The Foundation Of Security: Exploring LSA Protection In Windows 11
The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11
Related Articles: The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11
- 3.1 Understanding the LSA and Its Role
- 3.2 The Need for LSA Protection
- 3.3 LSA Protection in Windows 11: A Multifaceted Approach
- 3.4 Benefits of LSA Protection in Windows 11
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding LSA Protection in Windows 11
- 3.6 Tips for Maintaining LSA Protection
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11
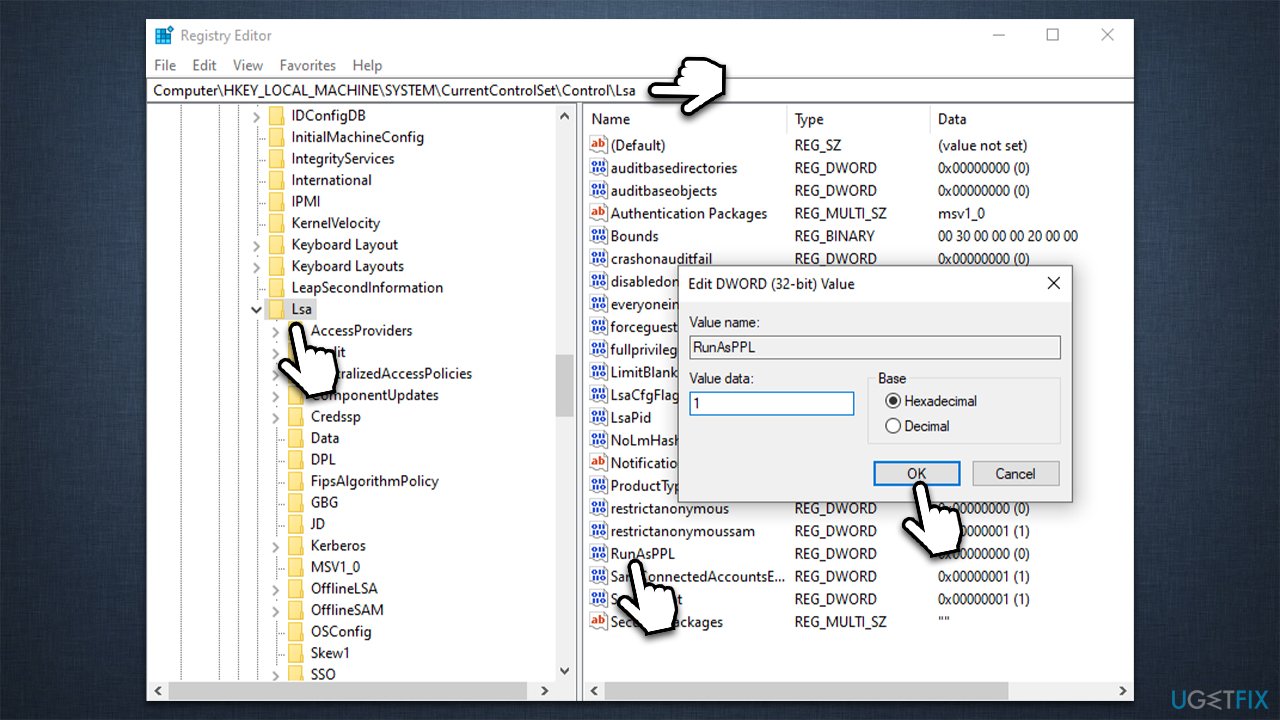
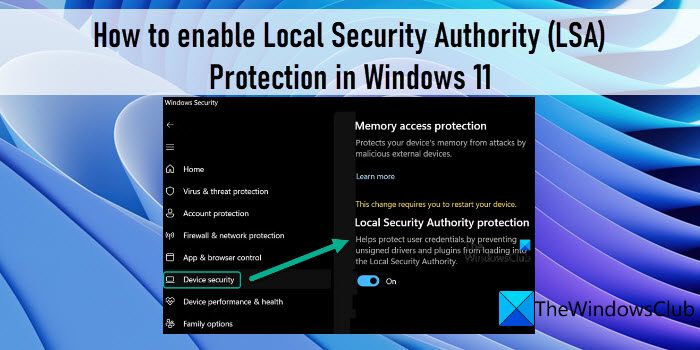
Windows 11, like its predecessors, is built upon a complex foundation of security mechanisms designed to protect users and their data. One crucial element within this architecture is the Local Security Authority (LSA), responsible for managing user authentication, security policies, and privileged operations. LSA protection, a core security feature, safeguards the LSA from malicious attacks, ensuring the integrity of these critical functions.
