Navigating Windows 11 Administrative Challenges: Troubleshooting And Optimization Strategies
Navigating Windows 11 Administrative Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11 Administrative Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11 Administrative Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Administrative Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies
Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, offers a refined user experience with a focus on visual aesthetics and performance enhancements. However, as with any complex software, administrative tasks can present challenges, requiring a nuanced understanding of system configurations and troubleshooting techniques. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide for navigating common administrative hurdles within Windows 11, empowering users to optimize system performance and maintain a stable, secure environment.
Understanding Administrative Privileges in Windows 11
Windows 11 operates on a hierarchical access control system, granting different levels of privileges to various user accounts. Standard users have limited access, primarily for personal usage, while administrators possess comprehensive control over the system, including installing software, managing user accounts, and modifying system settings.
Common Administrative Challenges in Windows 11
Navigating the administrative landscape of Windows 11 can be complex. Users often encounter issues related to:
- Software Installation and Updates: Difficulty installing or updating software due to permissions issues, compatibility problems, or system conflicts.
- User Account Management: Challenges creating, deleting, or modifying user accounts, including assigning appropriate permissions.
- System Configuration: Difficulty configuring system settings, managing network connections, or troubleshooting hardware issues.
- Security and Privacy: Concerns about system security, potential malware threats, and maintaining privacy settings.
- Troubleshooting and Error Resolution: Difficulty diagnosing and resolving system errors, application crashes, or performance issues.
Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies
Addressing these administrative challenges requires a systematic approach, encompassing troubleshooting techniques, optimization strategies, and preventative measures.
1. Troubleshooting Software Installation and Updates:
- Verify Administrator Privileges: Ensure the user account attempting to install or update software has administrative privileges.
- Check System Requirements: Confirm the software is compatible with Windows 11’s system requirements, including hardware specifications and operating system version.
- Run as Administrator: Right-click the installation file and select "Run as administrator" to execute the installation process with elevated privileges.
- Disable Antivirus Software Temporarily: Temporarily disable antivirus software to eliminate potential conflicts during installation.
- Clean Boot: Perform a clean boot to isolate the issue and determine if a third-party application is interfering with the installation.
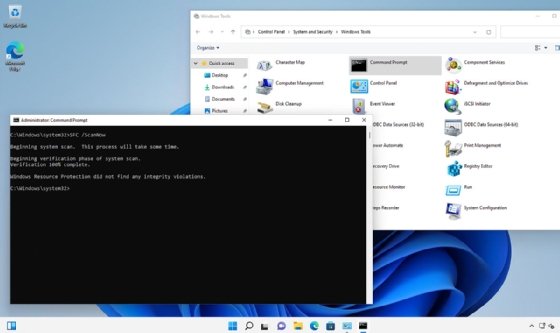
- Use System File Checker: Run the System File Checker (SFC) to scan for and repair corrupted system files that might be causing installation problems.
- Reinstall Software: If all else fails, consider uninstalling and reinstalling the software to resolve potential conflicts or corrupted installation files.
2. Managing User Accounts Effectively:
- Create New Accounts: Use the Control Panel or Settings app to create new user accounts with appropriate permissions.
- Modify Existing Accounts: Adjust permissions and settings for existing accounts based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Assign Administrator Privileges: Grant administrator privileges to specific accounts when necessary, ensuring a balance between security and usability.
- Use Local Administrator Accounts: Create a local administrator account for troubleshooting purposes, allowing access to critical system settings without affecting other user accounts.
3. Optimizing System Configuration:
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs: Use the Task Manager to identify and disable programs that automatically start with Windows, reducing startup time and improving overall performance.
- Adjust Power Settings: Configure power settings to balance energy efficiency with performance, optimizing battery life or maximizing system responsiveness.
- Manage Disk Space: Regularly check disk space, delete unnecessary files, and utilize disk cleanup tools to maintain optimal system performance.
- Optimize System Performance: Utilize the Windows Performance Monitor to identify system bottlenecks and optimize settings for improved performance.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all device drivers are up-to-date to enhance hardware compatibility and stability.
4. Enhancing Security and Privacy:
- Enable Windows Defender: Utilize Windows Defender, Microsoft’s built-in antivirus software, to protect against malware threats.
