Optimizing Windows 10: A Guide To Disabling Unnecessary Services
Optimizing Windows 10: A Guide to Disabling Unnecessary Services
Related Articles: Optimizing Windows 10: A Guide to Disabling Unnecessary Services
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Optimizing Windows 10: A Guide to Disabling Unnecessary Services. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Optimizing Windows 10: A Guide to Disabling Unnecessary Services

Windows 10, like any operating system, comes equipped with a plethora of services designed to enhance user experience and system functionality. However, not all services are equally essential for optimal performance, and some may even hinder system responsiveness. Understanding which services can be safely disabled can lead to noticeable improvements in system speed, resource utilization, and overall stability.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Windows 10 services that can be disabled without compromising essential system functionality. It is crucial to understand that disabling services should be approached with caution and only after careful consideration.
Understanding Windows Services
Windows services are background processes that run independently of user interaction, performing tasks like managing network connections, updating system files, or providing security features. These services are typically categorized based on their importance:
- Critical Services: These services are essential for the basic operation of Windows and cannot be disabled without causing significant system instability.
- Important Services: These services are crucial for specific system functions, but their absence might lead to limited functionality or reduced performance.
- Optional Services: These services provide additional features or enhancements that may not be necessary for all users. They can be safely disabled without affecting the core functionality of Windows.
Identifying Services for Disabling
The process of identifying services for disabling requires a systematic approach:
- Identify Services with High Resource Consumption: Use the Task Manager (press Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to observe the "Performance" tab and identify processes with high CPU or memory usage. These processes might correspond to services that consume significant resources.
- Analyze Services Based on Functionality: Research the purpose of each service using online resources like Microsoft documentation or community forums. This will help determine whether a particular service provides a feature you use regularly or if it can be safely disabled.
- Consult Community Resources: Explore online forums and communities dedicated to Windows optimization, where users share their experiences and recommendations for disabling specific services.
Important Considerations
Before disabling any service, it is crucial to consider the following:
- Impact on System Functionality: Understand the potential consequences of disabling a service. Ensure that the absence of the service will not significantly affect your daily usage or critical system functions.
- Reversibility: Always ensure that the process of disabling a service is reversible. This is crucial in case the disabled service is required for a specific task or application.
- System Stability: Monitor your system’s performance after disabling a service to identify any potential issues or instability. If any problems arise, immediately re-enable the service.
Recommended Services to Disable
The following services are commonly recommended for disabling, but it is essential to conduct thorough research and assess their relevance to your individual needs:
1. Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
- Function: BITS manages background downloads and uploads, including Windows updates.
- Disabling Impact: May slow down background downloads and updates.
- Recommendation: Disable if you prefer to manage downloads and updates manually or if you have a reliable internet connection with consistent download speeds.
2. Connected User Experiences and Telemetry
- Function: Collects data on user activity and system performance for Microsoft to improve Windows features.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents data collection, potentially affecting future feature development.
- Recommendation: Disable if you are concerned about privacy or want to minimize data usage.
3. Diagnostic Policy Service
- Function: Collects diagnostic data to identify and resolve system issues.
- Disabling Impact: May limit Microsoft’s ability to diagnose and resolve system problems.
- Recommendation: Disable if you are concerned about privacy or if you are confident in troubleshooting system issues independently.
4. Fax Service
- Function: Enables faxing capabilities, but rarely used in modern environments.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents faxing functionality.
- Recommendation: Disable unless you actively use faxing capabilities.
5. Function Discovery Resource Publication
- Function: Enables automatic discovery of network resources, but often redundant with other discovery mechanisms.
- Disabling Impact: Might affect the discovery of certain network devices.
- Recommendation: Disable if you do not rely heavily on automatic network resource discovery.
6. IP Helper Service
- Function: Provides support for IPv6 and other network protocols, but often redundant with other services.
- Disabling Impact: Might affect IPv6 connectivity or specific network functionalities.
- Recommendation: Disable if you are not actively using IPv6 or if you experience network issues related to this service.
7. Print Spooler
- Function: Manages printing tasks, but can consume resources if not actively used.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents printing functionality.
- Recommendation: Disable if you do not frequently print documents and prefer to manage printing tasks manually.
8. Secondary Logon Service
- Function: Enables secondary logins, but rarely used in typical user scenarios.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents secondary logins, which might be required for specific applications or scenarios.
- Recommendation: Disable unless you actively use secondary logins.
9. Shell Hardware Detection
- Function: Detects and configures hardware devices, but can consume resources and cause conflicts.
- Disabling Impact: Might affect the detection and configuration of certain hardware devices.
- Recommendation: Disable if you experience hardware detection issues or if you prefer to manage hardware configuration manually.
10. Windows Error Reporting Service
- Function: Collects error reports to improve Windows stability, but can be intrusive.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents automatic error reporting, potentially affecting future feature development.
- Recommendation: Disable if you are concerned about privacy or if you prefer to manage error reporting manually.
