Optimizing Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide To Enhance System Performance
Optimizing Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhance System Performance
Related Articles: Optimizing Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhance System Performance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Optimizing Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhance System Performance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Optimizing Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhance System Performance
The Windows 10 operating system, while robust and feature-rich, can sometimes encounter performance bottlenecks. These can manifest as slow startup times, sluggish application responses, or even system crashes. Fortunately, a multitude of techniques and strategies exist to optimize Windows 10, enhancing its responsiveness and overall efficiency. This guide will delve into the most effective methods for achieving peak performance, addressing common issues, and ensuring a smoother user experience.
Understanding Performance Bottlenecks
Before delving into optimization techniques, it’s crucial to grasp the underlying causes of performance issues. Common culprits include:
- Hardware limitations: Outdated or insufficient hardware, such as a slow processor, limited RAM, or a cluttered hard drive, can significantly hinder performance.
- Software conflicts: Incompatible or outdated software can create conflicts, leading to crashes, slowdowns, and resource depletion.
- System bloatware: Pre-installed applications, often referred to as bloatware, consume resources and can hinder overall system efficiency.
- Background processes: Numerous programs and services run in the background, consuming resources and impacting performance, especially during intensive tasks.
- Malware infections: Malicious software can consume system resources, slow down processes, and even compromise data security.
- Insufficient disk space: A full hard drive can lead to slow file access, program launches, and overall system sluggishness.
Strategies for Optimizing Windows 10 Performance
1. Hardware Optimization:
- Upgrade RAM: Insufficient RAM is a common culprit for slowdowns. Adding more RAM can dramatically improve responsiveness, especially when running multiple applications or demanding software.
- Replace Hard Drive with SSD: Solid-state drives (SSDs) offer significantly faster read/write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). Upgrading to an SSD can drastically reduce boot times, application loading times, and overall system responsiveness.
- Upgrade Processor: If the CPU is consistently reaching its maximum capacity, an upgrade to a faster processor can improve performance, particularly for demanding tasks like gaming or video editing.
- Ensure Proper Cooling: Overheating can lead to system slowdowns and instability. Ensure adequate cooling by cleaning fans, checking thermal paste, and optimizing airflow within the computer case.
2. Software Optimization:
- Uninstall Unnecessary Software: Removing unused applications and bloatware can free up disk space and reduce resource consumption.
- Keep Software Updated: Outdated software can be inefficient and prone to bugs. Regularly update applications and drivers to ensure optimal performance and security.
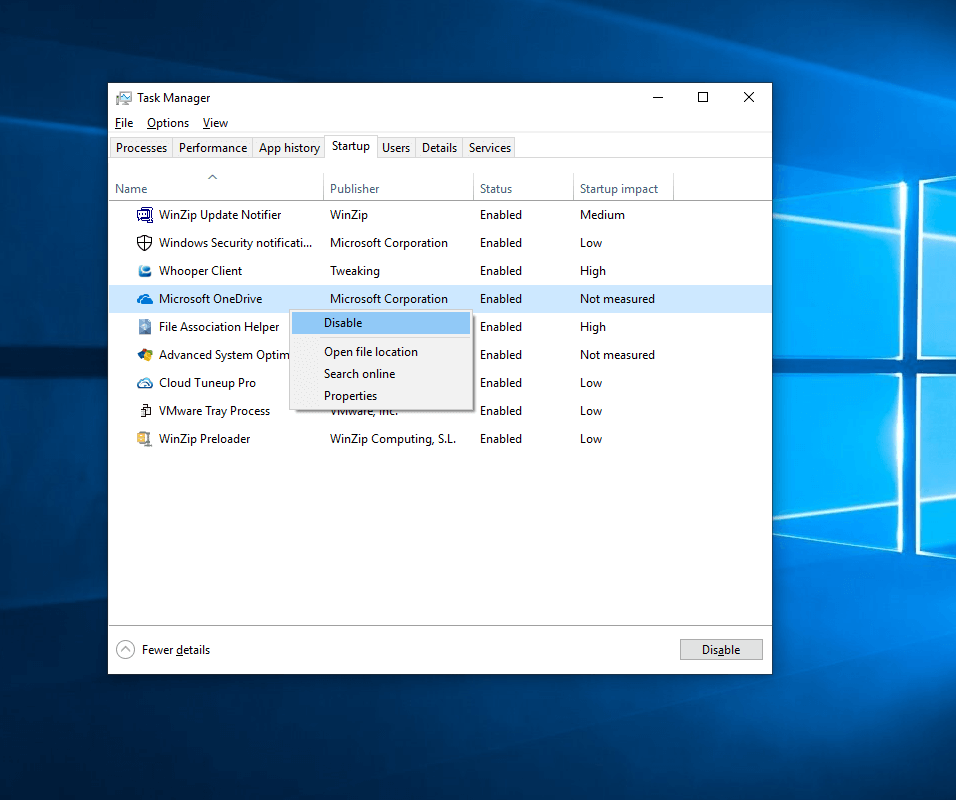
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs: Many programs automatically launch at startup, consuming resources and slowing down boot times. Disable unnecessary startup programs through the Task Manager or System Configuration settings.
