Safeguarding The Heart Of Windows 11: A Comprehensive Look At LSASS Protection
Safeguarding the Heart of Windows 11: A Comprehensive Look at LSASS Protection
Related Articles: Safeguarding the Heart of Windows 11: A Comprehensive Look at LSASS Protection
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Safeguarding the Heart of Windows 11: A Comprehensive Look at LSASS Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Safeguarding the Heart of Windows 11: A Comprehensive Look at LSASS Protection
The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) is a critical component of the Windows operating system, responsible for managing user authentication, password storage, and other security-related tasks. It holds the keys to the kingdom, so to speak, making it a prime target for malicious actors seeking to compromise a system. Windows 11 introduces a suite of enhanced security features designed to protect LSASS, bolstering the overall security posture of the operating system. This article delves into the intricacies of LSASS protection in Windows 11, exploring its multifaceted approach, benefits, and implications for system security.
Understanding the Threat: The Perils of LSASS Compromise
LSASS, due to its inherent functions, presents a tantalizing target for attackers. Compromising LSASS grants malicious actors access to sensitive data, including:
- User Credentials: Passwords, hashes, and other authentication information stored within the system are readily accessible.
- Security Tokens: These tokens grant access to system resources, enabling attackers to gain elevated privileges and control over the entire system.
- System Configuration: Attackers can manipulate system settings, potentially disabling security measures or opening backdoors for future exploitation.
The ramifications of LSASS compromise are severe, potentially leading to:
- Data Theft: Stolen credentials can be used to access sensitive information stored on the system or other accounts linked to the compromised user.
- Malware Infection: Attackers can install malware, enabling them to control the compromised system, steal data, or launch further attacks.
- Denial of Service: Attackers can disrupt normal system operations, rendering the system unusable.
Windows 11’s Multifaceted Approach to LSASS Protection
Windows 11 implements a layered defense strategy to protect LSASS, employing multiple security mechanisms to mitigate the risks associated with LSASS compromise. These include:
1. Enhanced Process Isolation:
- Process Guard: Introduced in Windows 10, Process Guard leverages hardware-based memory protection to isolate sensitive processes, including LSASS, from unauthorized access. This ensures that even if an attacker compromises another process, they cannot directly access the memory space of LSASS.
- Control Flow Guard: This technology prevents attackers from manipulating the execution flow of critical processes, including LSASS, by detecting and blocking malicious code that attempts to jump to unauthorized locations within the process’s memory.
2. Credential Guard:
- Virtualization-Based Security: This feature uses hardware virtualization to isolate the process responsible for storing and managing user credentials, effectively preventing attackers from accessing them even if they gain control of the main operating system.
3. Protected Process Light (PPL):
- Lightweight Protection: PPL provides a more lightweight form of process isolation, primarily targeting processes like LSASS that are not as critical as those protected by Process Guard. PPL relies on software-based protection mechanisms to restrict access to the process’s memory space.
4. Secure Boot:
- Verified Boot Sequence: Secure Boot ensures that only trusted operating system components are loaded during startup, preventing malicious software from hijacking the boot process and gaining control over the system before LSASS is initialized.
5. System Integrity Protection (SIP):
- Kernel-Level Protection: SIP, also known as "RootGuard," prevents unauthorized modifications to the operating system kernel, safeguarding critical system files and preventing attackers from disabling or bypassing security features like Process Guard.
6. Enhanced User Account Control (UAC):
- Elevated Privileges: UAC prompts users for permission before granting elevated privileges, hindering attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities that require administrative access.
Benefits of LSASS Protection in Windows 11
The robust LSASS protection mechanisms implemented in Windows 11 offer significant benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security Posture: The layered defense approach significantly reduces the risk of LSASS compromise, bolstering the overall security of the system.
- Improved Data Protection: Sensitive user credentials, security tokens, and system configuration data are better protected, minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Reduced Attack Surface: The isolation of LSASS makes it harder for attackers to gain control over the system, reducing the potential impact of successful attacks.
- Increased User Trust: The enhanced security measures instill greater confidence in the operating system, reassuring users that their data and privacy are well-protected.
FAQs on LSASS Protection in Windows 11
Q: Is LSASS protection enabled by default in Windows 11?