- Install Firewall: Configure the Windows Firewall to block unauthorized network access, safeguarding the system from external threats.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong passwords for user accounts and system access, using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Implement two-factor authentication for critical accounts, requiring an additional verification step beyond the password.
- Regularly Update Windows: Install the latest Windows updates to receive security patches and performance enhancements.
- Manage Privacy Settings: Review and customize privacy settings to control data collection and sharing by Windows and applications.
5. Troubleshooting and Resolving Errors:
- Use Event Viewer: Monitor the Event Viewer to identify system errors, application crashes, and other events that may indicate problems.
- Use the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) Information: When encountering a BSOD, record the error code and any other relevant information for troubleshooting.
- Perform a System Restore: Use the System Restore feature to revert to a previous system state before the error occurred.
- Run a Disk Check: Perform a disk check to identify and repair errors on the hard drive, potentially resolving issues related to file corruption or storage problems.
- Contact Microsoft Support: Seek assistance from Microsoft Support for complex issues or when troubleshooting efforts have been unsuccessful.
FAQs by It Administrator Windows 11 Fix
Q: How do I gain administrative privileges on my Windows 11 computer?
A: To gain administrative privileges, you must have an account with administrator rights. If you are not an administrator, you can request that the system administrator grants you these privileges. Alternatively, you can create a local administrator account for troubleshooting purposes, but remember to secure this account with a strong password.
Q: What are the benefits of running a clean boot in Windows 11?
A: A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and programs, allowing you to identify and isolate issues caused by third-party applications or conflicting drivers. This is particularly useful for troubleshooting software installation problems, performance issues, or system crashes.
Q: How do I use the System File Checker (SFC) in Windows 11?
A: To run SFC, open Command Prompt as administrator and type "sfc /scannow" (without quotes). This command will scan for corrupted system files and attempt to repair them.
Q: How can I prevent malware from infecting my Windows 11 computer?
A: Employ a multi-layered approach to security, including:
- Enable Windows Defender: Utilize the built-in antivirus software for basic protection.
- Install a reputable third-party antivirus: Consider a comprehensive antivirus solution for enhanced protection.
- Keep your software updated: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and antivirus software to receive the latest security patches.
- Be cautious about downloading files: Avoid downloading files from untrusted sources or clicking suspicious links.
- Use strong passwords: Create complex and unique passwords for all your online accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Implement two-factor authentication for critical accounts to add an extra layer of security.
Q: What are the best practices for optimizing system performance in Windows 11?
A: Implementing these best practices can enhance system performance:
- Disable unnecessary startup programs: Use Task Manager to identify and disable programs that start automatically with Windows.
- Adjust power settings: Configure power settings to balance energy efficiency with performance.
- Manage disk space: Regularly check disk space, delete unnecessary files, and utilize disk cleanup tools.
- Optimize system performance: Utilize the Windows Performance Monitor to identify system bottlenecks and optimize settings.
- Update drivers: Ensure all device drivers are up-to-date to enhance hardware compatibility and stability.
Tips by It Administrator Windows 11 Fix
- Regularly back up your data: Create regular backups of important files and system settings to prevent data loss in case of system failure or accidental deletion.
- Use a password manager: Utilize a password manager to store and manage your passwords securely, eliminating the need to remember numerous complex passwords.
- Stay informed about security threats: Keep abreast of emerging security threats and vulnerabilities to protect your system effectively.
- Monitor system resources: Regularly check system resource usage, including CPU, memory, and disk space, to identify potential performance bottlenecks.
- Seek professional assistance when needed: Don’t hesitate to contact a qualified IT professional for complex issues or when troubleshooting efforts have been unsuccessful.
Conclusion by It Administrator Windows 11 Fix
Navigating the administrative landscape of Windows 11 requires a combination of technical knowledge, troubleshooting skills, and a proactive approach to system maintenance. By understanding common administrative challenges, implementing effective troubleshooting strategies, and embracing preventative measures, users can optimize system performance, enhance security, and maintain a stable and reliable computing environment. Remember, ongoing vigilance and a commitment to best practices are crucial for ensuring a seamless and secure Windows 11 experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11 Administrative Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!