The Evolution Of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems: A Comprehensive History And Analysis
The Evolution of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems: A Comprehensive History and Analysis
Related Articles: The Evolution of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems: A Comprehensive History and Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems: A Comprehensive History and Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems: A Comprehensive History and Analysis
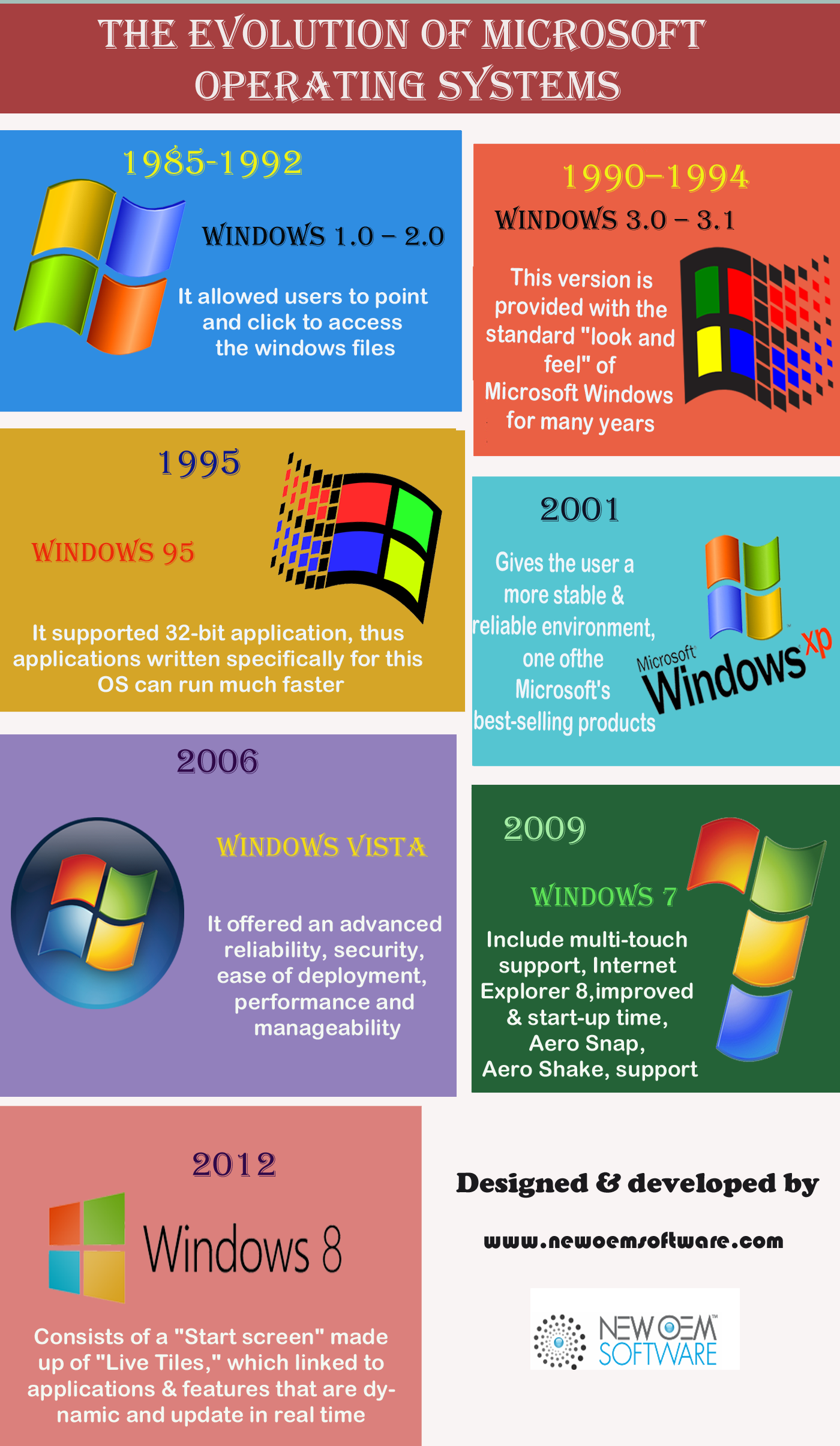
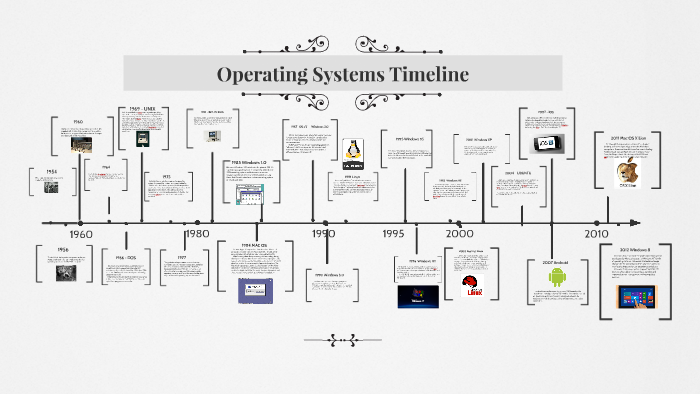
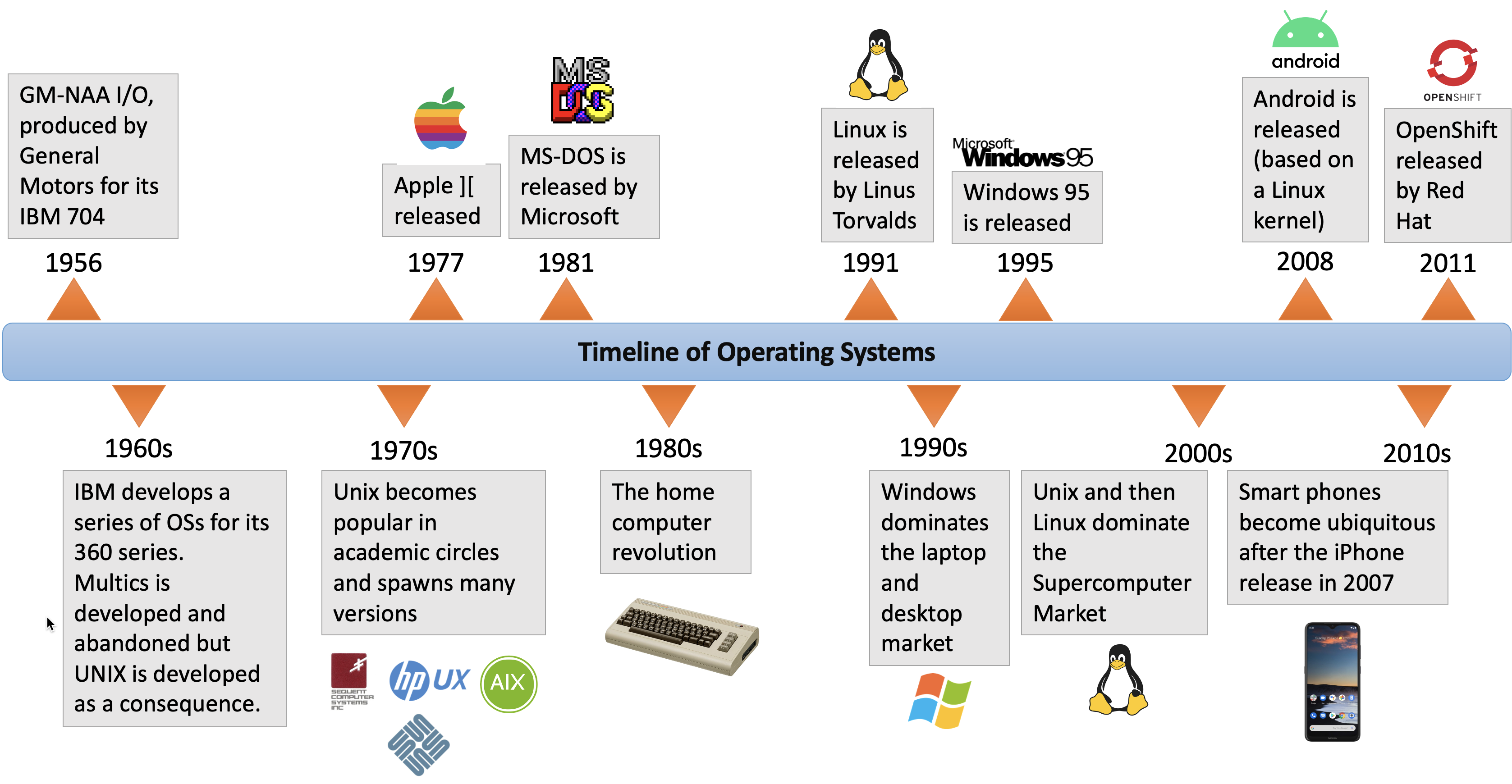
![The History Of Mobile Operating Systems [Infographic] Bit Rebels](http://www.bitrebels.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/Evolution-of-Mobile-Operating-Systems.jpg)
Microsoft’s foray into the mobile operating system (OS) market began in the late 1990s, driven by the burgeoning mobile phone industry and the desire to expand its reach beyond the desktop computer realm. The company’s initial efforts, while ambitious, faced significant challenges and ultimately failed to achieve widespread adoption. However, Microsoft’s persistence and strategic shifts resulted in the development of several noteworthy mobile operating systems, each with its own unique features and market impact.
Early Attempts: Pocket PC and Windows CE
The first major step towards a Microsoft-powered mobile OS came with the launch of Windows CE in 1996. Designed as a lightweight and adaptable platform, Windows CE aimed to power a range of devices, from handheld computers to automotive systems. The focus on flexibility and resource efficiency allowed for its implementation on devices with limited processing power and memory.
