Understanding Drive Letter Assignments In Desktop Computers: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Drive Letter Assignments in Desktop Computers: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Drive Letter Assignments in Desktop Computers: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Drive Letter Assignments in Desktop Computers: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Drive Letter Assignments in Desktop Computers: A Comprehensive Guide
![[Free Guide]: Use Diskpart Assign Drive Letter in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/others/others/diskpart-assign-drive-letter.png)
Drive letters, such as "J," are fundamental components of a desktop computer’s file system, serving as unique identifiers for different storage devices. While seemingly simple, the concept of drive letters plays a crucial role in organizing and accessing data within a computer. This article delves into the intricacies of drive letters, focusing on their significance, functionality, and management in the context of desktop computers.
The Role of Drive Letters in File Management
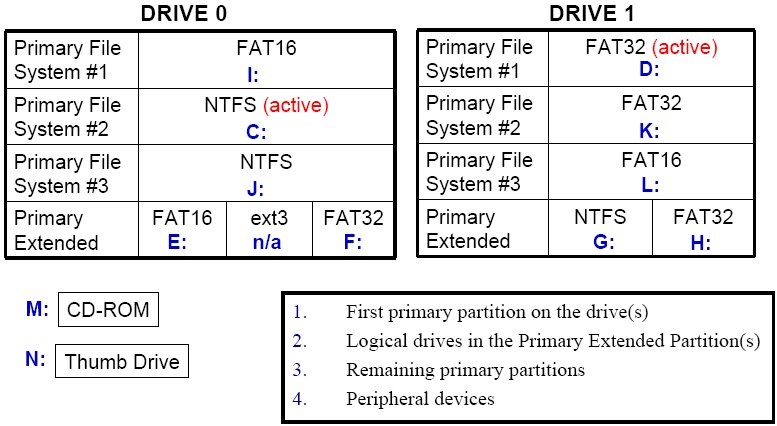
Drive letters act as labels, providing a structured way for the operating system to recognize and manage various storage devices connected to the computer. Each drive letter represents a distinct storage location, allowing the operating system to differentiate between hard drives, optical drives, external storage devices, and network shares.
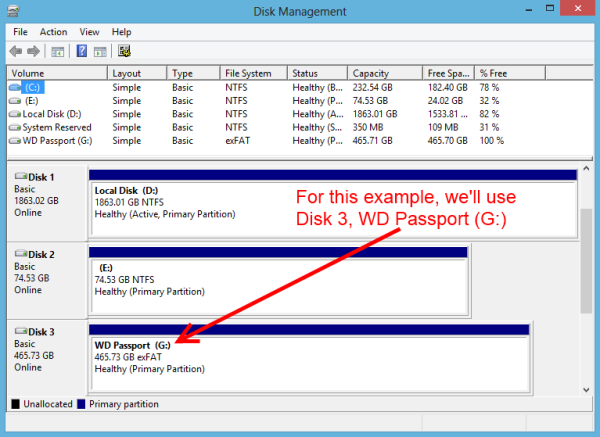
For instance, the letter "C" is traditionally assigned to the primary hard drive where the operating system is installed. Other letters, such as "D," "E," and "F," might be assigned to secondary hard drives, optical drives, or removable storage devices. The specific allocation of drive letters can vary depending on the computer’s configuration and the number of connected storage devices.
How Drive Letters are Assigned
The assignment of drive letters typically occurs during the boot process. The operating system scans for available storage devices and assigns them unique letters based on a predefined order. This order is determined by factors such as the device’s connection type, its physical location, and the operating system’s internal logic.
For instance, internal hard drives are usually assigned letters before external drives. The operating system might also prioritize drives connected via faster interfaces, such as SATA or NVMe, over those connected via USB or other slower interfaces.
Managing Drive Letters
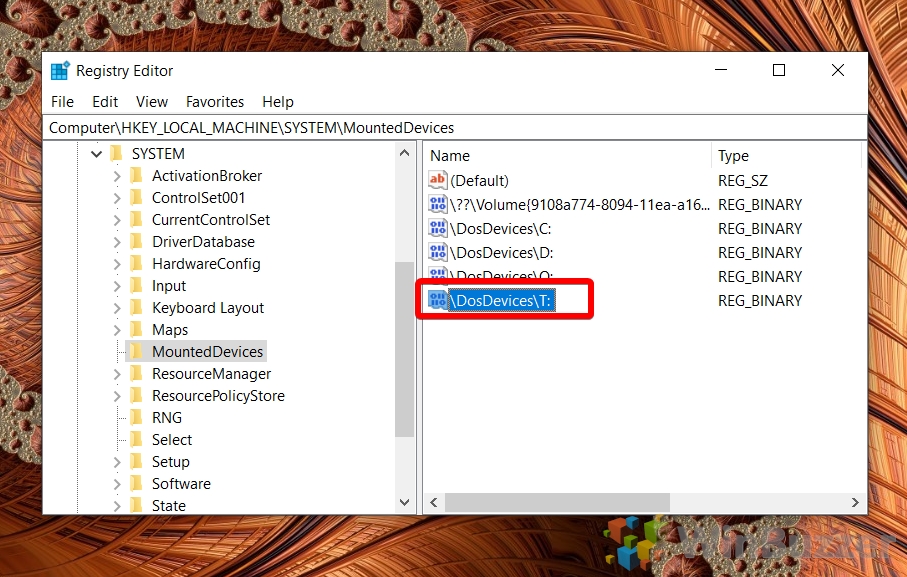
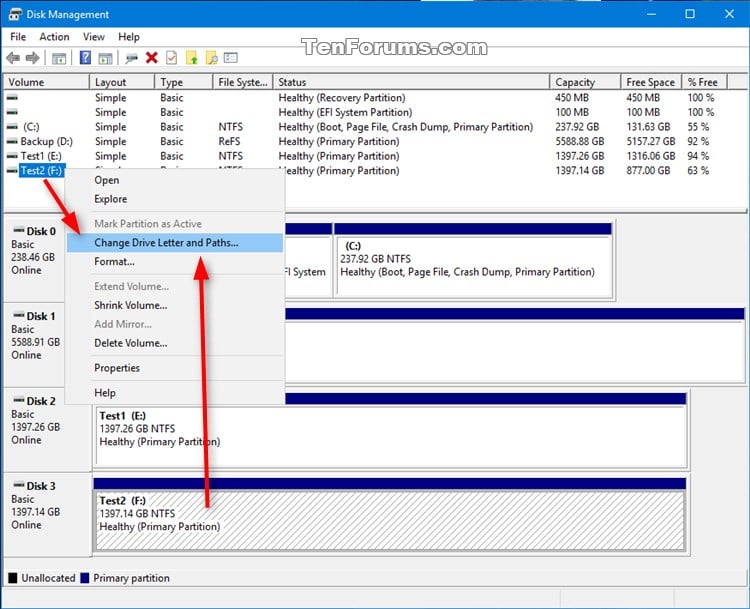
While the operating system automatically assigns drive letters during boot, users can manually change or reassign them if needed. This can be accomplished through various methods, including:
- Disk Management: The Disk Management tool in Windows allows users to modify drive letters, format drives, and manage partitions.
- Command Prompt: Advanced users can utilize commands such as "diskpart" and "assign letter" to manipulate drive letters.
- Third-party software: Specialized utilities can provide more granular control over drive letter assignment and management.
The Importance of Drive Letters
Drive letters are essential for several reasons:
- Organization: They provide a clear and concise way to organize data within the computer, enabling users to quickly locate and access files stored on different drives.
- Navigation: Drive letters facilitate easy navigation through the file system, allowing users to seamlessly move between different storage locations.
- Compatibility: Many applications and operating systems rely on drive letters for proper functioning, ensuring that data can be accessed and processed correctly.
- Troubleshooting: Drive letters aid in troubleshooting issues related to storage devices, allowing technicians to identify and isolate problems specific to individual drives.
The "J" Drive and its Implications