Understanding the LSA and Its Role
The Local Security Authority (LSA) acts as the central authority for security within Windows. It performs a multitude of functions, including:
- User Authentication: The LSA verifies user credentials, ensuring only authorized individuals can access the system.
- Security Policy Enforcement: It enforces security policies set by administrators, controlling access to resources and limiting user actions.
- Privilege Management: The LSA manages privileges, granting users the necessary permissions to perform specific tasks.
- Logon Session Management: It handles the creation and management of user sessions, controlling access to resources during login.
- Password Management: The LSA stores and manages user passwords, ensuring their secure storage and retrieval.
The LSA’s role is fundamental to the security of Windows. Its integrity is paramount, as a compromise of the LSA could lead to catastrophic consequences, including:
- Unauthorized Access: Attackers could gain access to sensitive data, including user credentials and system files.
- System-Wide Control: Compromising the LSA could allow attackers to take complete control of the system, potentially installing malware or altering system settings.
- Data Manipulation: Attackers could modify or delete critical system files, rendering the system unstable or unusable.
The Need for LSA Protection
The criticality of the LSA necessitates robust protection against malicious actors. LSA protection mechanisms are designed to address the following threats:
- Malware Attacks: Malicious software can attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in the LSA, gaining access to sensitive information or controlling system operations.
- Exploitation of System Vulnerabilities: Attackers may find and exploit security flaws in the LSA itself or in other system components that interact with it.
- Privilege Escalation: Attackers might attempt to gain higher privileges by compromising the LSA, allowing them to perform actions normally restricted to administrators.
LSA Protection in Windows 11: A Multifaceted Approach
Windows 11 employs a multi-layered approach to protect the LSA, encompassing:
