Understanding Drive Letters And Networked Storage In Windows 11
Understanding Drive Letters and Networked Storage in Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding Drive Letters and Networked Storage in Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Drive Letters and Networked Storage in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Drive Letters and Networked Storage in Windows 11
The concept of a "J drive" in Windows 11, or any other version of Windows, is not a specific drive designation like C: or D:. Instead, it refers to a networked storage location accessed through a drive letter. This drive letter, in this case, "J," is assigned by the operating system to represent a specific shared folder or resource on another computer or server within the network.
Networked Storage: A Foundation for Sharing and Collaboration
The ability to access shared resources over a network is fundamental to modern computing. It allows users to:
- Share files and folders: Collaboration becomes efficient as multiple users can access and modify the same documents, images, or other data.
- Centralize data storage: Instead of each user maintaining their own copies of files, data can be stored centrally, simplifying backup and management.
- Reduce storage demands on individual computers: By leveraging shared storage, users can access large files or applications without straining their local hard drive capacity.
Understanding Networked Drive Letters
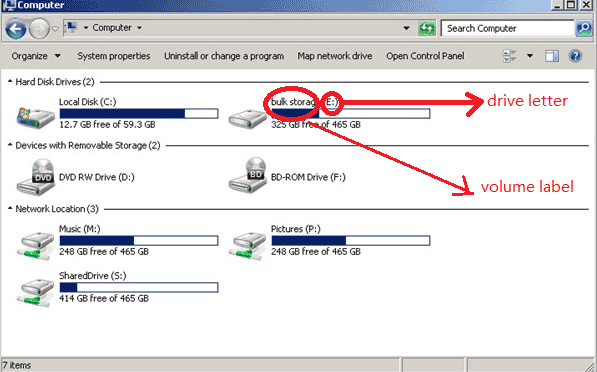
In Windows, networked storage is accessed through a drive letter, which is a single letter assigned to a specific network location. This drive letter functions just like any other local drive on your computer, allowing you to navigate folders, open files, and save data.
Examples of Networked Storage Scenarios
Here are some common scenarios where network drives are utilized:
- Shared network drive on a local server: A company might have a central server storing all employee files, accessible through a drive letter like "J:" or "S:".
- Cloud storage service: Services like Dropbox, OneDrive, and Google Drive can be accessed as network drives, providing a convenient way to manage cloud-based files.
- Remote desktop access: When accessing a remote computer via a remote desktop connection, the remote computer’s drives might appear as mapped network drives on your local machine.
How to Access a Networked Drive in Windows 11
To access a networked drive in Windows 11, you typically need the following information:
- Network path: This is the location of the shared resource, usually in the format "server nameshare name".
- Credentials: You might need to provide a username and password to access the shared resource.
Accessing Networked Drives Using Windows Explorer
- Open File Explorer: Click the File Explorer icon on the taskbar.
- Navigate to "This PC": In the left pane, click "This PC".
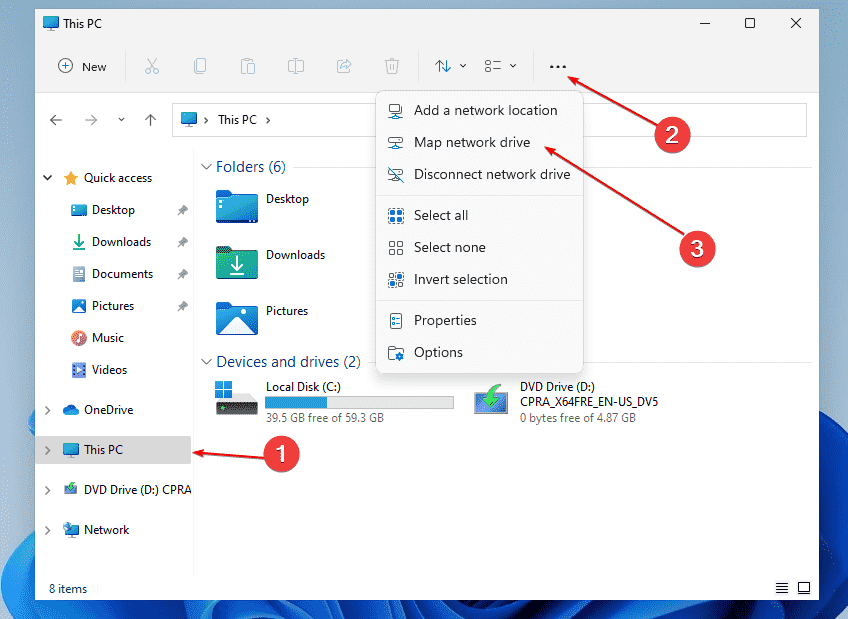
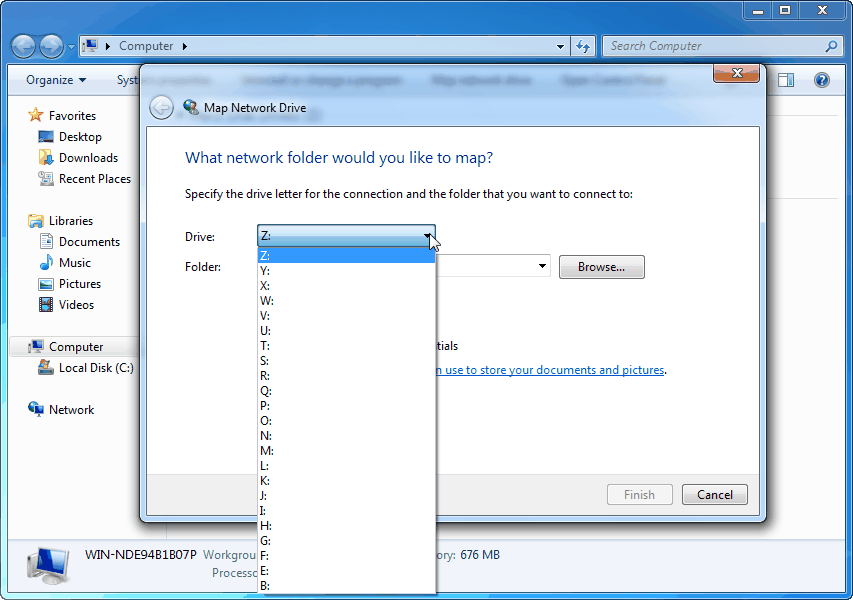
- Click "Map network drive": In the "Computer" tab, click "Map network drive".
