Understanding The Missing Local Users And Groups In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Importance of Local Users and Groups
- 3.2 Causes of Missing Local Users and Groups
- 3.3 Troubleshooting and Solutions
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
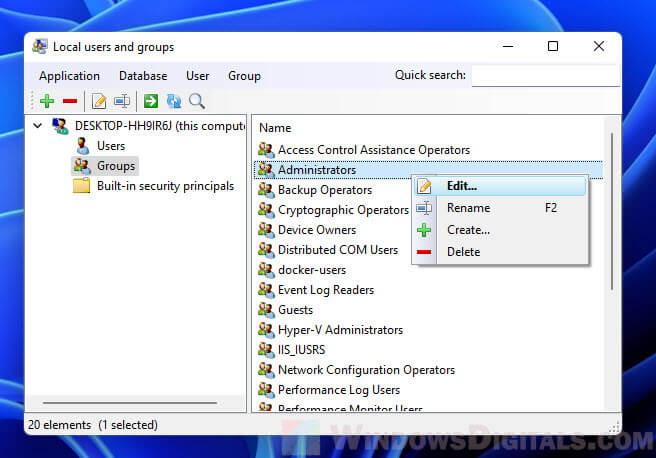
Windows 11, like its predecessors, relies on a robust system of local users and groups to manage access and permissions for various aspects of the operating system. These entities govern what users can do on the computer, from accessing specific files and folders to running applications and making system-level changes. However, instances where local users and groups fail to appear in the user interface can disrupt administrative tasks and lead to confusion. This article delves into the reasons behind this issue, providing a detailed understanding of its causes and offering practical solutions to restore visibility and functionality.
The Importance of Local Users and Groups
Local users and groups are fundamental to maintaining a secure and organized computing environment. They provide a framework for:
- Access Control: Local users and groups dictate which users can access specific files, folders, and applications. This ensures data security and prevents unauthorized access.
- Permission Management: Groups allow administrators to assign permissions to multiple users simultaneously, streamlining the process of granting access to resources.
- Account Management: Local users provide a distinct identity for each individual using the computer, enabling personalized settings, preferences, and data storage.
- System Administration: Administrators leverage local groups to delegate specific tasks and responsibilities to different users, simplifying system management and maintenance.
Causes of Missing Local Users and Groups
The absence of local users and groups in Windows 11 can stem from various factors, each requiring a specific approach to resolve:
1. Incorrect Group Policy Settings:
- Group Policy Object (GPO) Restrictions: Group policies, often implemented in enterprise environments, can restrict access to the local user and group management tools. These policies might be configured to prevent users from viewing or modifying local accounts.
- Hidden Administrative Tools: The "Local Users and Groups" tool might be hidden due to a Group Policy setting. This can occur when the "Administrative Tools" folder is hidden, preventing access to the necessary management tools.
2. Corrupted User Account Database:
- Registry Errors: Errors within the Windows Registry, particularly the sections related to user accounts, can disrupt the proper display of local users and groups.
- File System Issues: Damaged files within the user account database can also lead to inconsistencies and prevent the display of local users and groups.
3. Software Conflicts:
- Third-Party Applications: Certain software applications might interfere with the user account management system, causing inconsistencies in the display of local users and groups.
- Antivirus Software: Overly aggressive antivirus software might block access to critical system files, potentially affecting the display of user accounts.
4. User Account Control (UAC) Settings:
- Elevated Privileges: User Account Control (UAC) settings might require elevated privileges to access local user and group management tools. This can prevent users from viewing or modifying local accounts without proper authorization.
5. Windows Updates:
- Incomplete Updates: Incomplete or corrupted Windows updates can sometimes disrupt the user account management system, leading to the disappearance of local users and groups.
Troubleshooting and Solutions
Addressing the issue of missing local users and groups requires a systematic approach, starting with simple checks and progressing to more advanced solutions:
1. Check Group Policy Settings:
- Access Group Policy Editor: Open the "Run" dialog (Windows key + R) and type "gpedit.msc" to access the Local Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to User Configuration: Expand "User Configuration" and then "Administrative Templates."
- Verify Policy Settings: Check for policies related to "Local Users and Groups" or "Administrative Tools" that might be restricting access.
- Disable or Modify Policies: If necessary, disable or modify the relevant policies to restore access to the user account management tools.
2. Ensure Administrative Tools Visibility:
- Check Folder Visibility: Open File Explorer and navigate to "C:WindowsSystem32".
- Enable Hidden Items: In the "View" tab, select "Hidden Items" to ensure all files and folders are visible.
- Locate "lusrmgr.msc": Verify that the "lusrmgr.msc" file is present, which is the executable for the "Local Users and Groups" tool.
3. Verify Registry Integrity:
- Back Up Registry: Before making any changes, create a backup of the Windows Registry to prevent data loss.
- Check for Errors: Use the "regedit" tool (Windows key + R, type "regedit") to check for any errors in the registry keys related to user accounts (e.g., HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionProfileList).
- Repair Corrupted Entries: If errors are found, use caution when editing the registry. Incorrect modifications can damage the operating system. Consider consulting with a qualified technician for assistance.
4. Troubleshoot Software Conflicts:
- Temporarily Disable Third-Party Applications: Disable any recently installed software or applications that might be interfering with user account management.
- Check Antivirus Settings: Review your antivirus software settings and ensure they are not blocking access to critical system files related to user accounts.
5. Adjust User Account Control Settings:
- Access UAC Settings: Open "Control Panel" and navigate to "User Accounts."
