Understanding Administrative Privileges In Windows 10
Understanding Administrative Privileges in Windows 10
Related Articles: Understanding Administrative Privileges in Windows 10
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Administrative Privileges in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Administrative Privileges in Windows 10
Windows 10, like any operating system, employs a hierarchical user account system to manage access and permissions. This system categorizes users into different levels, each with varying degrees of control over the computer’s resources and settings. At the apex of this hierarchy sits the Administrator account.
The Administrator Account: The Gatekeeper of System Control
The Administrator account, as its name suggests, holds the highest level of privileges within Windows 10. This account has unfettered access to all aspects of the operating system, allowing for the following:
- Installation and Removal of Software: Administrators can install and remove programs, drivers, and updates without any restrictions.
- System Configuration Changes: They can modify system settings, including security configurations, network settings, and user accounts.
- Hardware Management: Administrators can manage hardware components, including adding new devices, configuring drivers, and modifying hardware settings.
- Access to All Files and Folders: Administrators have read and write access to every file and folder on the system, including those belonging to other users.
Why Employ Administrative Privileges?
The Administrator account serves as a crucial tool for managing and maintaining the stability and security of a Windows 10 system. It empowers users to:
- Troubleshoot and Resolve Issues: Administrators can diagnose and fix system errors, troubleshoot software conflicts, and repair corrupted files.
- Enhance Security: They can configure security settings, install anti-virus software, and manage firewalls to protect the system from malicious threats.
- Optimize Performance: Administrators can adjust system settings, manage resources, and optimize performance for specific applications or tasks.
- Manage User Accounts: They can create, modify, and delete user accounts, assign permissions, and control access to system resources.
Navigating the Administrative Account: A Balanced Approach
While the Administrator account provides extensive control, it also presents potential risks:
- Security Vulnerability: Using the Administrator account for everyday tasks exposes the system to vulnerabilities. Malicious software can potentially exploit these privileges to gain control of the system.
- Accidental System Changes: Unintentional modifications made with administrative privileges can lead to system instability or data loss.
Best Practices for Using the Administrator Account:
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to follow best practices:
- Limit Administrator Usage: Avoid using the Administrator account for everyday tasks. Instead, create a standard user account for daily operations and switch to the Administrator account only when necessary.
- Create a Separate Administrator Account: For increased security, create a dedicated Administrator account solely for administrative tasks and avoid using it for regular browsing or file management.
- Use Administrative Privileges Judiciously: Only use the Administrator account for specific administrative tasks and avoid using it for routine operations.
- Enable User Account Control (UAC): UAC prompts users for confirmation before making significant changes to the system, reducing the risk of unintentional modifications.
Understanding the Different Ways to Log In as Administrator
There are several methods to access the Administrator account in Windows 10:
1. Direct Log-In:
- Standard Method: If the Administrator account is not disabled, you can directly log in using the Administrator username and password during the initial login screen.
2. Using the "Run as Administrator" Option:
- Contextual Privileges: This method allows you to temporarily elevate the privileges of an application or program without needing to log in to the Administrator account directly.
- Accessing the Menu: Right-click on the program or shortcut you wish to run and select "Run as administrator."
3. Using the Command Prompt:
- Power User Access: The Command Prompt provides a text-based interface for interacting with the operating system.
