Understanding Memory Usage In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Memory Usage in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Memory Usage in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Memory Usage in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Memory Usage in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

Windows 11, like any modern operating system, relies heavily on system memory (RAM) to function efficiently. Understanding how memory is utilized and managing it effectively is crucial for ensuring a smooth and responsive computing experience. This article delves into the intricacies of memory usage in Windows 11, providing a comprehensive overview of its importance, factors influencing its consumption, and practical strategies for optimization.
The Role of Memory in Windows 11
Memory, or Random Access Memory (RAM), serves as the primary workspace for your computer. It temporarily stores data and instructions that the CPU (Central Processing Unit) needs to access quickly. Think of it as a temporary holding area for active programs, files, and information that the system is currently working with.
Key Functions of Memory in Windows 11:
- Program Execution: When you launch an application, its code and associated data are loaded into memory. This allows the CPU to access and execute the program’s instructions rapidly.
- Data Storage: Memory stores temporary data that is actively being used by programs, such as open documents, spreadsheets, and browser tabs.
- Operating System Operations: Windows 11 itself requires a significant amount of memory to manage system processes, run background services, and handle various system tasks.
Factors Influencing Memory Usage:
Several factors contribute to the amount of memory your Windows 11 system consumes. Understanding these factors can help you identify potential areas for optimization:
- Number of Running Programs: Each application you have open consumes a portion of your system’s memory. The more programs you run concurrently, the higher the memory usage.
- Program Complexity: Some applications, especially resource-intensive ones like video editing software, gaming platforms, and web browsers with multiple tabs, demand substantial memory to operate effectively.
- Background Processes: Windows 11 runs various background processes, such as system updates, antivirus scans, and indexing services, that contribute to memory usage.