Building upon Windows CE, Microsoft introduced Pocket PC in 2000, specifically tailored for handheld computers. Pocket PC featured a user interface optimized for touch input and included a suite of productivity applications, such as email, calendar, and web browsing. While Pocket PC gained some traction in the early 2000s, it faced stiff competition from Palm OS and Symbian, which held dominant positions in the handheld market.
The Rise of Smartphones: Windows Mobile
The emergence of smartphones in the mid-2000s brought a new wave of competition in the mobile OS landscape. Microsoft responded with Windows Mobile in 2003, a significant upgrade over Pocket PC, designed to cater to the growing demand for mobile devices with advanced functionalities. Windows Mobile introduced key features like touch-screen support, a more modern user interface, and integration with Microsoft’s desktop software suite.
Windows Mobile gained momentum, particularly with the launch of the HTC TyTN in 2005, one of the first smartphones to offer a full QWERTY keyboard and a touchscreen interface. The platform also saw significant adoption among business users, attracted by its seamless integration with Microsoft Exchange Server and other enterprise solutions.
However, Windows Mobile faced increasing competition from the likes of Symbian, BlackBerry OS, and the newly emerging Android and iOS platforms. While Windows Mobile continued to evolve with features like Wi-Fi and GPS integration, it struggled to keep pace with the rapid advancements in the mobile market.