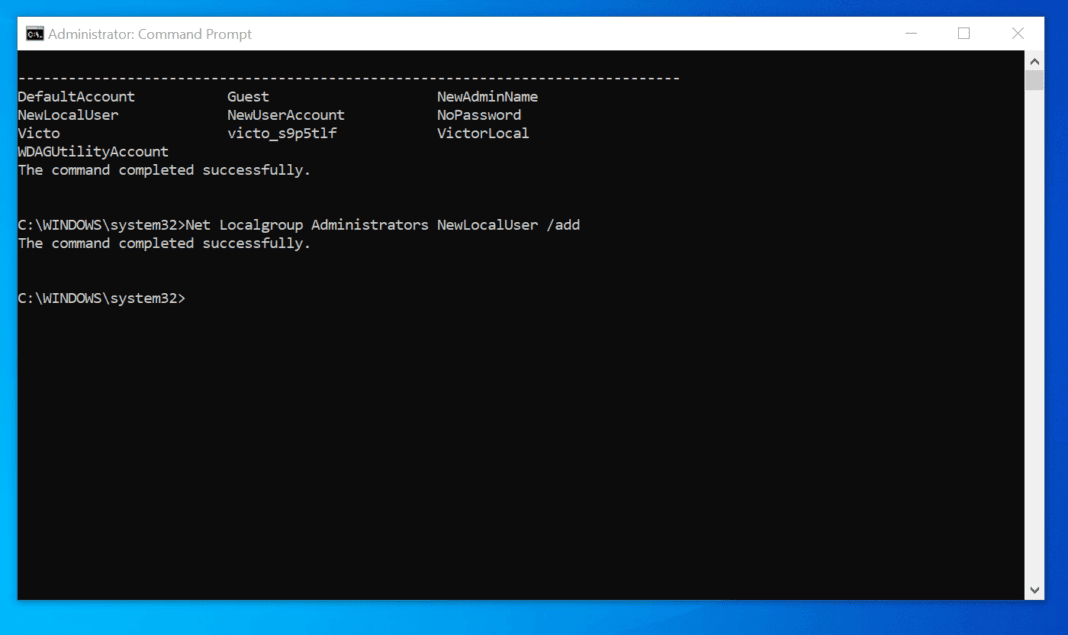
- Elevated Privileges: You can open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges by searching for "cmd" in the Start menu, right-clicking on the result, and selecting "Run as administrator."
4. Using the Task Manager:
- Process Management: The Task Manager allows you to manage running processes, applications, and services.
- Administrator Access: To access the Task Manager with administrative privileges, right-click on the taskbar and select "Task Manager."
5. Using the Settings App:
- System Configuration: The Settings app allows you to manage various system settings, including user accounts.
- Administrative Access: To access the Settings app with administrative privileges, search for "settings" in the Start menu, right-click on the result, and select "Run as administrator."
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Regarding Administrative Privileges
Q1. What is the difference between a standard user account and an Administrator account?