- System Configuration: The configuration of your Windows 11 system, including the amount of installed RAM, the number of virtual memory pages, and the settings of various system services, can significantly impact memory consumption.
- Hardware: The capabilities of your hardware, including the speed of your CPU and the type of RAM installed, also play a role in memory usage.
Monitoring Memory Usage in Windows 11:
Windows 11 provides built-in tools for monitoring memory usage:
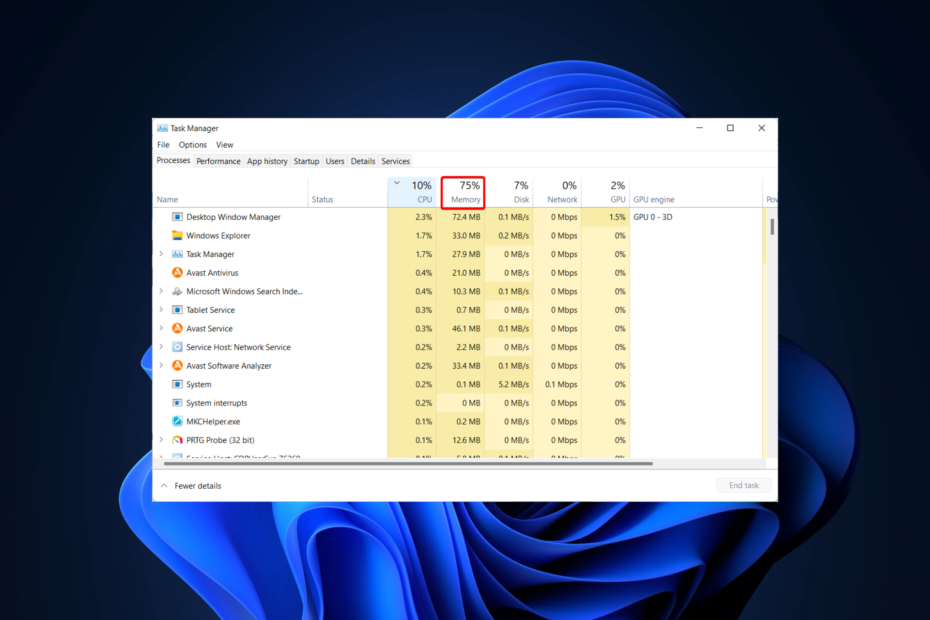
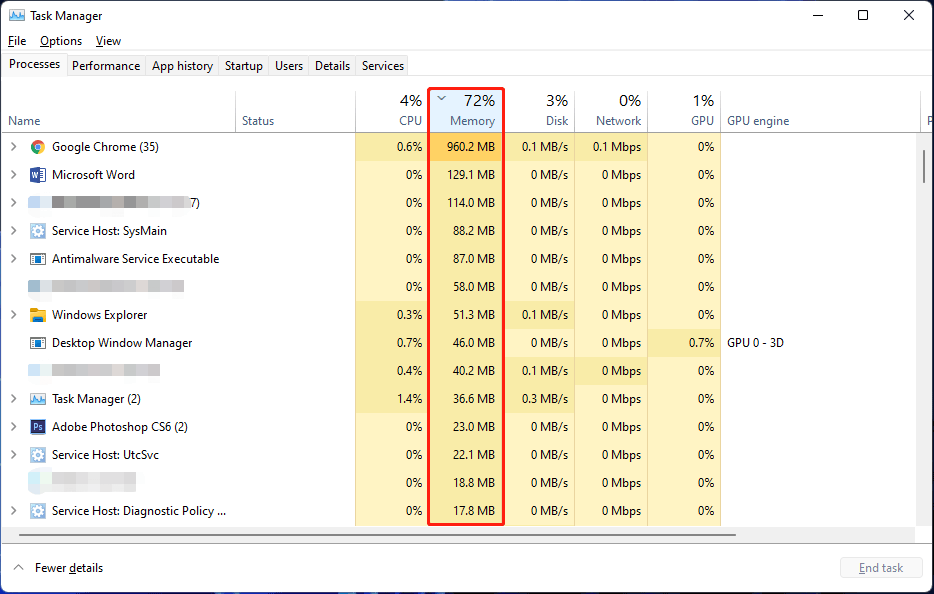
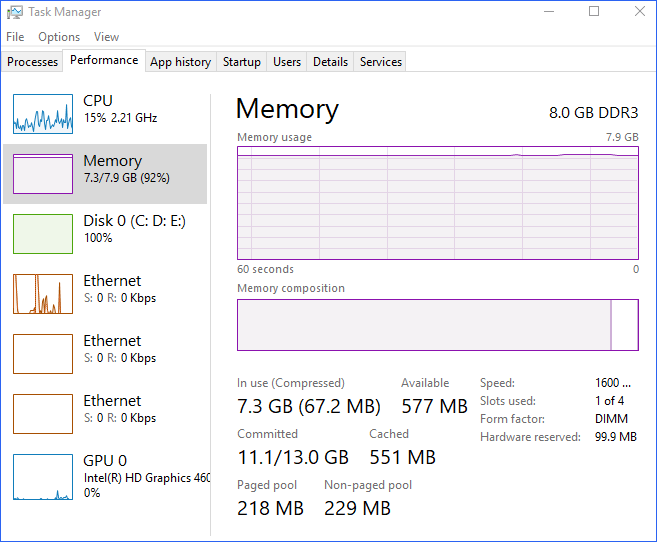
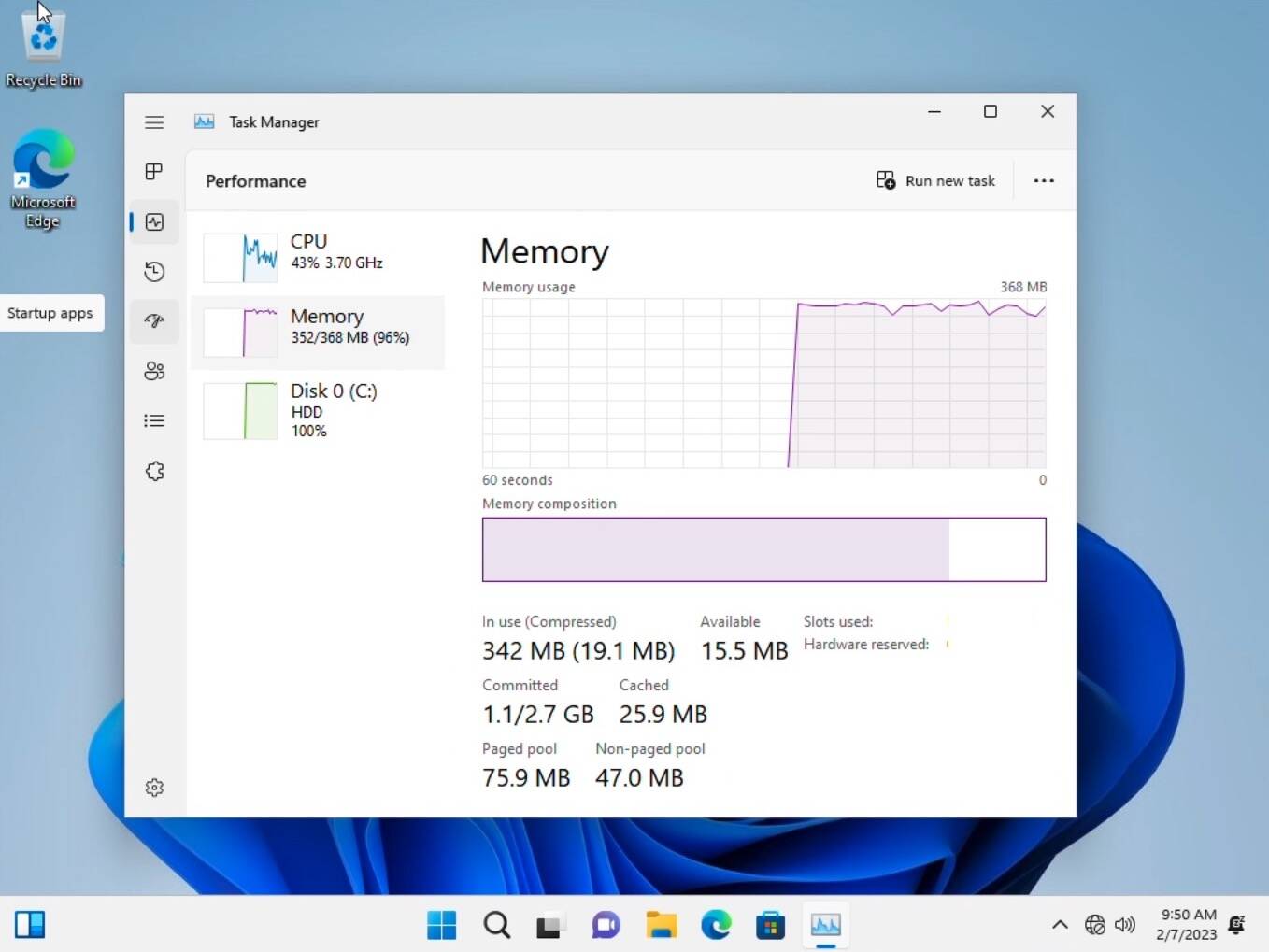
- Task Manager: Access Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc. The "Performance" tab provides a detailed overview of memory usage, including the amount of physical memory available, the amount currently being used, and the breakdown of memory consumption by different processes.
- Resource Monitor: For a more comprehensive analysis, use Resource Monitor, accessible through the "Performance" tab in Task Manager. This tool offers a detailed breakdown of memory usage across various categories, including system processes, user processes, and hardware components.