Windows Phone: A Fresh Start
In 2010, Microsoft announced a complete overhaul of its mobile strategy with the launch of Windows Phone. This new operating system was designed from the ground up with a focus on user experience, simplicity, and a unique interface known as Metro, characterized by its vibrant colors, large tiles, and intuitive navigation.
Windows Phone aimed to differentiate itself from the competition by offering a streamlined and user-friendly experience. Key features included:
- Live Tiles: Dynamic tiles that displayed real-time updates from apps and services, providing users with quick access to information.
- People Hub: A centralized location for managing contacts and social media interactions.
- Xbox Live Integration: Seamless integration with Microsoft’s gaming platform, offering access to games and entertainment.
- Windows Phone Marketplace: A curated app store with a focus on quality and user experience.
Windows Phone received positive reviews for its intuitive interface and unique features. However, despite its strong start, it faced significant challenges in gaining market share. The lack of a robust app ecosystem compared to Android and iOS, combined with the limited availability of Windows Phone devices, hampered its growth.
Windows 10 Mobile: Convergence and Decline
In 2015, Microsoft unveiled Windows 10 Mobile, an update to Windows Phone that aimed to unify the user experience across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and PCs. Windows 10 Mobile offered features like Continuum, allowing users to connect their smartphone to an external display and use it as a desktop computer.