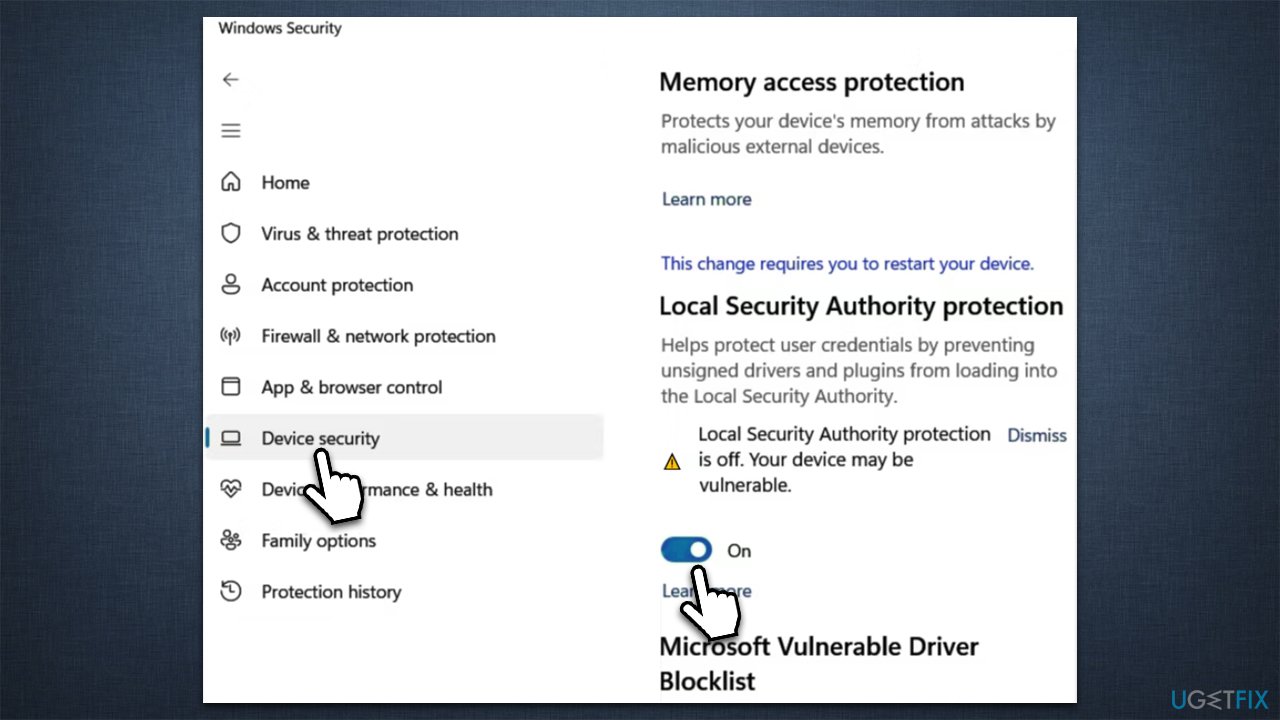
A: Most of the LSASS protection features, including Process Guard, Control Flow Guard, and Credential Guard, are enabled by default in Windows 11. However, certain features, such as Secure Boot, might require specific system configurations or BIOS settings.
Q: Can I disable LSASS protection features in Windows 11?
A: While it is possible to disable some LSASS protection features, it is strongly discouraged as it significantly weakens the system’s security posture and increases the risk of compromise.
Q: How can I verify if LSASS protection features are enabled on my system?
A: You can check the status of LSASS protection features using the following methods:
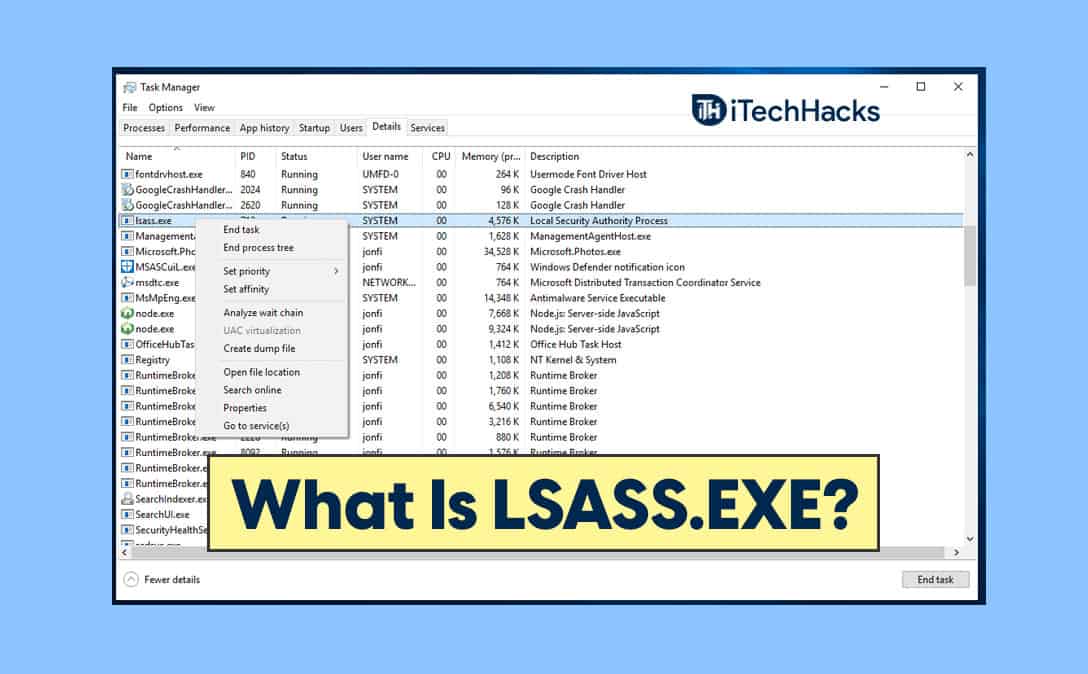
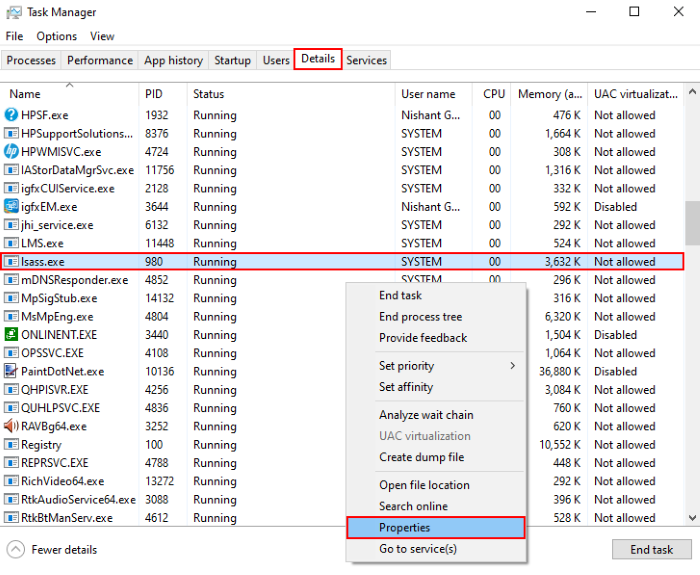
- Task Manager: Open Task Manager and navigate to the "Details" tab. Look for the "LSASS.exe" process and check if it is marked as "Protected Process" or "Virtualized."
- Command Prompt: Open Command Prompt as administrator and execute the command "systeminfo" to display system information, including the status of Secure Boot and other security features.
Q: What are the system requirements for LSASS protection features in Windows 11?
A: Most LSASS protection features rely on hardware-based security mechanisms, such as virtualization extensions (Intel VT-x or AMD-V), which are typically available on modern PCs. However, specific requirements might vary depending on the feature.
Q: Are there any known vulnerabilities or limitations in LSASS protection in Windows 11?
A: While Windows 11’s LSASS protection is robust, it’s important to note that no security system is perfect. New vulnerabilities might be discovered, and attackers constantly devise new techniques to circumvent security measures. Keeping your system up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates is crucial for mitigating potential vulnerabilities.
