The Windows 11 Upgrade: A Comprehensive Guide
The Windows 11 Upgrade: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Windows 11 Upgrade: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Windows 11 Upgrade: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Windows 11 Upgrade: A Comprehensive Guide

The release of Windows 11 marked a significant shift in the operating system landscape. While Microsoft offered a free upgrade path for eligible users, the conditions and process were not always clear. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the Windows 11 upgrade, addressing key aspects and addressing common queries.
Understanding the Eligibility Criteria:
The free upgrade to Windows 11 was not universally available. Microsoft established specific hardware requirements to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. These requirements encompassed:
- Processor: A 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster, with at least two cores.
- RAM: 4 gigabytes (GB) of RAM.
- Storage: 64 GB or larger storage device.
- System Firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable.
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0.
- Display: A high-definition (720p) display with at least 9 inches diagonally.
- Graphics Card: Compatible with DirectX 12 or later.
- Internet Connection: Required for some features and activation.
Meeting these minimum requirements was essential for accessing the free upgrade. Users with older systems that did not meet the criteria could still upgrade, but they would need to purchase a license.
The Upgrade Process:
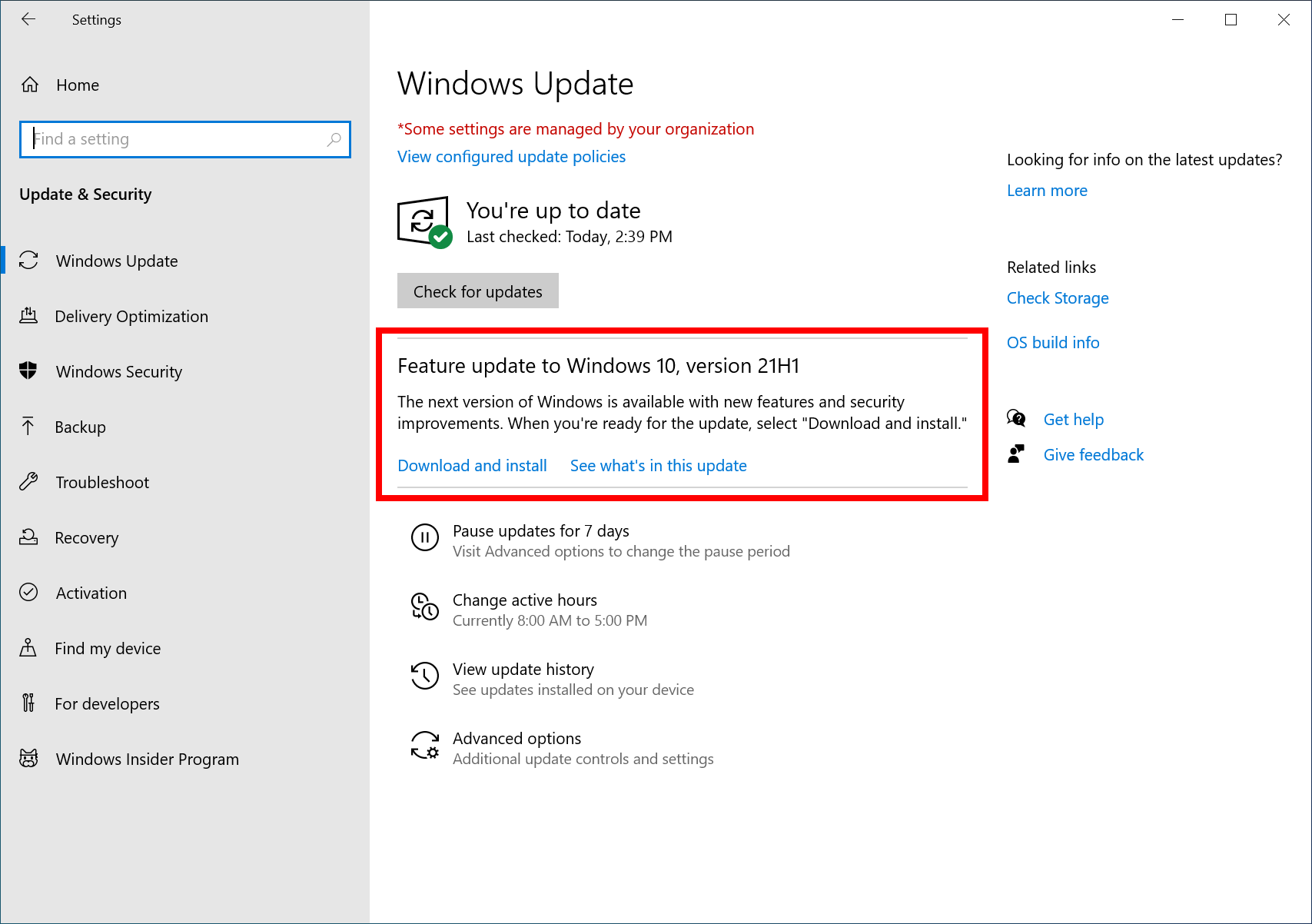
For eligible users, the Windows 11 upgrade was a relatively straightforward process. Microsoft offered a dedicated upgrade tool that could be downloaded from its website. This tool assessed system compatibility, downloaded the necessary files, and performed the upgrade. The process typically involved several steps:
- Checking Compatibility: The upgrade tool first verified if the system met the minimum hardware requirements.