- Adjust UAC Level: Depending on your needs, adjust the User Account Control (UAC) level to either "Never notify" or "Notify me only when apps try to make changes to my computer."
6. Perform System File Check:
- Open Command Prompt: Open the "Run" dialog (Windows key + R) and type "cmd" to open Command Prompt.
- Run System File Checker: Type "sfc /scannow" and press Enter. This will scan for and repair corrupted system files.
7. Reinstall Windows (Last Resort):
- Backup Data: Before reinstalling Windows, back up all important data and files.
- Reinstall Operating System: Use the Windows installation media to reinstall the operating system, which will restore the user account management system to a default state.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why are local users and groups important?
Local users and groups are essential for managing access and permissions on your computer. They ensure data security, prevent unauthorized access, and streamline system administration.
2. What are the most common causes of missing local users and groups?
The most common causes include incorrect Group Policy settings, corrupted user account databases, software conflicts, UAC settings, and Windows update issues.
3. How can I troubleshoot the issue of missing local users and groups?
Troubleshooting involves checking Group Policy settings, verifying registry integrity, troubleshooting software conflicts, adjusting UAC settings, performing a system file check, and, as a last resort, reinstalling Windows.
4. Can I create new local users if I can’t see the existing ones?
Creating new local users might be possible even if existing ones are not visible. However, it is recommended to address the underlying cause of the issue before creating new accounts.
5. What are some tips for preventing this issue in the future?
To prevent future issues, ensure regular system maintenance, including running system file checks, updating Windows regularly, and avoiding unnecessary software installations.
Conclusion
The absence of local users and groups in Windows 11 can be a frustrating issue, but with a methodical approach and the right troubleshooting steps, you can restore their visibility and functionality. Understanding the potential causes and their corresponding solutions provides the necessary tools to address this problem effectively. Remember to back up your data before making any significant changes to the system, and if you encounter difficulties, consider seeking assistance from a qualified technician. By maintaining a proactive approach to system management and security, you can ensure a smooth and reliable computing experience.
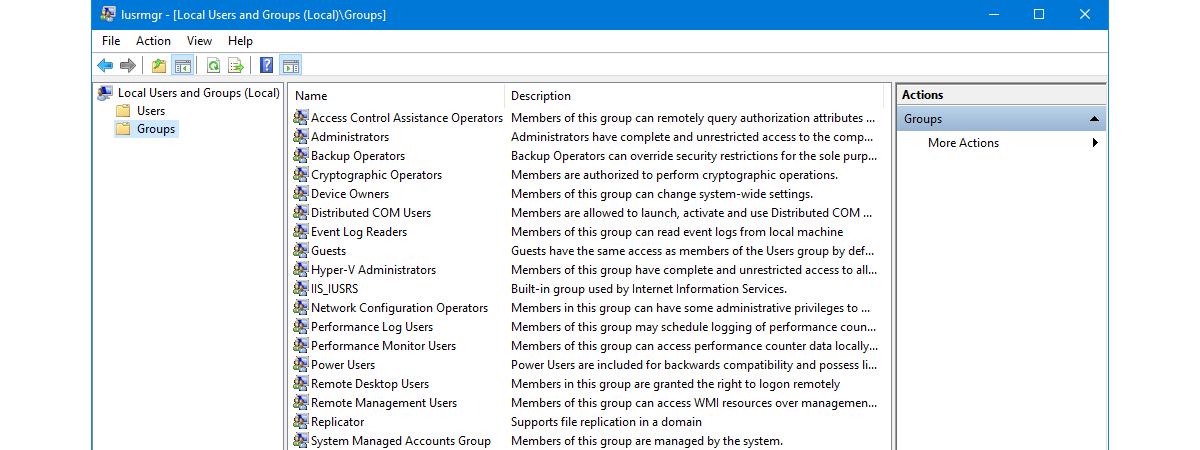


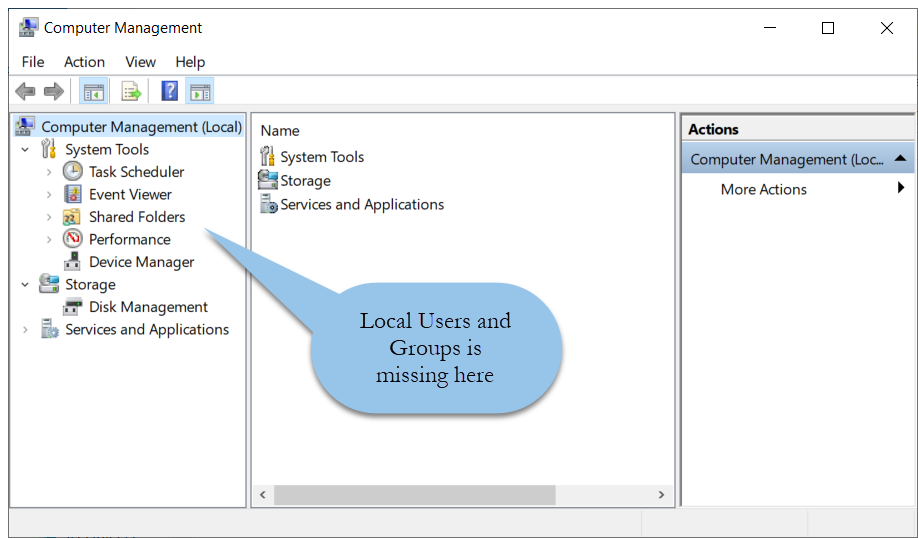
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Missing Local Users and Groups in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!