Tips for Enhancing LSASS Protection in Windows 11
- Keep your system up-to-date: Regularly install the latest security updates and patches to address known vulnerabilities and enhance the effectiveness of LSASS protection features.
- Use strong passwords: Create complex and unique passwords for all your accounts, including your Windows user account, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even if they steal your password.
- Be cautious of suspicious emails and links: Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown or untrusted sources as they could contain malicious software that targets LSASS.
- Use a reputable antivirus solution: A comprehensive antivirus program can help detect and remove malware that might target LSASS or other critical system components.
Conclusion: A Strong Foundation for Enhanced Security
Windows 11’s robust LSASS protection mechanisms are a testament to Microsoft’s commitment to enhancing system security and safeguarding user data. The layered defense approach, employing a combination of software and hardware-based security features, significantly reduces the risk of LSASS compromise, providing a strong foundation for enhanced security. While no security system is foolproof, the comprehensive protection offered by Windows 11 empowers users to navigate the digital landscape with greater confidence, knowing that their sensitive data and system integrity are well-protected.
It is essential to remain vigilant and follow best practices for cybersecurity, including keeping your system updated, using strong passwords, and being wary of suspicious activity. By adopting a proactive approach to security, users can further bolster the effectiveness of LSASS protection and minimize the risk of cyberattacks.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Safeguarding the Heart of Windows 11: A Comprehensive Look at LSASS Protection. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!