- Code Integrity: Windows 11 enforces code integrity policies, ensuring that only trusted and verified software can interact with the LSA. This helps prevent malicious code from injecting itself into the LSA process or altering its behavior.
- Secure Boot: Secure Boot, a feature enabled by UEFI firmware, ensures that only trusted operating system components are loaded at boot time. This helps prevent attackers from modifying the boot process and injecting malicious code before the LSA is initialized.
- User Account Control (UAC): UAC prompts users for permission before applications attempt to make changes that could affect system security. This helps prevent malware from silently modifying LSA settings or gaining unauthorized privileges.
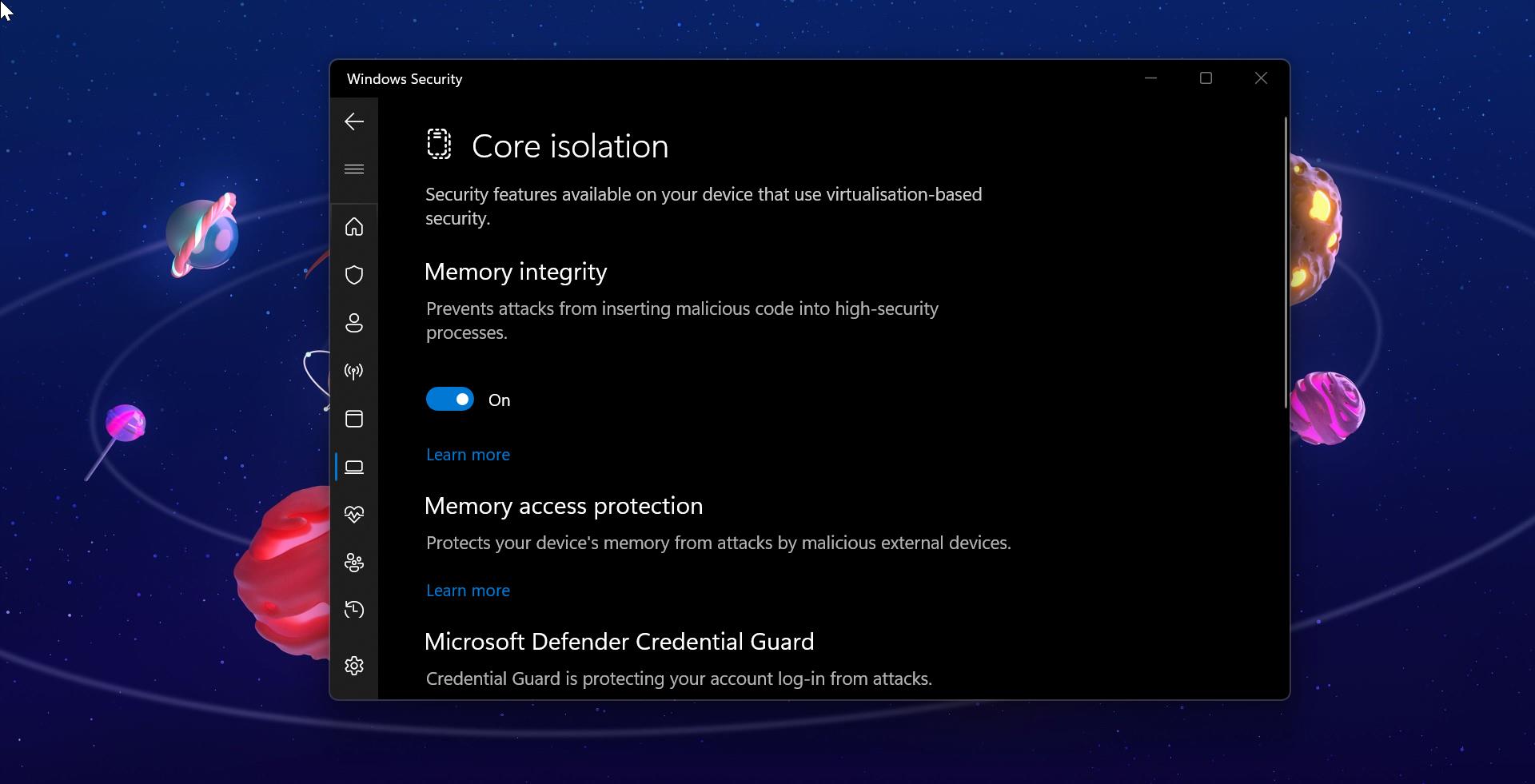
- Virtualization-Based Security (VBS): VBS isolates critical system components, including the LSA, within a protected environment, making them less susceptible to attack.
- Hardware-Level Security: Windows 11 leverages hardware-level security features like Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and Secure Encrypted Virtualization (SEV) to further enhance LSA protection.
Benefits of LSA Protection in Windows 11
The robust LSA protection mechanisms in Windows 11 provide several benefits:
- Enhanced System Security: LSA protection reduces the risk of malicious attacks, safeguarding the system from unauthorized access, control, and data manipulation.
- Increased User Trust: Stronger LSA protection helps instill confidence in users, knowing that their data and system are better protected from threats.
- Improved System Stability: By preventing malicious code from interfering with the LSA, LSA protection contributes to a more stable and reliable operating system.
- Reduced Attack Surface: LSA protection reduces the attack surface for attackers, making it more difficult for them to find vulnerabilities and exploit them.
FAQs Regarding LSA Protection in Windows 11
1. What is the difference between LSA protection and other security features in Windows 11?
LSA protection specifically targets the security of the Local Security Authority, which is a central component of Windows security. While other security features like Windows Defender and Firewall protect the system as a whole, LSA protection focuses on safeguarding the integrity and functionality of the LSA itself.