A1. A standard user account has limited privileges and can only access and modify files and settings within their own user profile. An Administrator account has full control over the system and can access and modify all files, folders, and settings.
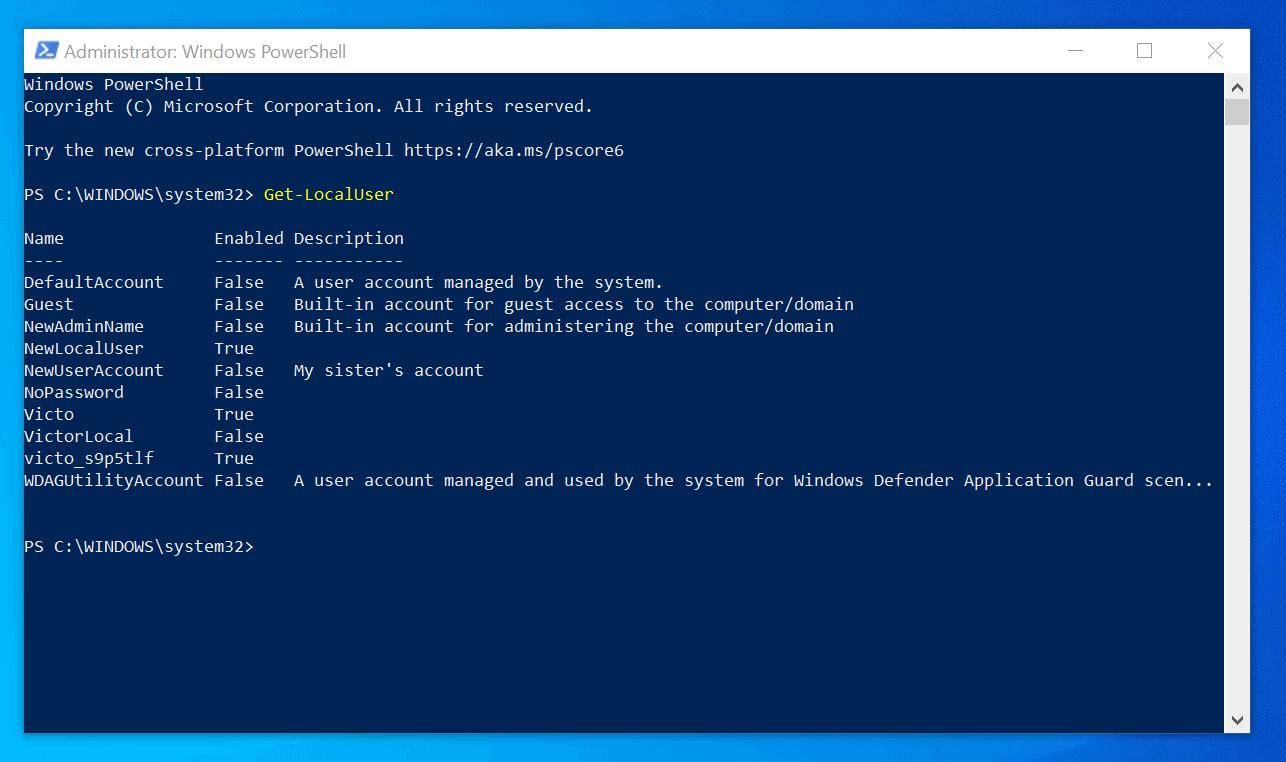
Q2. How do I create a new Administrator account in Windows 10?
A2.
- Open the Settings app by searching for "settings" in the Start menu.
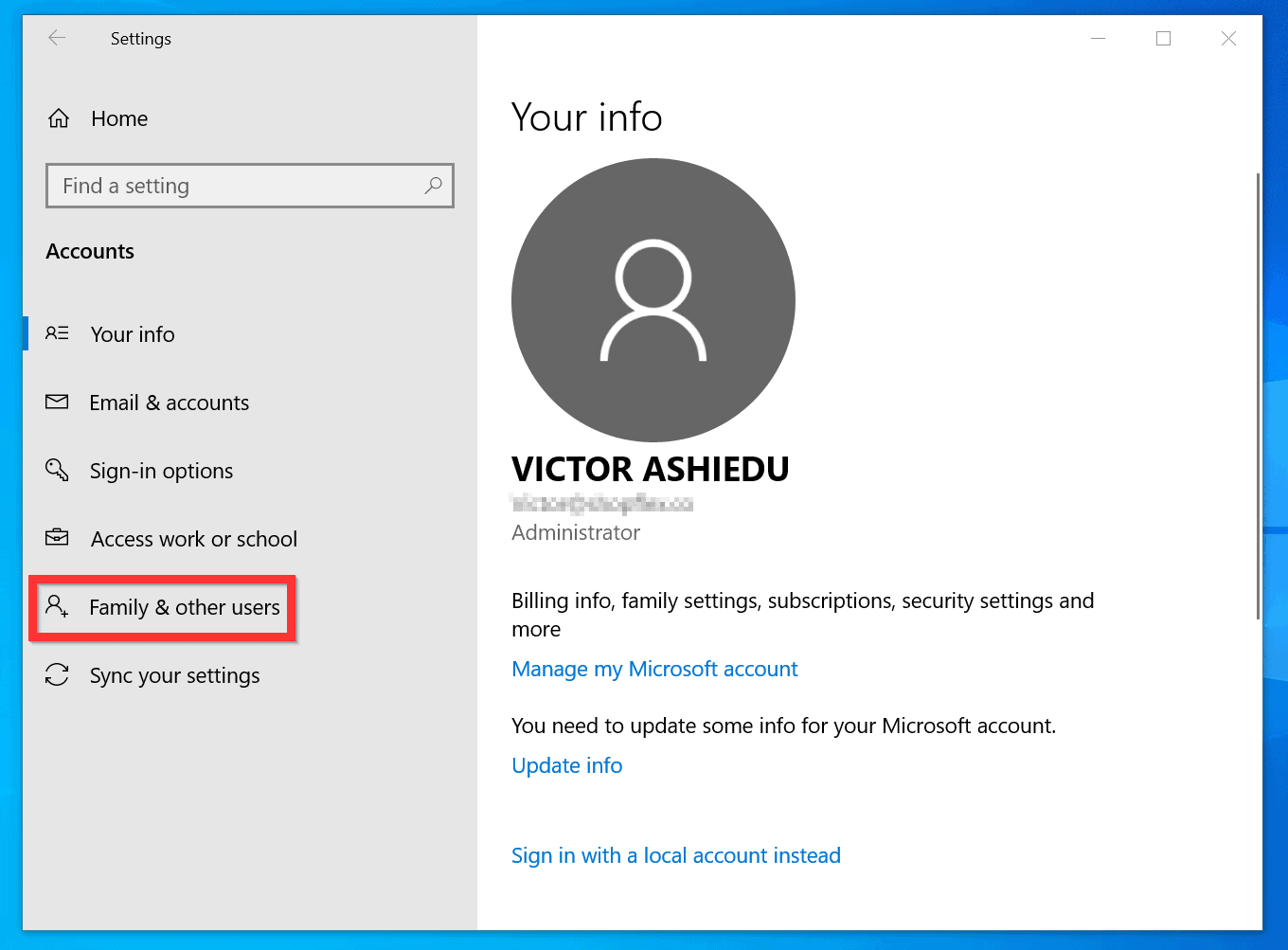
- Navigate to Accounts > Family & other users.
- Click on Add someone else to this PC.
- Select I don’t have this person’s sign-in information.
- Choose Add a user without a Microsoft account.
- Enter a username and password for the new account.
- After creating the account, open Settings > Accounts > Family & other users.
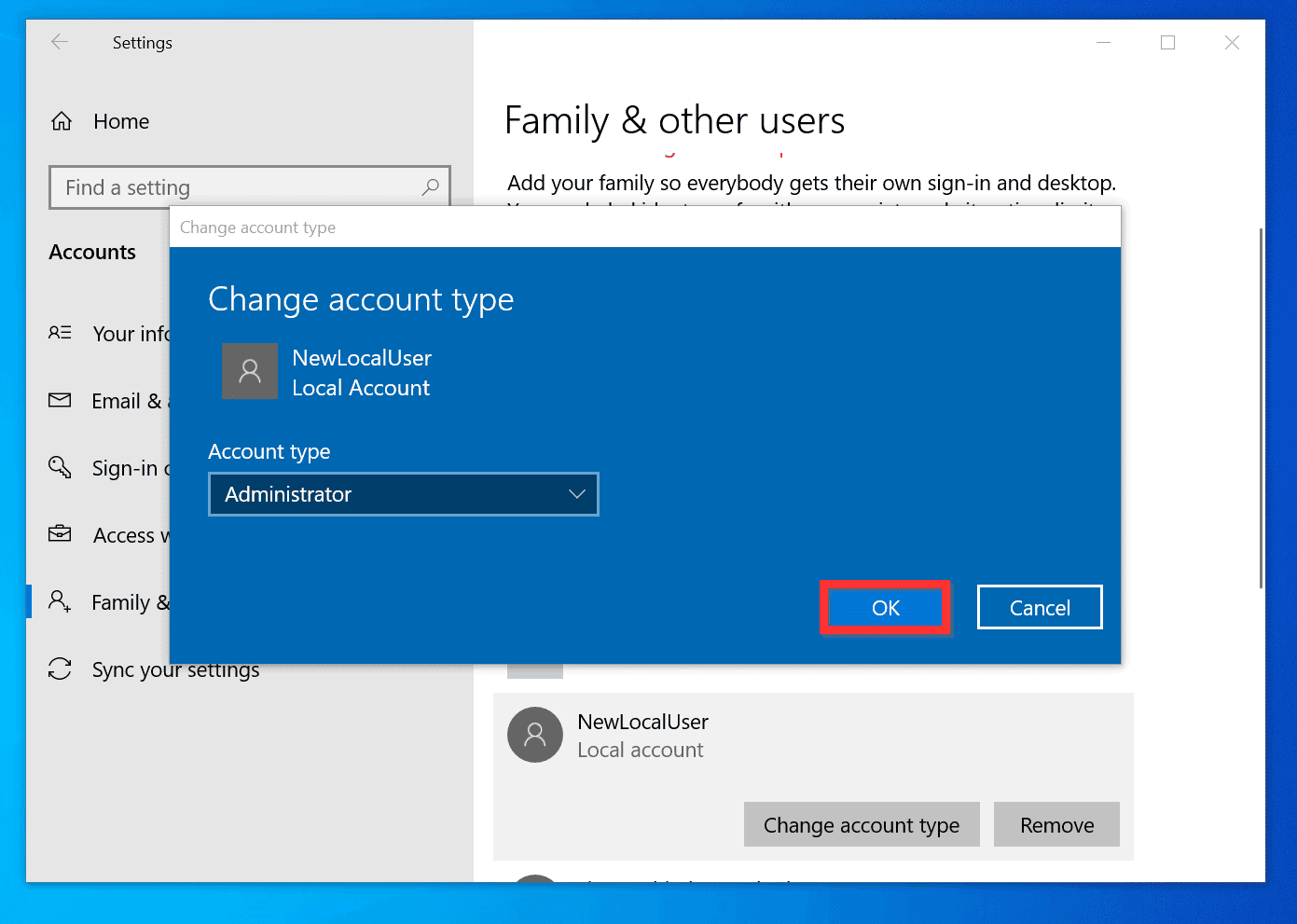
- Click on the new user account, then click Change account type.
- Select Administrator from the dropdown menu.
Q3. Can I disable the Administrator account in Windows 10?
A3. Yes, you can disable the built-in Administrator account for security reasons. However, it is recommended to create a separate Administrator account before disabling the built-in one to ensure you can still access administrative privileges if needed.