- Downloading Files: If the system was compatible, the tool downloaded the necessary Windows 11 installation files.
- Installing Windows 11: The tool initiated the installation process, which involved restarting the computer and completing the setup steps.
- Activation: Once the installation was complete, Windows 11 was activated, confirming that the user was entitled to the free upgrade.
Factors Affecting Upgrade Eligibility:
While meeting the minimum hardware requirements was crucial, other factors could influence upgrade eligibility:
- Windows Version: The free upgrade was primarily available for users running Windows 10. Users with older versions of Windows, like Windows 7 or Windows 8, were not eligible for the free upgrade.
- System Health: The upgrade tool also assessed the overall health of the system, including drivers and compatibility. If the system had critical issues or outdated drivers, the upgrade process might be blocked.
- Active Windows 10 License: The free upgrade required an active Windows 10 license. Users with expired licenses or pirated copies of Windows 10 were not eligible.
The End of the Free Upgrade Offer:
The free upgrade offer for Windows 11 was initially available for a limited time. Microsoft eventually phased out the free upgrade, making it necessary to purchase a license for new installations or upgrades. This shift aimed to encourage users to adopt the latest operating system and generate revenue for Microsoft.
Benefits of Upgrading to Windows 11:
The Windows 11 upgrade offered a range of improvements and new features, making it a compelling option for users:
- Enhanced Security: Windows 11 incorporated advanced security features, including TPM 2.0, Secure Boot, and enhanced malware protection.
- Improved Performance: The operating system boasted faster boot times, improved multitasking, and optimized performance for modern hardware.
- Modern User Interface: Windows 11 introduced a redesigned user interface with rounded corners, centered taskbar icons, and a streamlined Start menu.
- New Features: The upgrade included new features like the Widgets panel, Snap Layouts for efficient window management, and Android app support.
- Enhanced Gaming: Windows 11 offered improved gaming performance with features like Auto HDR and DirectStorage.
Addressing Common Queries:
Q: Can I still upgrade to Windows 11 for free?
A: The free upgrade offer for Windows 11 has ended. Users now need to purchase a license to upgrade or install the operating system.
Q: What if my system does not meet the minimum requirements?
A: If your system does not meet the minimum requirements, you can still upgrade to Windows 11, but you will need to purchase a license.
Q: Will my files be deleted during the upgrade?
A: During the upgrade process, your personal files and settings are typically preserved. However, it is always advisable to create a backup before upgrading.
Q: Can I downgrade to Windows 10 after upgrading to Windows 11?
A: Downgrading to Windows 10 after upgrading to Windows 11 is possible, but it may involve reinstalling Windows 10 from scratch.
Q: What are the system requirements for Windows 11?
A: The system requirements for Windows 11 include a 1 GHz or faster processor, 4 GB of RAM, 64 GB of storage, UEFI with Secure Boot, TPM 2.0, a 720p display, DirectX 12 compatible graphics card, and an internet connection.
Q: What happens if my Windows 10 license expires?
A: If your Windows 10 license expires, you will no longer be eligible for the free upgrade to Windows 11. You will need to purchase a new license.
Tips for a Smooth Upgrade:
- Backup Your Data: Before upgrading, create a backup of your important data to avoid any potential data loss.
- Check for Compatibility: Ensure that your system meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11 and that your drivers are up-to-date.
- Review the Upgrade Tool: Carefully review the information provided by the upgrade tool before proceeding with the installation.
- Disconnect Peripherals: Disconnect any unnecessary peripherals to minimize potential conflicts during the upgrade.
- Perform a Clean Install (Optional): For a fresh start, consider performing a clean install of Windows 11, which involves formatting the drive and reinstalling the operating system.
Conclusion:
The Windows 11 upgrade offered a free path to the latest operating system for eligible users. While the free upgrade offer has ended, Windows 11 remains a compelling option with its enhanced security, improved performance, modern user interface, and new features. Users considering upgrading should carefully assess their system requirements, backup their data, and follow the recommended tips for a smooth and successful upgrade. By understanding the eligibility criteria, benefits, and potential challenges, users can make an informed decision about whether upgrading to Windows 11 is the right choice for their needs.

![Download and Upgrade to Windows 11 for Free [Step-by-Step Guide]](https://www.debugpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/win11upgrade.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Windows 11 Upgrade: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!