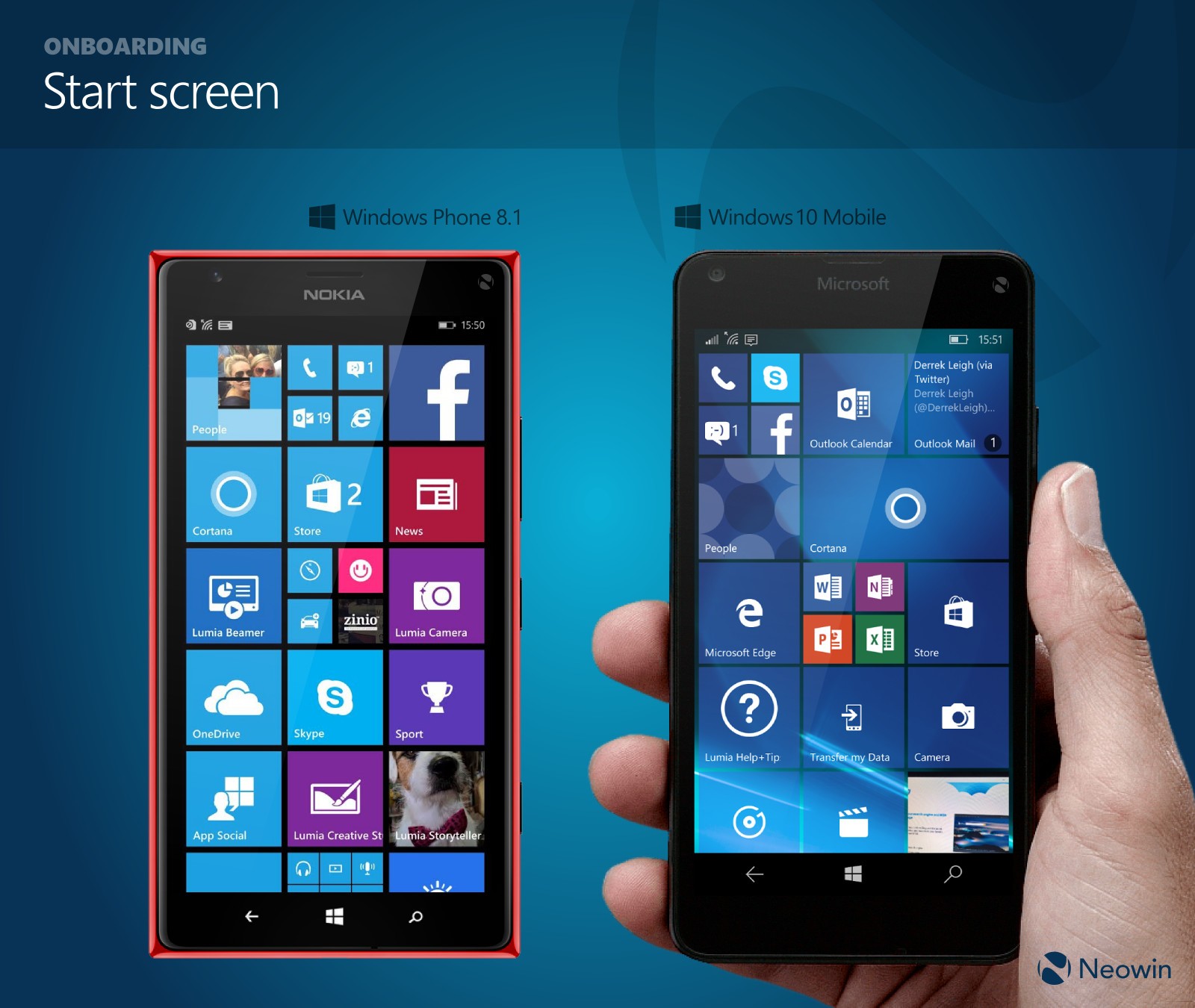
Windows 10 Mobile, released in 2015, represented Microsoft’s ambitious attempt to reclaim a significant share of the mobile operating system market. While ultimately unsuccessful in achieving this goal, the platform offered a unique blend of features and functionality, leaving a lasting impact on the mobile landscape. This article delves into the history, features, and legacy of Windows 10 Mobile, examining its strengths and weaknesses, and its ultimate impact on the mobile ecosystem.
The Rise and Fall of Windows Phone
Prior to Windows 10 Mobile, Microsoft had already ventured into the mobile operating system market with Windows Phone. Released in 2010, Windows Phone aimed to differentiate itself from its dominant competitors, Android and iOS, by emphasizing a user-friendly interface, live tiles, and integration with Microsoft services. This strategy initially garnered positive reception, particularly among users seeking a unique and intuitive mobile experience.
However, Windows Phone struggled to gain widespread adoption. Despite its strengths, the platform faced several challenges. The lack of a robust app ecosystem, compared to its rivals, hindered its appeal to a broader audience. Furthermore, the limited hardware availability and a lack of aggressive marketing hampered its growth.