- Optimize Power Settings: Adjust power settings to balance performance and energy consumption. Selecting a high-performance power plan can boost system responsiveness but may increase energy consumption.
- Defragment Hard Drive (HDD Only): While not necessary for SSDs, defragmenting an HDD can improve performance by organizing fragmented files and optimizing disk access.
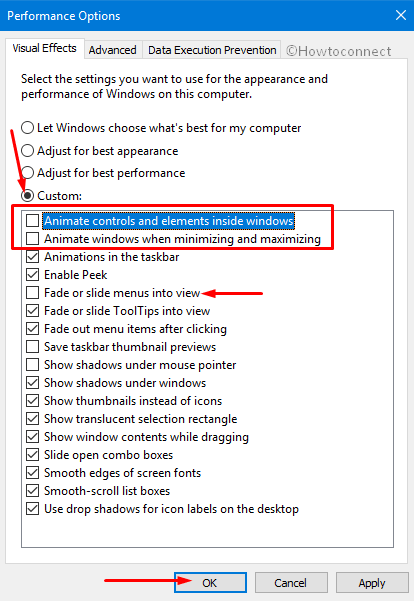
- Disable Visual Effects: Windows 10 includes various visual effects that can enhance the user experience but consume resources. Disabling these effects can improve performance, especially on older hardware.
- Optimize Disk Space: Regularly clear temporary files, browser cache, and unnecessary files to free up disk space and improve performance.
3. System Optimization:
- Run Disk Cleanup: The Disk Cleanup utility removes temporary files, system files, and other unnecessary data to free up disk space.
- Run System File Checker (SFC): This tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files, which can cause performance issues.
- Run Check Disk (CHKDSK): This command-line tool checks for and repairs errors on the hard drive.
- Disable Indexing: Indexing helps Windows search files quickly but can consume resources. Disabling indexing for specific drives or folders can improve performance.
- Manage Background Processes: Limit background processes that are not actively used to reduce resource consumption. Use Task Manager to identify and terminate unnecessary programs.
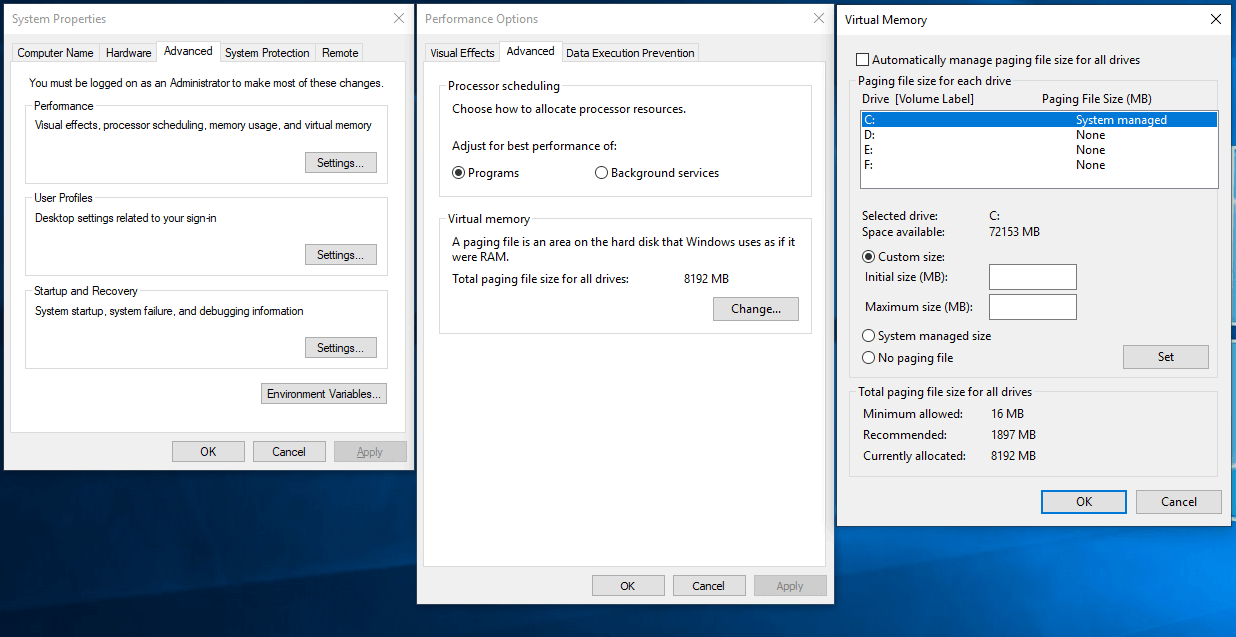
- Enable Performance Options: Windows 10 offers performance options that can adjust the system’s behavior to prioritize responsiveness over visual effects.
