Navigating The Modern Desktop: A Beginner’s Guide To Windows 11
Navigating the Modern Desktop: A Beginner’s Guide to Windows 11
Related Articles: Navigating the Modern Desktop: A Beginner’s Guide to Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Modern Desktop: A Beginner’s Guide to Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Modern Desktop: A Beginner’s Guide to Windows 11
Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s iconic operating system, offers a streamlined and visually appealing interface designed to enhance user experience. This guide provides a comprehensive introduction to Windows 11 for beginners, covering essential aspects from basic navigation to utilizing core features.
1. The Windows 11 Interface: A Visual Tour
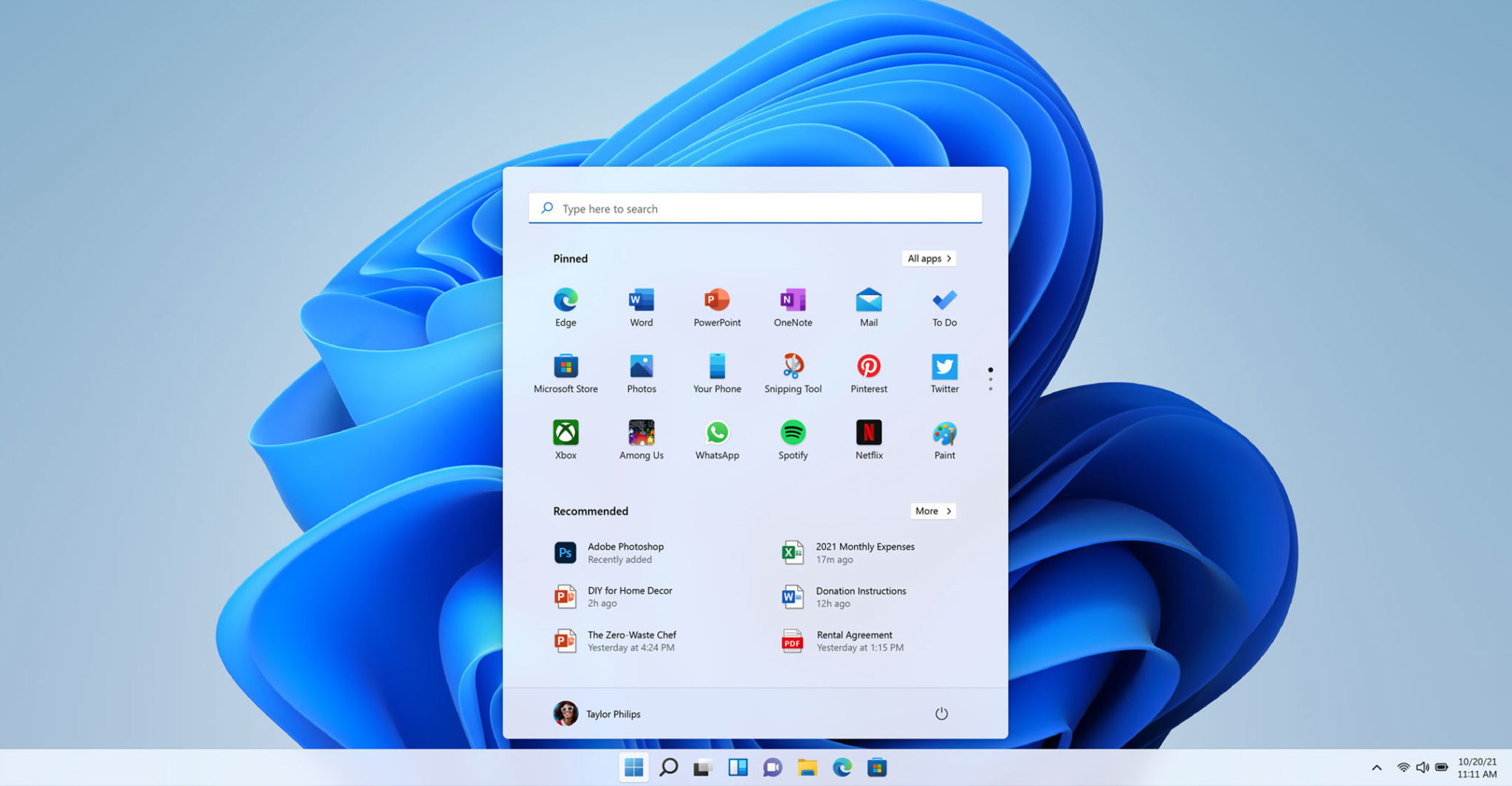
Upon booting up, users are greeted by the Start Menu, a central hub for accessing applications, settings, and system information. The Start Menu, positioned at the bottom left corner of the screen, features a search bar for quickly finding files, programs, or online content. It also houses a list of frequently used applications, pinned programs, and a "Recommended" section for personalized suggestions.
