Optimizing Windows 10 Performance: A Comprehensive Guide
Optimizing Windows 10 Performance: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Optimizing Windows 10 Performance: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Optimizing Windows 10 Performance: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Optimizing Windows 10 Performance: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 10, despite its robust features and widespread adoption, can sometimes fall prey to sluggish performance, impacting user experience and productivity. However, numerous strategies can be employed to enhance system responsiveness and overall efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores various methods for optimizing Windows 10, encompassing both simple adjustments and more advanced techniques.
Understanding Performance Bottlenecks:
Before delving into optimization strategies, it is crucial to understand the common culprits behind slow Windows 10 performance:
- Insufficient RAM: Limited RAM can lead to excessive disk swapping, causing noticeable lag and slowdowns.
- Cluttered Hard Drive: A fragmented or overloaded hard drive can hinder file access, impacting application loading times and overall system responsiveness.
- Resource-Intensive Programs: Running numerous background programs, especially resource-heavy applications, can consume valuable system resources, leading to sluggishness.
- Outdated Drivers: Outdated drivers can lead to compatibility issues and inefficient resource utilization, affecting device performance and overall system stability.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can drain system resources, consume bandwidth, and compromise security, impacting system performance and stability.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause hardware components to throttle their performance, leading to slowdowns and potential system instability.
Optimization Techniques:
1. Freeing Up Disk Space:
- Deleting Unnecessary Files: Regularly remove temporary files, downloaded files, and unused programs to free up disk space.
- Utilizing Disk Cleanup: Windows’ built-in Disk Cleanup tool effectively removes temporary files, system files, and other unnecessary data.
- Moving Files to External Storage: Transfer large files, such as movies and music, to external drives to reduce the load on the internal hard drive.
- Uninstalling Unused Programs: Remove applications that are no longer used to free up disk space and reduce startup time.
2. Managing Startup Programs:
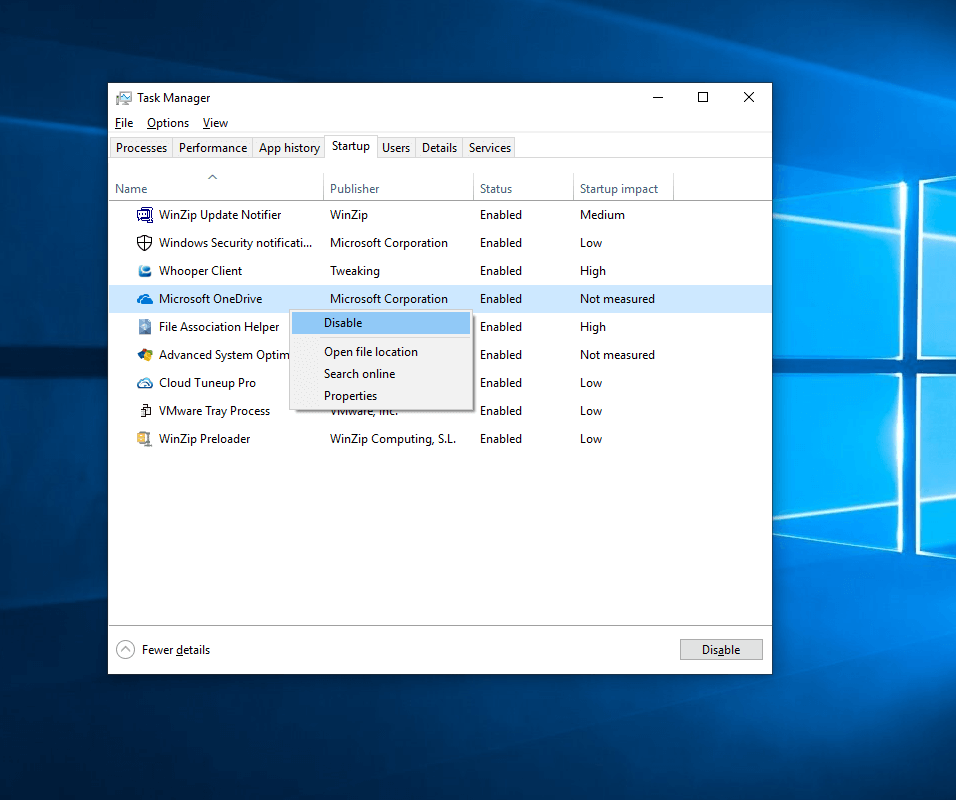
- Disabling Unnecessary Programs: Disable programs that launch automatically at startup to reduce the initial load on the system.
- Using Task Manager: Access Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to view and manage startup programs.
- Utilizing Startup Apps Settings: Navigate to Settings > Apps > Startup to manage applications that launch automatically.