11. Windows Search
- Function: Indexes files and content for faster searching, but can consume significant resources.
- Disabling Impact: Slows down search functionality.
- Recommendation: Disable if you do not use Windows Search frequently or if you prefer alternative search methods.
12. Windows Update
- Function: Automatically downloads and installs Windows updates, but can interrupt workflow.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents automatic updates, potentially delaying important security patches.
- Recommendation: Disable if you prefer to manage updates manually or if you have a reliable internet connection with consistent download speeds.
13. Wireless Zero Configuration
- Function: Automatically connects to Wi-Fi networks, but can cause connection issues.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents automatic Wi-Fi connections.
- Recommendation: Disable if you experience Wi-Fi connectivity problems or if you prefer to manage Wi-Fi connections manually.
14. World Wide Web Services
- Function: Provides web server functionality, but rarely used in typical user scenarios.
- Disabling Impact: Prevents web server functionality.
- Recommendation: Disable unless you actively use web server capabilities.
Disabling Services
To disable a service, follow these steps:
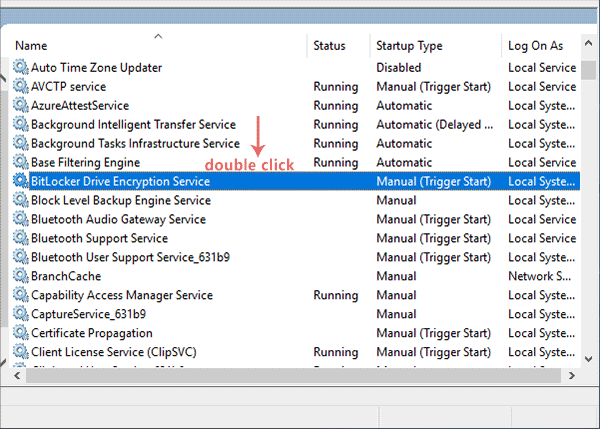
- Open the Services window: Press Windows key + R, type services.msc, and press Enter.
- Locate the service: Scroll through the list of services and find the one you want to disable.
- Right-click the service: Select Properties.
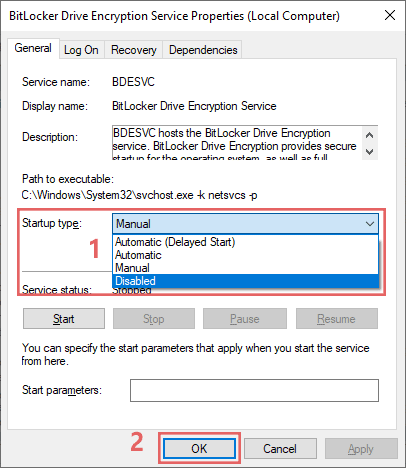
- Change the startup type: In the "Startup type" dropdown, select Disabled.
- Apply the changes: Click Apply and then OK.
Restarting the Computer:
After disabling services, it is recommended to restart your computer to ensure that the changes take effect properly.
Monitoring System Performance:
After disabling services, carefully monitor your system’s performance for any unexpected behavior or issues. If you experience any problems, immediately re-enable the disabled service.
FAQs
Q: Is disabling services safe?
A: Disabling services can be safe if done correctly and with careful consideration. However, it is crucial to understand the potential consequences and ensure that the disabled service is not essential for your system’s functionality.
Q: Can I disable all services?
A: No, you cannot disable all services without causing significant system instability. Critical services are essential for the basic operation of Windows and cannot be disabled.
Q: What if I disable a service I need later?
A: You can always re-enable a disabled service by following the same steps as above, but selecting Automatic or Manual in the "Startup type" dropdown.
Q: How do I know which services are safe to disable?
A: Research the purpose of each service and consult community resources for recommendations. It is always best to start with services that are less critical and gradually explore other options.
Tips
- Backup your system: Before making any changes to your system, create a system restore point or backup your data to ensure you can revert to a previous state if necessary.
- Start with a few services: Begin by disabling a few services that are less critical and monitor your system’s performance. Gradually explore other options based on your experience.
- Document your changes: Keep a record of the services you disable and their original startup types. This will help you easily re-enable them if needed.
- Be cautious with critical services: Avoid disabling critical services unless you have a specific reason and are confident in your understanding of the system’s dependencies.
- Seek professional assistance: If you are unsure about disabling services or encounter any issues, seek professional assistance from a qualified IT specialist.
Conclusion
Disabling unnecessary services in Windows 10 can lead to noticeable improvements in system speed, resource utilization, and overall stability. However, it is crucial to approach this process with caution and only disable services after careful research and consideration. By understanding the potential impact of disabling services and following the recommendations outlined in this guide, users can optimize their Windows 10 experience without compromising essential functionality. Remember to monitor system performance after disabling services and revert to the original settings if any issues arise.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Optimizing Windows 10: A Guide to Disabling Unnecessary Services. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!