Optimizing Memory Usage in Windows 11:
Several strategies can help you optimize memory usage in Windows 11, enhancing system performance and responsiveness:
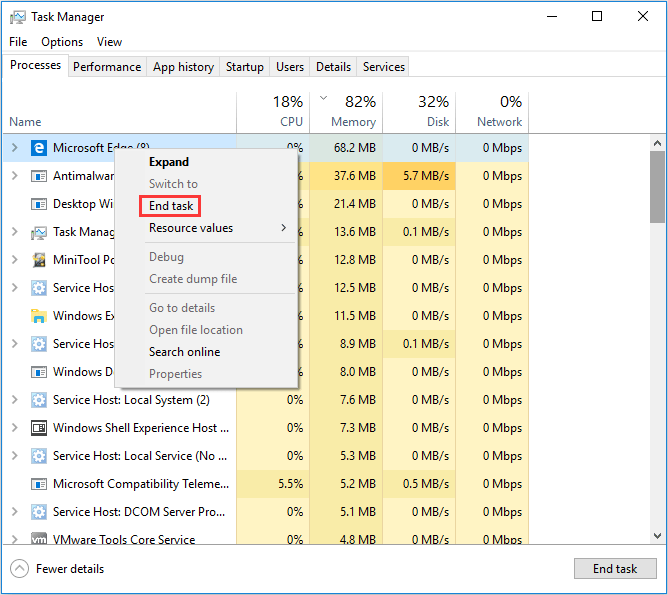
- Close Unused Programs: Regularly close applications you are not actively using. This frees up memory for other programs and processes.
- Manage Startup Programs: Reduce the number of programs that automatically launch when you start Windows 11. Many unnecessary programs can consume memory without providing any immediate benefit.
- Disable Background Processes: Review and disable unnecessary background processes that consume significant memory. Use the Task Manager’s "Startup" tab to manage startup programs and the "Processes" tab to view and disable background processes.
- Adjust Virtual Memory: Virtual memory, also known as a "page file," allows Windows 11 to use hard drive space as temporary memory when physical memory is insufficient. By adjusting the size of the virtual memory file, you can optimize memory management.
- Upgrade RAM: If you consistently experience high memory usage and performance issues, consider upgrading your computer’s RAM. More RAM provides more space for programs and processes to run efficiently.
- Regular System Maintenance: Regularly perform system maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, and updating drivers, to ensure optimal system performance and memory management.
FAQs about Memory Usage in Windows 11:
Q: What is the recommended amount of RAM for Windows 11?
A: The recommended amount of RAM for Windows 11 depends on your usage needs. For basic tasks like web browsing and document editing, 8GB of RAM is generally sufficient. For more demanding activities like gaming, video editing, or running multiple applications simultaneously, 16GB or more is recommended.
Q: How do I know if my computer has enough RAM?
A: If you frequently experience slow performance, lagging applications, or excessive page file usage, your computer may be running low on RAM. You can check your available RAM in the Task Manager’s "Performance" tab.
Q: What happens when my computer runs out of memory?
A: When your computer runs out of physical memory, it starts using virtual memory, which is slower and can lead to performance degradation. You might notice lag, stuttering, or application crashes.
Q: What are the signs of a memory leak?
A: A memory leak occurs when a program fails to release memory it no longer needs, leading to a gradual increase in memory usage over time. Signs of a memory leak include slow performance, application crashes, and a high percentage of memory usage even when running few programs.
Q: How can I fix a memory leak?
A: To fix a memory leak, you need to identify the program causing the issue. You can use Task Manager or Resource Monitor to track down the culprit. Once identified, you may need to update the program, reinstall it, or contact the developer for support.
Tips for Managing Memory Usage in Windows 11:
- Use a memory optimization tool: Third-party memory optimization tools can help analyze your system’s memory usage and identify potential areas for improvement.
- Monitor memory usage regularly: Regularly check your system’s memory usage to identify potential issues or patterns.
- Keep your system updated: Ensure you have the latest Windows 11 updates and driver updates to improve system performance and memory management.
- Avoid running too many programs simultaneously: Limit the number of programs you have open at once to reduce memory consumption.
- Consider using a lightweight browser: Some web browsers consume more memory than others. Consider using a lightweight browser like Opera or Vivaldi for better memory efficiency.
Conclusion:
Understanding memory usage in Windows 11 is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance and responsiveness. By monitoring memory consumption, identifying factors influencing usage, and implementing optimization strategies, you can ensure your system runs smoothly and efficiently. Remember, regular system maintenance, monitoring, and a proactive approach to memory management are key to a seamless computing experience.

![FIX Windows 11 High Memory Usage RAM Usage In Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/q--cLG7MnGM/maxresdefault.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Memory Usage in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!