Q4. How do I switch between different user accounts in Windows 10?
A4.
- Click on the user icon in the taskbar.
- Select the desired user account from the list.
- Enter the password for the selected account.
Q5. What are some common administrative tasks that require Administrator privileges?
A5. Common administrative tasks that require Administrator privileges include:
- Installing and uninstalling software
- Modifying system settings
- Managing user accounts
- Running system diagnostics
- Installing and configuring hardware drivers
- Accessing system files and folders
Tips for Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10
- Use a Strong Password: Create a complex and memorable password for the Administrator account to prevent unauthorized access.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Add an extra layer of security by enabling two-factor authentication for the Administrator account.
- Regularly Review System Logs: Monitor system logs for suspicious activity and take appropriate action if necessary.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update Windows and all software applications to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use a Security Software: Install and maintain a reputable anti-virus and anti-malware software to protect your system from threats.
Conclusion
The Administrator account in Windows 10 is a powerful tool for managing and maintaining the system. While it offers extensive control, it is crucial to use it responsibly and with caution to avoid security risks and system instability. By adhering to best practices, limiting Administrator usage, and employing appropriate security measures, you can effectively leverage the benefits of administrative privileges while safeguarding your system from potential threats.


![[指南]如何在Windows 10上获取管理员权限](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/05/get-admin-rights-on-windows-10.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Administrative Privileges in Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!