3. Optimizing System Settings:
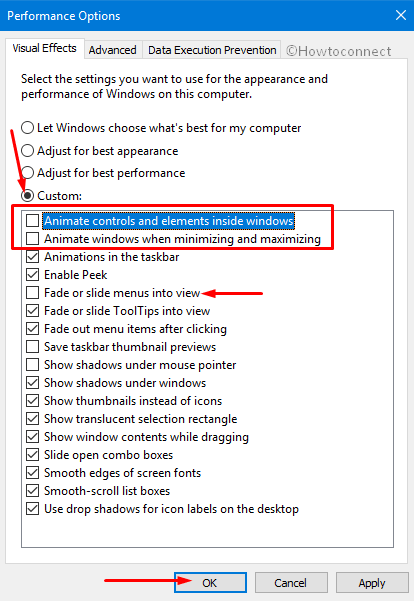
- Adjusting Visual Effects: Disable unnecessary visual effects, such as animations and transparency, to improve system responsiveness.
- Enabling Performance Mode: Select "Best performance" in the Visual Effects settings to prioritize speed over aesthetics.
- Disabling Transparency Effects: Disable transparency effects in the Settings > Personalization > Colors menu to reduce resource consumption.
- Optimizing Power Settings: Choose a balanced or high-performance power plan to ensure adequate power for demanding tasks.
4. Managing Background Processes:
- Limiting Background Apps: Reduce the number of applications running in the background to conserve system resources.
- Disabling Background Processes: Use the Task Manager to disable unnecessary background processes.
- Adjusting App Permissions: Limit the permissions of certain applications to prevent them from accessing system resources or running in the background.
5. Updating Drivers and Software:
- Checking for Updates: Regularly update device drivers and software to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- Utilizing Windows Update: Windows Update automatically delivers crucial security patches and system enhancements.
- Using Manufacturer Websites: Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers for specific devices.
6. Defragmenting Hard Drive:
- Understanding Defragmentation: Defragmentation reorganizes fragmented files on the hard drive, improving file access times and system responsiveness.
- Using Disk Defragmenter: Windows’ built-in Disk Defragmenter tool helps optimize hard drive performance.
- Utilizing Third-Party Defragmentation Tools: Consider using specialized defragmentation tools for more efficient optimization.
7. Running System Scans:
- Checking for Malware: Regularly scan for malware and viruses using reputable antivirus software.
- Running Disk Check: Use the "chkdsk" command to check for and repair hard drive errors.
- Performing System File Checker: Utilize the "sfc /scannow" command to verify and repair system files.
8. Utilizing System Resources Effectively:
- Closing Unused Tabs and Programs: Regularly close unnecessary browser tabs and applications to free up system resources.
- Managing RAM Usage: Monitor RAM usage using Task Manager and close resource-intensive applications when not in use.
- Optimizing Virtual Memory: Adjust virtual memory settings to ensure adequate space for program execution.
9. Upgrading Hardware:
- Increasing RAM: Adding more RAM can significantly improve system performance, especially when running demanding applications.
- Upgrading Hard Drive: Replacing a traditional hard drive with a solid-state drive (SSD) can dramatically enhance boot times and overall system responsiveness.
- Upgrading CPU: Upgrading the CPU can provide a significant performance boost for demanding tasks, such as gaming or video editing.
FAQs
Q: How do I know if my computer is running slow due to insufficient RAM?
A: Signs of insufficient RAM include slow application loading times, frequent program crashes, and noticeable lag when switching between applications.
Q: Is it safe to disable startup programs?
A: Disabling startup programs is generally safe, but it’s crucial to avoid disabling essential system processes. Use caution and research the purpose of each program before disabling it.
Q: How often should I defragment my hard drive?
A: Defragmentation is less critical for modern SSDs, as they do not suffer from fragmentation. For traditional hard drives, defragmentation is recommended once a month or when performance noticeably degrades.
Q: Can upgrading my CPU significantly improve system performance?
A: Upgrading the CPU can provide a substantial performance boost, especially for demanding tasks. However, the impact of an upgrade depends on the existing CPU and the specific workload.
Tips
- Prioritize Performance: Consider prioritizing system performance over visual effects, especially for demanding tasks.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement regular system maintenance practices, such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, and driver updates, to prevent performance degradation.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Use Task Manager to monitor resource usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Research Optimization Tools: Explore third-party optimization tools for advanced system optimization, but proceed with caution and choose reputable software.
Conclusion
Optimizing Windows 10 performance involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing various techniques from simple adjustments to hardware upgrades. By understanding the common performance bottlenecks and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, users can significantly enhance system responsiveness, improve application loading times, and maximize overall efficiency. Regular maintenance, resource management, and a focus on performance optimization will ensure a smooth and productive Windows 10 experience.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Optimizing Windows 10 Performance: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!