Navigating The Windows 11 File System: A Comprehensive Guide To The Dir Command
Navigating the Windows 11 File System: A Comprehensive Guide to the dir Command
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 File System: A Comprehensive Guide to the dir Command
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 11 File System: A Comprehensive Guide to the dir Command. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows 11 File System: A Comprehensive Guide to the dir Command

The Windows command prompt, a powerful tool for system administration and automation, offers a diverse set of commands. Among them, the dir command stands out as an indispensable tool for navigating and managing the file system. While not as commonly known as its Linux counterpart, ls, the dir command provides a similar functionality, offering users a way to list directory contents, explore file attributes, and gain valuable insights into the structure of their system.
Understanding the dir Command: A Gateway to the File System
The dir command, short for "directory," serves as a primary means of interacting with the file system within the Windows command prompt environment. It allows users to view the contents of a specific directory or the entire system, providing information about files and subdirectories.
Basic Usage: Unveiling the Structure of Directories
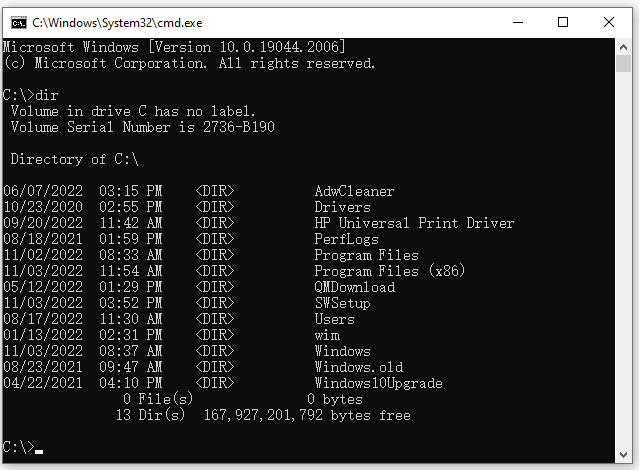
At its core, the dir command is remarkably simple to use. Executing dir without any additional parameters displays the contents of the current directory, presenting a list of files and subdirectories along with their attributes, date and time of last modification, and file size.
C:UsersYourUsername> dirThis command will list the contents of the current directory, which in this case is the "YourUsername" directory within the "Users" folder.
Exploring the Options: Refining the Output
The dir command offers a variety of options that can be combined to tailor the output to specific needs. Here are some key options:
-
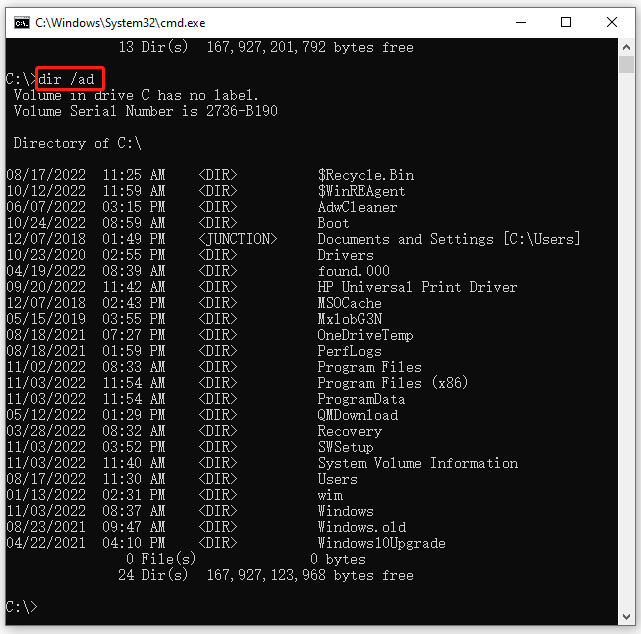
/A(Attribute): Displays files and directories based on specific attributes.-
/A:D– Shows only directories -
/A:H– Shows hidden files and directories -
/A:S– Shows system files -
/A:-H– Hides hidden files and directories -
/A:-S– Hides system files
-
-
/B(Bare): Displays only the file or directory names, without additional information. -
/D(Date): Displays the date and time of last modification in a compact format. -
/L(Long): Displays a detailed listing of files and directories, including their size, date and time of last modification, and attributes. -
/P(Pause): Pauses the output after each screenful, allowing for easier reading. -
/Q(Owner): Displays the owner of each file and directory. -
/R(Recursive): Displays the contents of all subdirectories within the specified directory. -
/S(Subdirectories): Displays the contents of all subdirectories within the specified directory, but without recursing into further subdirectories. -
/W(Wide): Displays the file and directory names in a wide format, with multiple names per line.