While the "J" drive is not inherently special, it is important to understand that it represents a specific storage location within the computer’s file system. The "J" drive could be assigned to a variety of devices, including:
- Secondary hard drive: A second hard drive installed within the computer, potentially used for data storage, backup, or specific applications.
- External storage device: A removable drive such as a USB flash drive, external hard drive, or SD card.
- Network share: A folder or drive accessible over a network, allowing users to share files with other computers.
The actual device assigned to the "J" drive depends entirely on the computer’s configuration and the user’s preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I manually assign a drive letter to a specific device?
A: Yes, you can manually assign drive letters using the Disk Management tool in Windows. However, it is recommended to exercise caution when altering drive letter assignments, as it can impact the functionality of applications and operating system components.
Q: Why do drive letters sometimes change after a reboot?
A: Drive letter assignments can change after a reboot if a new storage device is connected or if the operating system encounters conflicts with existing assignments. This is a common occurrence, and it usually resolves itself after the system restarts.
Q: Can I assign a drive letter to a virtual hard drive?
A: Yes, you can assign drive letters to virtual hard drives created within virtualization software. This allows you to treat virtual drives as physical drives, enabling you to store and access data within the virtual environment.
Q: What happens if I delete a drive letter?
A: Deleting a drive letter does not physically erase the data stored on the corresponding drive. It simply removes the label associated with that drive, making it inaccessible through the file system. To access the data, you will need to reassign a new drive letter.
Tips for Managing Drive Letters
- Avoid using reserved letters: Letters such as "A," "B," and "C" are often reserved for specific purposes and should not be manually assigned to other devices.
- Use consistent naming conventions: Establish a clear and consistent naming convention for drive letters, ensuring that similar devices are assigned similar letters across different computers.
- Back up important data: Before making any changes to drive letter assignments, ensure that you have backed up any important data stored on the affected drives.
- Consult documentation: Refer to the documentation of your operating system or hardware for specific instructions and guidelines regarding drive letter management.
Conclusion
Drive letters are an integral part of a desktop computer’s file system, providing a structured way to organize and access data. Understanding their role and significance is essential for managing storage devices effectively and navigating the file system seamlessly. By applying the principles outlined in this article, users can leverage the power of drive letters to enhance their computing experience and ensure efficient data management.
![Full Guide on Diskpart Assign Drive Letter in Windows 11/10/8/7 [Step-by-Step Guide] - EaseUS](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/diskpart-assign-drive-letter-cover.png)
![Full Guide on Diskpart Assign Drive Letter in Windows 11/10/8/7 [Step-by-Step Guide] - Qiling](https://www.idiskhome.com/resource/partition/images/windows-command-prompt-diskpart-assign-letter.png)
![Diskpart Unassign Drive Letter in Windows 11/10 [Full Guide] - MiniTool Partition Wizard](https://www.partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/news/2023/06/diskpart-unassign-letter/diskpart-unassign-letter-3.png)
![[Free Guide]: Use Diskpart Assign Drive Letter in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/std/change-drive-letter/assign-drive-letter.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Drive Letter Assignments in Desktop Computers: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!