- Enter the network path: In the "Folder" field, enter the network path of the shared resource.
- Enter credentials (if required): If prompted, provide your username and password.
- Choose a drive letter: Select a drive letter from the "Drive" dropdown menu.
- Connect: Click "Finish" to connect the network drive.
Accessing Networked Drives Using Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt: Search for "cmd" in the Start menu and run as administrator.
-
Use the "net use" command: Enter the following command, replacing the placeholder values:
net use J: server nameshare name /user:username password- J: The desired drive letter.
- server nameshare name: The network path.
- username: The username for the shared resource.
- password: The password for the shared resource.
Managing Networked Drives
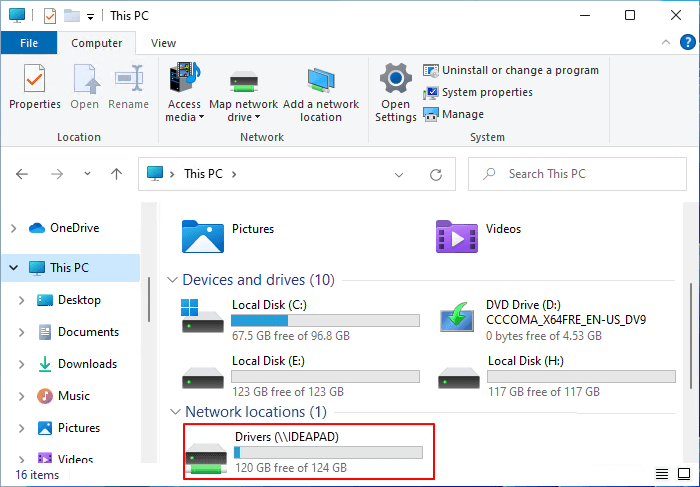
Once a network drive is connected, it appears in File Explorer alongside your local drives. You can manage these drives like any other drive:
- Open files and folders: Browse and access files and folders as usual.
- Save files: Save new files directly to the network drive.
- Disconnect the drive: Right-click the network drive in File Explorer and select "Disconnect".
Troubleshooting Network Drive Issues
If you encounter problems accessing a network drive, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check network connectivity: Ensure your computer is connected to the network.
- Verify network path and credentials: Double-check the network path and ensure you are using the correct username and password.
- Check for network security issues: Firewalls or antivirus software might be blocking access to the network drive.
- Restart services: Restart the "Server" service on the server computer and the "Network Location Awareness" service on your computer.
- Run network troubleshooter: Use the built-in Windows network troubleshooter to diagnose and fix common network issues.
FAQs about Networked Storage
Q: What are the benefits of using network drives?
A: Network drives offer several benefits, including:
- Centralized data storage: Simplifies data management and backups.
- Enhanced collaboration: Multiple users can access and modify shared files.
- Reduced local storage demands: Frees up space on individual computers.
- Increased accessibility: Files are accessible from any device connected to the network.
Q: How do I ensure data security on network drives?
A: Data security on network drives is crucial. Implement the following measures:
- Strong passwords: Use complex passwords to protect access to the shared resources.
- Access permissions: Restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Regular backups: Back up data regularly to prevent data loss.
- Network security measures: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures to protect the network.
Q: Can I access network drives remotely?
A: Yes, with proper configuration, you can access network drives remotely:
- Remote desktop connections: Use a remote desktop connection to connect to the server hosting the shared resources.
- VPN connections: Establish a secure VPN connection to access the network and its resources.
- Cloud storage services: Cloud storage services offer remote access to your files from any device.
Tips for Using Networked Drives Effectively
- Use clear naming conventions: Name shared folders and files descriptively to make them easy to find.
- Implement file sharing policies: Establish guidelines for file sharing and access permissions.
- Regularly monitor network drive usage: Monitor storage space usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Automate data backups: Schedule regular backups to protect your data.
Conclusion
Networked drives are a powerful tool for sharing data, collaborating on projects, and centralizing storage in Windows 11. By understanding the fundamentals of network drive access and implementing best practices for security and management, you can leverage the benefits of networked storage to enhance your workflow and productivity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Drive Letters and Networked Storage in Windows 11. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!