Safeguarding Your Digital Life: A Guide To Ransomware Protection In Windows 11
Safeguarding Your Digital Life: A Guide to Ransomware Protection in Windows 11
Related Articles: Safeguarding Your Digital Life: A Guide to Ransomware Protection in Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Safeguarding Your Digital Life: A Guide to Ransomware Protection in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Safeguarding Your Digital Life: A Guide to Ransomware Protection in Windows 11
Ransomware, a malicious software designed to encrypt data and hold it hostage until a ransom is paid, poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. The impact of a ransomware attack can be devastating, leading to data loss, financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruption. However, with the right preventative measures and proactive strategies, the risk of falling victim to ransomware can be significantly mitigated. This guide delves into the robust security features built into Windows 11, offering insights into how to effectively manage ransomware protection and safeguard your digital assets.
Understanding the Threat: The Evolution of Ransomware
Ransomware has evolved from simple file-encrypting malware to sophisticated, targeted attacks leveraging social engineering, phishing campaigns, and vulnerability exploitation. These attacks can infiltrate systems through various means, including:
- Phishing Emails: Malicious emails containing infected attachments or links that, when clicked, install ransomware onto the device.
- Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities: Hackers exploit known vulnerabilities in software applications to gain unauthorized access and deploy ransomware.
- Malicious Websites: Visiting compromised websites can lead to ransomware infections through drive-by downloads or exploit kits.
- Removable Media: Infected USB drives or external hard drives can spread ransomware when connected to a computer.
Windows 11’s Built-in Defense Mechanisms
Windows 11 incorporates a comprehensive suite of security features designed to proactively combat ransomware threats. These features work in tandem to create a robust defense system, offering a multi-layered approach to protection:
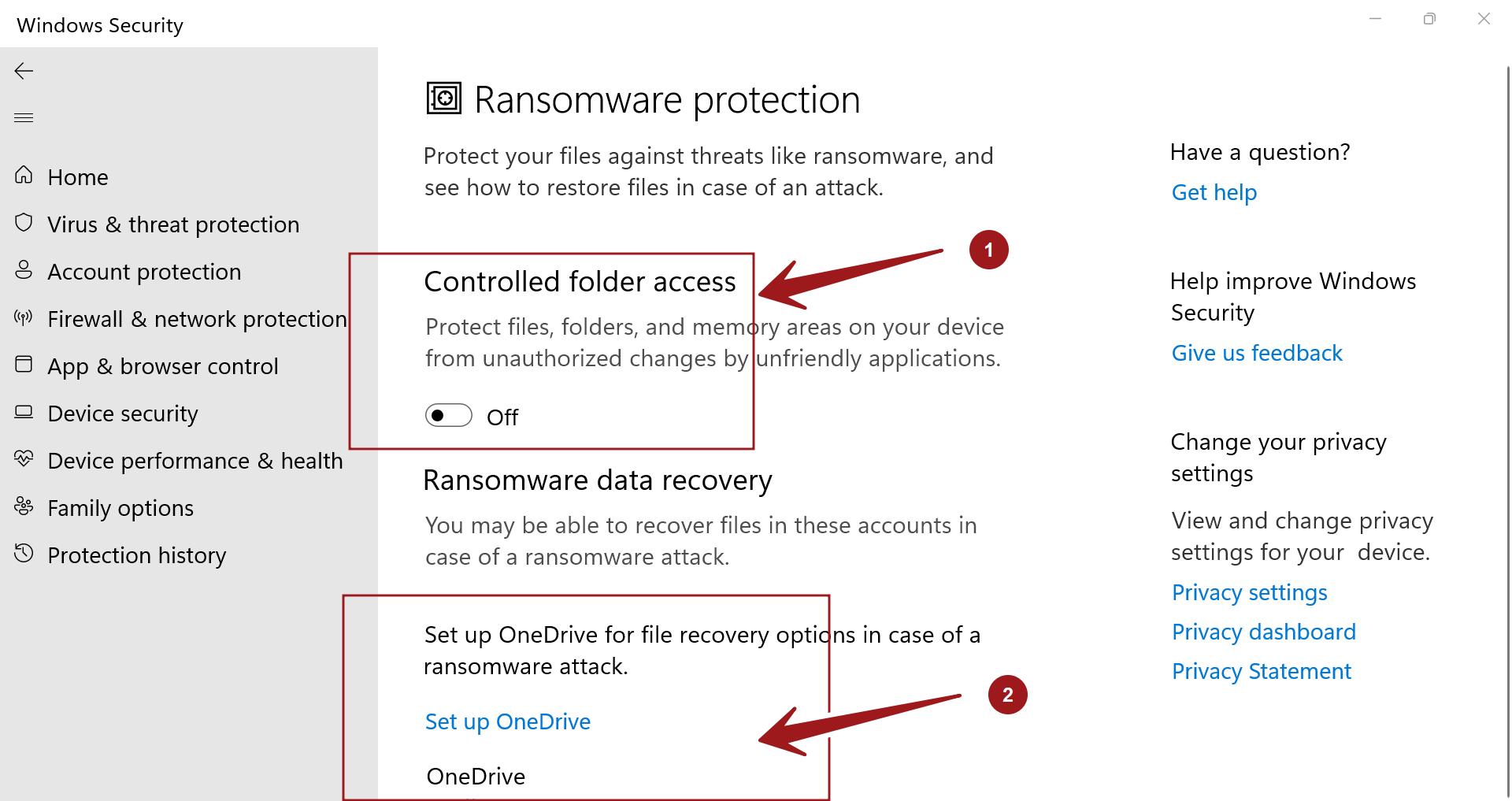
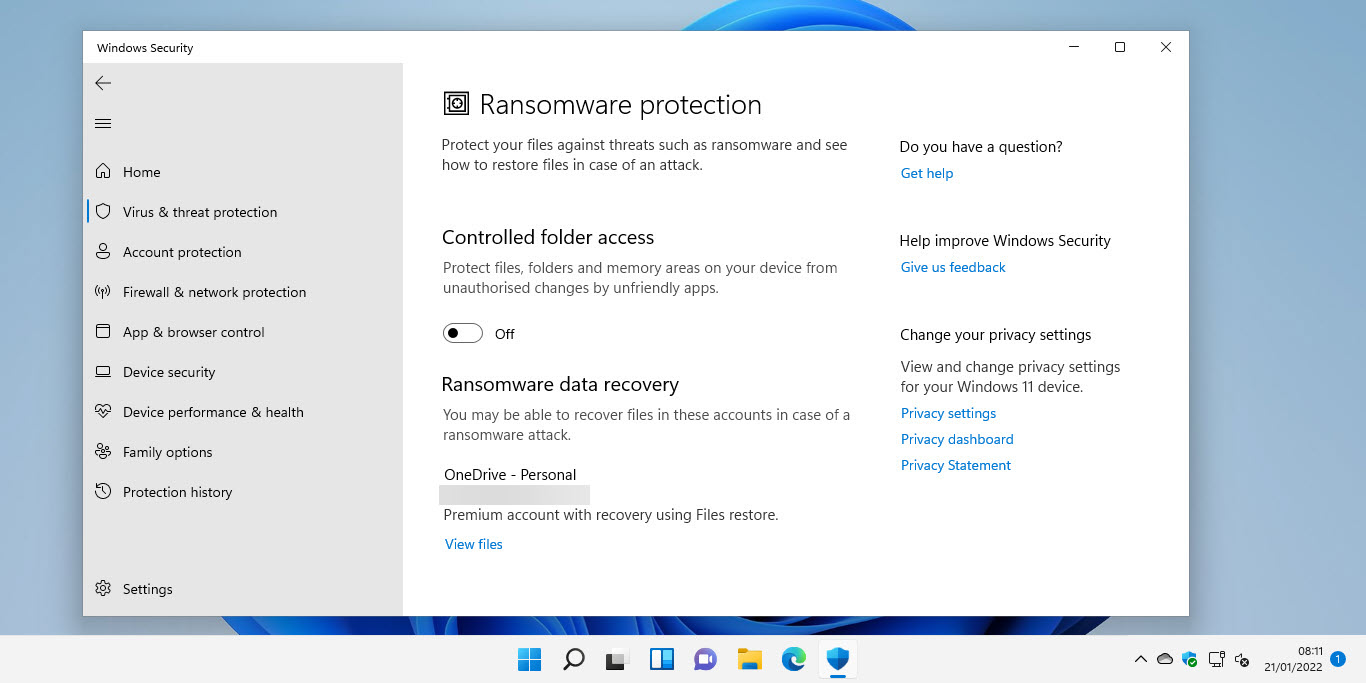
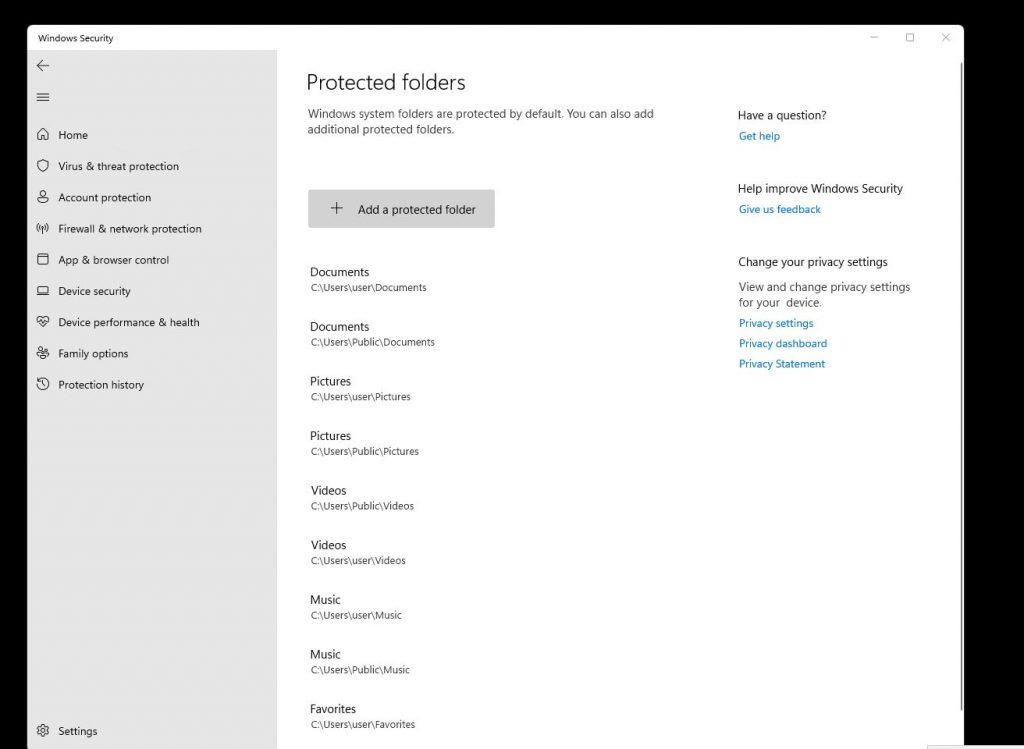
1. Controlled Folder Access (CFA)
CFA is a powerful feature that restricts unauthorized access to designated folders, effectively acting as a shield against ransomware attacks. By default, CFA protects critical folders like Documents, Pictures, Videos, Desktop, and Downloads. Users can further customize the list of protected folders to include other important directories.
- How it works: CFA monitors applications for suspicious behavior and blocks any unauthorized attempts to modify or delete files within protected folders.
- Configuration: CFA is enabled by default in Windows 11, but users can fine-tune its settings by navigating to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection > Manage settings > Controlled folder access.
- Benefits: CFA provides an additional layer of protection by preventing ransomware from encrypting critical data, even if the system is compromised.
2. Ransomware Protection (RWP)
RWP is a specialized feature that detects and mitigates ransomware behavior by monitoring for suspicious file encryption patterns and blocking potential threats.
- How it works: RWP analyzes file access patterns and identifies activities that resemble ransomware behavior, such as rapid encryption of multiple files or attempts to modify system files.
- Configuration: RWP is enabled by default in Windows 11 and can be accessed via Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection > Manage settings > Ransomware protection.
- Benefits: RWP enhances system security by proactively identifying and blocking ransomware attacks before they can cause significant damage.
3. Windows Defender Antivirus
Windows Defender Antivirus, a built-in security solution, plays a crucial role in detecting and removing known ransomware threats.
- How it works: Windows Defender Antivirus uses real-time protection to scan files and applications for malicious code, including ransomware signatures. It also leverages cloud-based intelligence to detect and block emerging threats.
- Configuration: Windows Defender Antivirus is automatically enabled and updated in Windows 11. Users can access its settings and customize its behavior through Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection.
- Benefits: Windows Defender Antivirus provides continuous protection against a wide range of malware, including ransomware, ensuring that your system is shielded from known threats.
4. Windows Security Center
Windows Security Center acts as a central hub for managing various security settings, including those related to ransomware protection.
- How it works: Windows Security Center provides a consolidated view of system security status, including alerts, notifications, and recommendations for improving security posture.