2. How can I verify if LSA protection is enabled on my Windows 11 system?
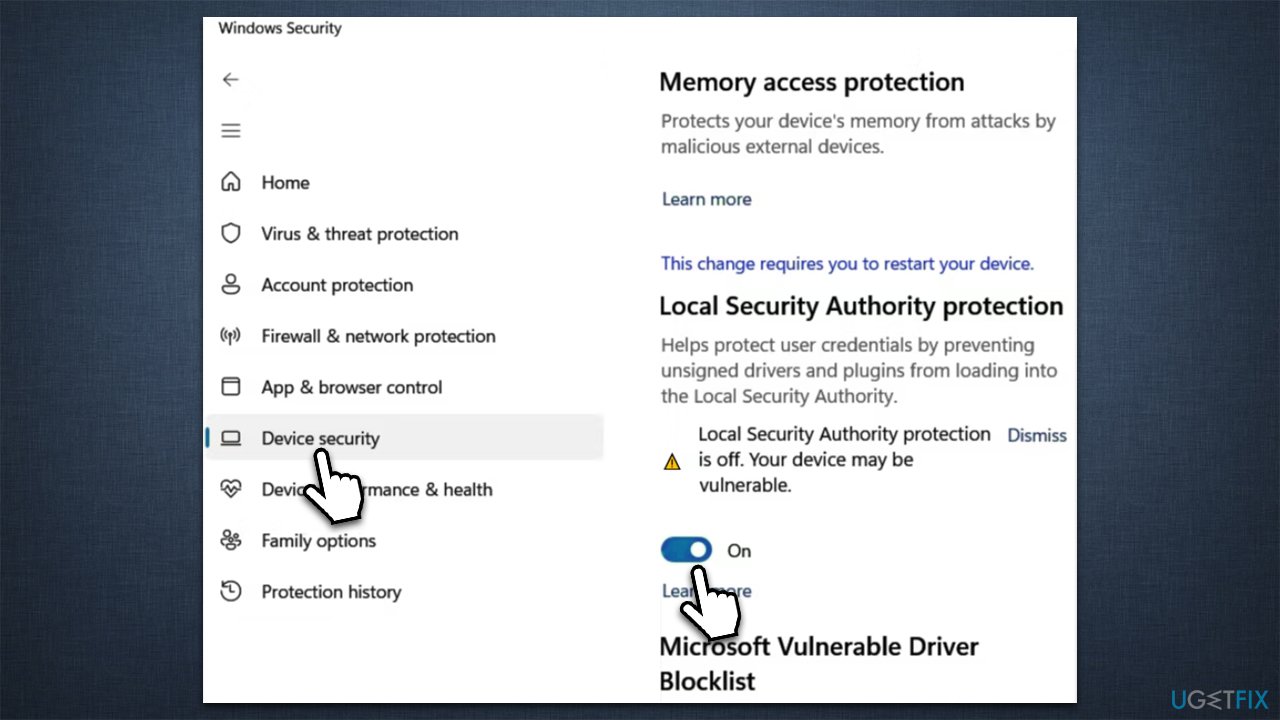
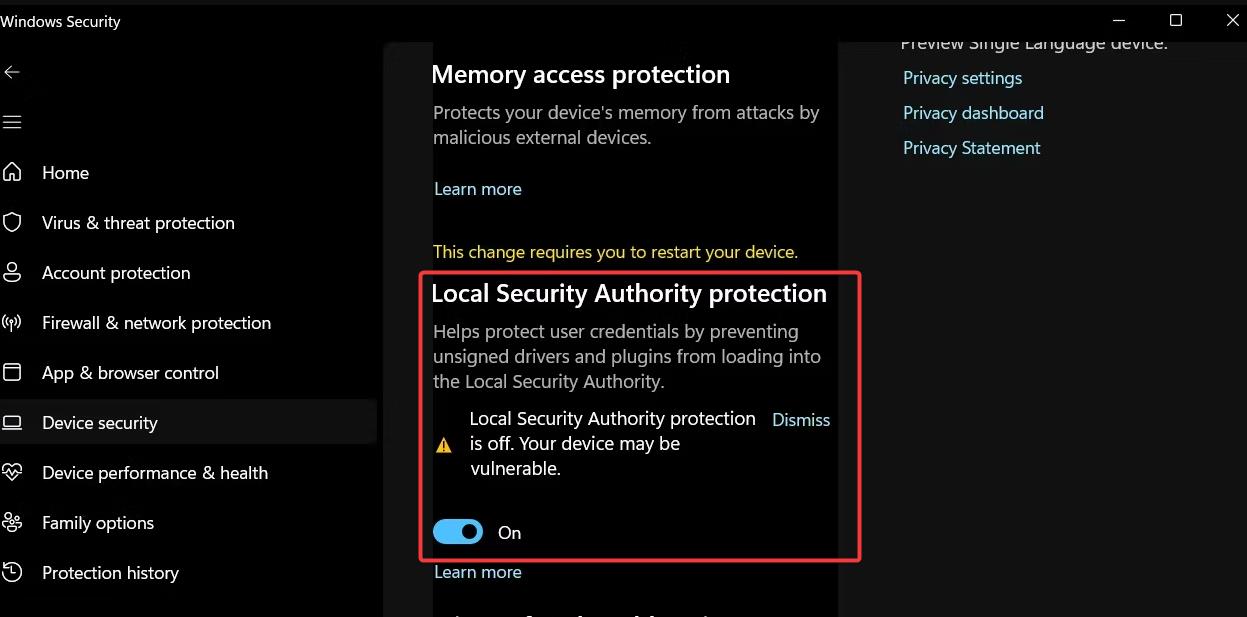
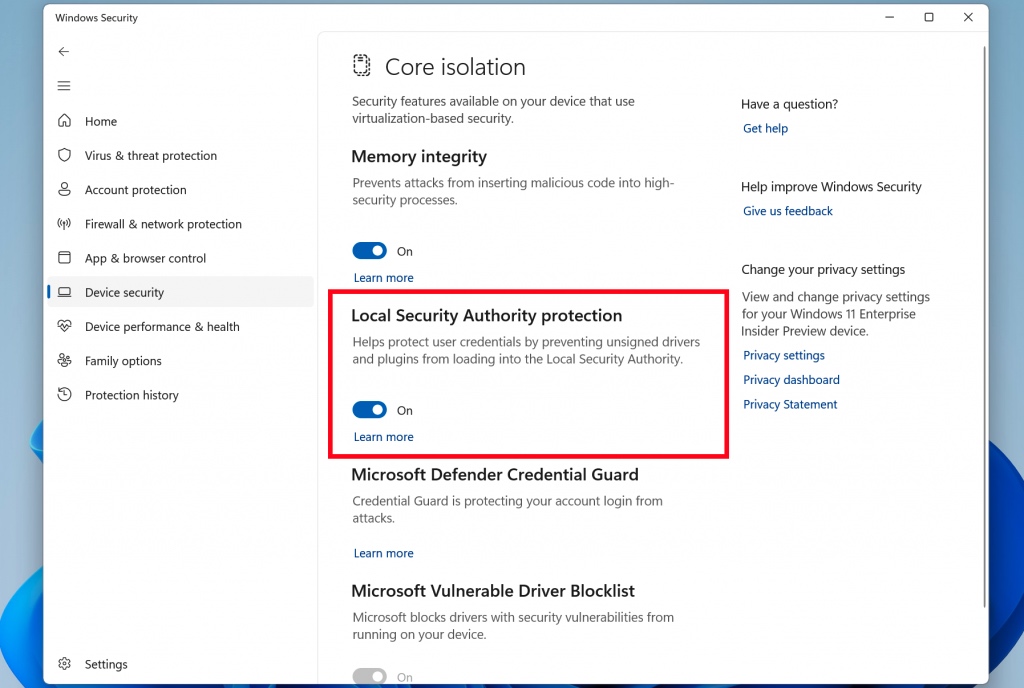
You can check the status of LSA protection by examining your system’s security settings. Review the settings related to code integrity, Secure Boot, User Account Control, and virtualization-based security. These features, when enabled, contribute to the overall security of the LSA.
3. Are there any risks associated with disabling LSA protection?
Disabling LSA protection significantly weakens the security of your system. It exposes the LSA to a higher risk of malicious attacks, compromising user accounts, system control, and data integrity. Disabling LSA protection is generally not recommended unless absolutely necessary and with a clear understanding of the associated risks.
4. Can I further enhance LSA protection beyond what is provided by Windows 11?
While Windows 11 provides a robust set of LSA protection features, you can further strengthen your system’s security by:
- Keeping your system updated: Regularly update your Windows 11 system to benefit from the latest security patches and improvements.
- Using strong passwords: Employ complex passwords for all user accounts and enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Installing reputable security software: Consider using reputable antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and remove potential threats.
- Avoiding suspicious websites and downloads: Be cautious about visiting untrusted websites or downloading files from unknown sources, as they could contain malware.
5. How can I learn more about LSA protection in Windows 11?
For detailed information about LSA protection, consult the official Microsoft documentation and security resources. These resources provide in-depth technical details about the implementation and functionality of LSA protection in Windows 11.
Tips for Maintaining LSA Protection
- Keep your system updated: Regularly install the latest security updates and patches to address potential vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords: Employ complex passwords for all user accounts and enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Be cautious about downloads and attachments: Only download files from trusted sources and be wary of opening email attachments from unknown senders.
- Enable User Account Control (UAC): UAC prompts users for permission before applications attempt to make changes that could affect system security.
- Install reputable security software: Consider using antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and remove potential threats.
- Practice safe browsing habits: Avoid visiting untrusted websites and be cautious about clicking on links from unknown sources.
Conclusion
LSA protection in Windows 11 is a crucial element of the operating system’s security architecture. By safeguarding the integrity and functionality of the Local Security Authority, LSA protection helps prevent malicious attacks, protect user accounts, and ensure the stability and reliability of the system. Understanding the importance of LSA protection and implementing best practices for maintaining its effectiveness is essential for ensuring a secure and reliable computing experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Foundation of Security: Exploring LSA Protection in Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!