Windows 10 Mobile: A New Beginning
In 2015, Microsoft launched Windows 10 Mobile, a significant evolution of its mobile platform. This iteration aimed to address the shortcomings of Windows Phone by introducing a unified operating system across multiple devices, including smartphones, tablets, and PCs. This strategy aimed to leverage the strengths of Windows 10’s desktop ecosystem and extend its reach to the mobile realm.
Windows 10 Mobile featured several key improvements over its predecessor:
- Unified Platform: The shared codebase with Windows 10 for desktop devices facilitated a seamless experience across different platforms, enabling users to switch between their phone and PC with ease.
- Enhanced App Ecosystem: The platform benefited from the growing library of Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps, designed to run on both desktops and mobile devices. This broadened the appeal of Windows 10 Mobile by offering access to a wider range of applications.
- Continuum: This feature allowed users to connect their Windows 10 Mobile phone to an external monitor, keyboard, and mouse, transforming it into a desktop experience. This functionality aimed to bridge the gap between mobile and desktop computing, providing users with a flexible and versatile platform.
- Improved Security: Windows 10 Mobile incorporated robust security features, including a secure boot process and Windows Defender, to protect user data from malware and unauthorized access.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite these improvements, Windows 10 Mobile faced persistent challenges that ultimately led to its demise:
- Limited App Availability: While the UWP app ecosystem grew, it still lagged behind the vast app libraries available on Android and iOS. This limited the appeal of Windows 10 Mobile for many users, particularly those seeking a wide range of popular applications.
- Hardware Fragmentation: The lack of a robust hardware ecosystem from various manufacturers hindered the platform’s growth. Unlike Android, which boasted a wide range of device manufacturers, Windows 10 Mobile primarily relied on Microsoft’s own Lumia line of smartphones. This limited the choice and availability of devices for consumers.
- Market Dominance: The dominant market share held by Android and iOS presented a significant hurdle for Windows 10 Mobile to overcome. The established ecosystems of these platforms, coupled with their extensive app libraries and hardware availability, made it difficult for Windows 10 Mobile to compete effectively.
Legacy and Impact
Despite its ultimate failure to gain significant market share, Windows 10 Mobile left a lasting impact on the mobile landscape. Its focus on a unified platform and its innovative features, such as Continuum, demonstrated Microsoft’s commitment to pushing boundaries in mobile computing.
The platform’s legacy also lies in its influence on the development of other mobile operating systems. The concept of a unified platform, with applications designed to run across multiple devices, became a prominent feature in subsequent versions of Android and iOS.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What was the main reason for the failure of Windows 10 Mobile?
The failure of Windows 10 Mobile can be attributed to a combination of factors, including limited app availability, lack of hardware diversity, and the dominant market share of Android and iOS. The platform struggled to gain traction due to its smaller app ecosystem and limited device options, making it difficult to compete with established mobile giants.
2. What were the key features of Windows 10 Mobile?
Windows 10 Mobile featured a unified platform with Windows 10 for desktops, a growing UWP app ecosystem, the Continuum feature for transforming the phone into a desktop experience, and improved security measures.
3. What happened to Windows 10 Mobile?
Microsoft officially discontinued support for Windows 10 Mobile in December 2019. The company shifted its focus to other platforms, including its cloud-based services and its Azure platform.
4. What are some of the lasting impacts of Windows 10 Mobile?
Windows 10 Mobile’s focus on a unified platform and its innovative features, such as Continuum, influenced the development of other mobile operating systems. The concept of a unified platform, with applications designed to run across multiple devices, became a prominent feature in subsequent versions of Android and iOS.
Tips for Windows 10 Mobile Users
1. Explore the UWP App Ecosystem: While the UWP app ecosystem was smaller than those of its competitors, it still offered a wide range of applications. Explore the Windows Store and discover the available apps for various needs.
2. Utilize Continuum: Leverage the Continuum feature to transform your Windows 10 Mobile phone into a desktop experience. Connect your phone to an external monitor, keyboard, and mouse for a more productive and versatile computing environment.
3. Explore Windows 10 Features: Take advantage of the features shared with Windows 10 for desktops, such as the Microsoft Edge browser and Cortana, for a seamless experience across devices.
4. Consider Alternative Options: Since Windows 10 Mobile is no longer supported, consider switching to other mobile operating systems, such as Android or iOS, for access to a wider range of apps and hardware options.
Conclusion
Windows 10 Mobile represents a chapter in Microsoft’s mobile history that ultimately ended in failure. However, the platform’s efforts to bridge the gap between mobile and desktop computing, its focus on a unified platform, and its innovative features left a lasting impact on the mobile landscape. While Windows 10 Mobile may no longer be supported, its legacy serves as a reminder of Microsoft’s ambition and its continued pursuit of innovation in the evolving world of mobile technology.
![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows 10 Mobile: A Retrospective on Microsoft’s Mobile Ambitions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!