- Configuration: Users can access Windows Security Center through Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security.
- Benefits: Windows Security Center simplifies security management by offering a single interface for monitoring and configuring various security features, including ransomware protection.
Beyond Windows 11: Essential Practices for Robust Ransomware Protection
While Windows 11 offers robust built-in protection, implementing a comprehensive ransomware mitigation strategy requires a multi-pronged approach. Here are some additional essential practices to consider:
1. Regular Backups: Implementing a regular data backup strategy is crucial for recovering from a ransomware attack. Back up important files to a separate storage device, cloud storage service, or network location. Ensure that backups are stored offline and are not accessible to the infected system.
2. Strong Passwords: Employ strong and unique passwords for all online accounts and ensure that they are not reused across different services. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
3. Software Updates: Keep all software applications, including operating systems, antivirus software, and third-party applications, updated with the latest security patches. These updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities that ransomware exploits.
4. User Education: Train users to recognize and avoid phishing emails, malicious websites, and suspicious attachments. Educate them about the risks of clicking on unknown links or downloading files from untrusted sources.
5. Network Security: Secure your network with a strong firewall and ensure that all devices connected to the network are protected with up-to-date antivirus software.
6. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA for all critical accounts, requiring users to provide an additional verification factor beyond just a password. This adds an extra layer of security and makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
7. Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit using strong encryption algorithms. This ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains inaccessible without the decryption key.
8. Incident Response Plan: Develop and implement a comprehensive incident response plan to guide your actions in the event of a ransomware attack. This plan should outline steps for containment, recovery, and communication.
9. Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about emerging ransomware threats and vulnerabilities by subscribing to threat intelligence feeds and security advisories. This knowledge will help you stay ahead of attackers and proactively mitigate risks.
10. Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in your systems and networks. These audits can help you detect and remediate potential weaknesses before they are exploited by attackers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What happens if my computer gets infected with ransomware?
A: If your computer is infected with ransomware, your data will be encrypted and held hostage until you pay a ransom. The encrypted data may become inaccessible, and recovering it without paying the ransom can be extremely challenging.
Q: How do I know if my computer is infected with ransomware?
A: Some common signs of a ransomware infection include:
- Files becoming inaccessible or encrypted.
- Unusual file extensions or strange characters appended to file names.
- Ransom demands appearing on your screen or in pop-up messages.
- System performance slowing down significantly.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my computer is infected with ransomware?
A: If you suspect a ransomware infection, take the following steps:
- Disconnect your computer from the internet and any network.
- Do not attempt to decrypt the files yourself or pay the ransom.
- Contact a cybersecurity professional or your IT department for assistance.
Q: Can I prevent ransomware from infecting my computer?
A: While no system is 100% immune to ransomware attacks, implementing a robust security strategy can significantly reduce the risk.
Q: Is it safe to pay the ransom?
A: Paying the ransom is not recommended. There is no guarantee that you will regain access to your data even after paying. Paying the ransom also encourages cybercriminals and fuels their activities.
Tips for Enhanced Ransomware Protection
- Enable Windows 11’s built-in security features: Utilize Controlled Folder Access, Ransomware Protection, and Windows Defender Antivirus to bolster your system’s defenses.
- Backup your data regularly: Implement a reliable backup strategy to ensure that you have copies of your important data stored offline.
- Stay informed about emerging threats: Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds and security advisories to stay ahead of the latest ransomware tactics.
- Educate yourself and your users: Train users to identify and avoid phishing emails, malicious websites, and suspicious attachments.
- Keep your software up to date: Regularly update your operating system, antivirus software, and other applications to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication: Protect your accounts with strong, unique passwords and enable MFA for critical services.
- Encrypt sensitive data: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Implement a comprehensive incident response plan: Prepare for a potential ransomware attack by developing a plan that outlines steps for containment, recovery, and communication.
Conclusion
Ransomware poses a serious threat to individuals and organizations, but with proactive measures and a comprehensive security strategy, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these attacks. Windows 11 provides a robust foundation for ransomware protection, offering a suite of built-in security features designed to safeguard your data. By leveraging these features and implementing additional security best practices, you can create a multi-layered defense system that effectively mitigates the risk of ransomware infections and protects your digital assets. Remember, staying informed about emerging threats, maintaining vigilant security practices, and prioritizing data backup are key to securing your digital life in today’s evolving threat landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Safeguarding Your Digital Life: A Guide to Ransomware Protection in Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!