However, despite its ambitious goals, Windows 10 Mobile failed to achieve widespread adoption. The lack of developer support and a dwindling number of available devices led to a decline in the platform’s popularity. Microsoft eventually discontinued support for Windows 10 Mobile in 2019, effectively ending its journey in the mobile operating system market.
The Legacy of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems
Despite its ultimate failure to achieve dominance in the mobile market, Microsoft’s journey through the world of mobile operating systems provides valuable lessons and insights. The company’s early attempts with Windows CE and Pocket PC paved the way for the development of more sophisticated platforms like Windows Mobile and Windows Phone. While these platforms ultimately failed to reach the heights of Android and iOS, they showcased Microsoft’s innovative spirit and its commitment to developing user-friendly mobile experiences.
FAQs on Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems:
Q: What was the main reason for Microsoft’s failure to gain significant market share in the mobile operating system market?
A: Several factors contributed to Microsoft’s struggles, including:
- Limited App Ecosystem: Compared to Android and iOS, Windows Phone and Windows 10 Mobile lacked a wide range of available apps, deterring users and developers alike.
- Limited Device Availability: The availability of Windows Phone and Windows 10 Mobile devices was restricted, making it difficult for users to access the platform.
- Marketing and Promotion: Microsoft’s marketing efforts for its mobile operating systems were often seen as less effective than its competitors.
- Developer Support: Developers were hesitant to invest in developing apps for Windows Phone and Windows 10 Mobile due to the platform’s limited user base.
Q: What were the key features and innovations introduced by Microsoft’s mobile operating systems?
A: Microsoft’s mobile operating systems introduced several innovative features, including:
- Windows CE: Introduced the concept of a lightweight and adaptable operating system for embedded devices.
- Pocket PC: Pioneered the use of touchscreens and a dedicated user interface for handheld computers.
- Windows Mobile: Integrated features like touch-screen support, a modern user interface, and seamless integration with Microsoft’s desktop software suite.
- Windows Phone: Introduced a unique and user-friendly interface with Live Tiles, People Hub, and Xbox Live integration.
- Windows 10 Mobile: Focused on convergence, allowing users to connect their smartphone to an external display and use it as a desktop computer.
Q: What impact did Microsoft’s mobile operating systems have on the mobile industry?
A: Microsoft’s mobile operating systems played a significant role in shaping the evolution of the mobile industry:
- Early Adoption of Touchscreens: Pocket PC and Windows Mobile were among the first platforms to widely adopt touchscreens, paving the way for the touchscreen revolution in mobile devices.
- Integration with Microsoft’s Ecosystem: Windows Mobile and Windows Phone offered seamless integration with Microsoft’s desktop software suite, attracting business users and promoting interoperability.
- Innovation in User Interface Design: Windows Phone introduced a unique and user-friendly interface that inspired other mobile operating systems.
- Focus on Security and Enterprise Solutions: Microsoft’s mobile operating systems emphasized security features and enterprise-grade solutions, catering to business users.
Tips for Users of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems:
- Back Up Your Data: Regularly back up your data to ensure that you don’t lose important files and information.
- Install Security Software: Protect your device from malware and viruses by installing reputable antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system and apps to benefit from security patches and new features.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong and unique passwords for your accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Be Aware of Phishing Scams: Be cautious of suspicious emails and websites that may try to steal your personal information.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s journey in the mobile operating system market was marked by both successes and setbacks. The company’s early attempts with Windows CE and Pocket PC laid the groundwork for more advanced platforms, while Windows Mobile and Windows Phone introduced innovative features and user experiences. However, despite its efforts, Microsoft ultimately failed to gain a significant market share in the mobile OS landscape. While the company’s mobile operating systems may have been short-lived, they left a lasting impact on the industry, contributing to the development of key features and functionalities that are now commonplace in modern smartphones. The lessons learned from Microsoft’s mobile ventures continue to inform the company’s strategies in the evolving world of technology and innovation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of Microsoft’s Mobile Operating Systems: A Comprehensive History and Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!