- Clean Boot: Performing a clean boot disables unnecessary startup programs and services, helping identify potential conflicts that affect performance.
4. Security Optimization:
- Install Anti-Malware Software: Protect your system from malware infections that can significantly impact performance. Regularly scan for and remove threats.
- Keep Windows Updated: Windows updates include security patches and performance improvements. Ensure your system is up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities and enhance efficiency.
- Enable Windows Defender: Windows Defender offers real-time protection against malware and other threats. Keep it enabled and updated for optimal security.
- Use Strong Passwords: Strong passwords protect your system from unauthorized access and potential malware attacks.
5. User Habits Optimization:
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Minimize the number of applications running simultaneously to reduce resource consumption.
- Avoid Excessive Background Downloads: Limit background downloads, especially large files, to avoid slowing down the system.
- Limit Browser Extensions: Browser extensions can consume resources and slow down browsing. Only install necessary extensions and disable those you don’t use.
- Regularly Restart Your Computer: Restarting your computer clears cached data and closes background processes, improving overall system performance.
Troubleshooting Common Performance Issues:
- Slow Startup: Analyze startup programs, check for hardware limitations, and consider using a faster boot drive.
- Lagging Applications: Ensure sufficient RAM, check for software conflicts, and optimize power settings.
- Frequent System Crashes: Check for hardware errors, update drivers, and run system file checks.
- High CPU Usage: Identify resource-intensive programs, disable unnecessary background processes, and consider upgrading hardware.
- Slow Internet Speeds: Check network connectivity, optimize internet settings, and consider upgrading your internet plan.
FAQs
Q: Does upgrading to the latest version of Windows 10 improve performance?
A: While newer versions of Windows 10 may offer performance improvements, they may also require more resources. Upgrading is generally recommended for security updates and bug fixes but may not significantly boost performance on older hardware.
Q: Is it safe to disable background processes?
A: Disabling background processes can improve performance but may affect system functionality. It’s recommended to disable only those processes that are not essential or known to be resource-intensive.
Q: How often should I defragment my hard drive?
A: Defragmenting an HDD is recommended only when performance noticeably declines. Modern HDDs have built-in defragmentation features that run automatically, so manual defragmentation is usually not necessary.
Q: Can I optimize my system without upgrading hardware?
A: While hardware upgrades can significantly improve performance, software optimization techniques can also make a noticeable difference, especially on systems with sufficient resources.
Q: How do I identify and disable bloatware?
A: Bloatware is often pre-installed on new computers. You can identify them by their unusual names, lack of use, and large file sizes. Use the "Programs and Features" control panel to uninstall them.
Tips for Maximizing Performance:
- Monitor system performance: Use the Task Manager or Performance Monitor to identify resource-intensive processes and bottlenecks.
- Regularly clean your system: Delete temporary files, clear browser cache, and remove unnecessary files to free up disk space.
- Optimize power settings for performance: Choose a high-performance power plan if responsiveness is a priority.
- Create a system restore point: This allows you to revert to a previous system state if performance issues arise after making changes.
- Seek professional help: If you encounter persistent performance issues, consider consulting a computer technician for diagnosis and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Optimizing Windows 10 performance involves a multi-faceted approach that encompasses hardware, software, system settings, and user habits. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, users can significantly enhance their system’s responsiveness, efficiency, and overall user experience. Regular maintenance, proactive optimization, and awareness of potential performance bottlenecks are key to ensuring a smooth and productive computing environment. Remember, optimizing your system is an ongoing process, and continuous attention to its health and performance is crucial for a seamless and enjoyable computing experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Optimizing Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhance System Performance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!