Example Usage: Tailoring the Output for Specific Needs
To illustrate the power of these options, consider the following examples:
-
Listing only directories:
dir /A:D -
Listing hidden files:
dir /A:H -
Listing files in a specific directory:
dir C:Program Files -
Listing files and directories in a wide format:
dir /W -
Listing files and directories recursively:
dir /S /B
Beyond Basic Listing: Unveiling Hidden Information
The dir command can also be used to obtain valuable information about individual files and directories.
-
/O(Order): Sorts the output based on different criteria.-
/O:D– Sort by date and time -
/O:N– Sort by name -
/O:S– Sort by size
-
-
/T(Time): Displays the date and time of last modification in a specific format.-
/T:C– Displays the date and time in compact format -
/T:G– Displays the date and time in long format -
/T:Y– Displays the date and time in year format
-
Example Usage: Extracting Specific Information
-
Listing files sorted by size:
dir /O:S -
Listing files and directories with the date and time in long format:
dir /T:G -
Listing files and directories with the date and time in year format:
dir /T:Y
The dir Command: A Powerful Tool for System Management
The dir command, while seemingly straightforward, serves as a vital tool for navigating and managing the Windows file system. Its ability to list directory contents, explore file attributes, and provide detailed information about files and directories makes it indispensable for system administrators, developers, and power users alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the dir Command
Q: What is the difference between dir and ls?
A: dir is the Windows command prompt equivalent of ls in Linux. While both commands serve the same purpose of listing directory contents, they have different syntax and options. dir offers a wider range of options for customizing the output and accessing file attributes.
Q: How can I use dir to find a specific file?
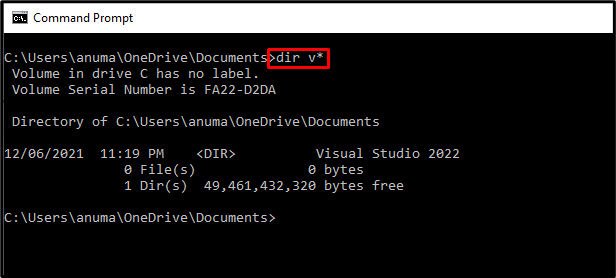
A: You can use the dir command with wildcards to search for files. For example, dir *.txt will list all files with the ".txt" extension in the current directory. You can also use the /S option to search recursively through subdirectories.
Q: How can I use dir to identify the size of a specific file?
A: The dir command with the /L option displays a detailed listing of files and directories, including their size.
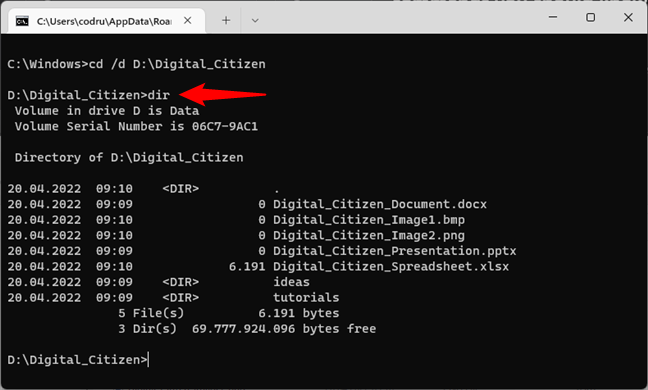
Q: How can I use dir to view the contents of a specific directory?
A: Simply type dir [directory path] to list the contents of the specified directory. For example, dir C:Windows will list the contents of the "Windows" directory.
Tips for Using the dir Command Effectively
-
Use wildcards: Wildcards like
*and?can be used to match multiple files or directories. -
Use the
/Roption: The/Roption is useful for listing the contents of all subdirectories within a specified directory. -
Use the
/Ooption: The/Ooption allows you to sort the output based on different criteria, making it easier to find specific files. -
Use the
dircommand in conjunction with other commands: Thedircommand can be combined with other commands likecopy,move, anddeleteto perform various file management tasks.
Conclusion: Mastering the dir Command for Enhanced File Management
The dir command, a fundamental tool within the Windows command prompt, empowers users to navigate and manage the file system effectively. Its versatility and wide range of options allow for tailored output, providing valuable insights into the structure and contents of the system. By mastering the dir command, users can unlock a new level of control and efficiency in their file management practices.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dir-help-command-5a858437959144ccb21041217879195f.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 11 File System: A Comprehensive Guide to the dir Command. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!