The taskbar, located at the bottom of the screen, displays running applications, the system clock, and icons for quick access to frequently used features like the notification center and the system tray.
The desktop serves as the primary workspace, displaying icons for various files and folders. Users can personalize the desktop by customizing the background image, adding widgets, and arranging icons according to their preferences.
2. Essential Navigation: Understanding the Basics
a) Mouse and Keyboard Interactions:
Windows 11 utilizes a point-and-click interface, primarily controlled by the mouse. Clicking the left mouse button selects an item, while right-clicking opens a context menu with various options. The keyboard plays a crucial role in navigating menus, entering text, and utilizing keyboard shortcuts.
b) Windows Explorer: Managing Files and Folders:
Windows Explorer serves as the file manager, allowing users to browse, organize, and manage files and folders. To access Windows Explorer, click the "This PC" icon on the Start Menu or use the keyboard shortcut "Windows key + E."
c) The Taskbar and Task View:
The taskbar displays running applications, allowing users to switch between them by clicking on their icons. The Task View, accessible by clicking the "Task View" icon on the taskbar or using the keyboard shortcut "Alt + Tab," provides a visual overview of all open windows, enabling efficient multi-tasking.
3. Exploring the Start Menu: Your Gateway to Applications
The Start Menu acts as the central hub for launching applications, accessing settings, and finding system information.
a) Searching for Applications and Files:
The search bar in the Start Menu allows users to quickly find applications, files, or online content. Simply type the desired keyword, and relevant results will appear.
b) Pinning Applications for Easy Access:
Users can pin frequently used applications to the Start Menu for quick access. Right-click on an application icon and select "Pin to Start" to add it to the pinned list.
c) Accessing System Settings and Information:
The Start Menu also provides access to system settings, power options, and other system information. Click the "Settings" icon to configure various aspects of the operating system, including personalization, network settings, and privacy options.
4. Personalizing Windows 11: Making it Your Own
Windows 11 offers extensive customization options, allowing users to personalize their desktop environment according to their preferences.
a) Changing the Desktop Background:
To personalize the desktop background, right-click on an empty area of the desktop and select "Personalize." In the "Background" section, choose from a variety of options, including solid colors, images, or slideshows.
b) Adding Widgets to the Desktop:
Widgets provide quick access to frequently used information, such as weather, news, and calendar events. To add widgets, click the "Widgets" icon on the taskbar.
c) Customizing the Taskbar:
The taskbar can be customized to display various icons and features. Right-click on the taskbar and select "Taskbar settings" to configure its appearance, behavior, and the icons that appear.
5. Getting Connected: Managing Networks and Internet Access
Windows 11 offers seamless connectivity options for accessing the internet and connecting to various networks.
a) Connecting to Wi-Fi Networks:
To connect to a Wi-Fi network, click the network icon in the system tray and select the desired network from the list. Enter the network password if prompted.
b) Managing Network Settings:
Access network settings by clicking the "Settings" icon in the Start Menu and selecting "Network & internet." Here, users can configure network connections, manage Wi-Fi profiles, and access advanced network settings.
6. Essential Applications: Utilizing Built-in Tools
Windows 11 comes equipped with a suite of essential applications designed to enhance productivity and user experience.
a) Microsoft Edge: A Modern Web Browser:
Microsoft Edge, the default web browser, offers a fast and secure browsing experience with features like tab groups, reading view, and integrated search.
b) Microsoft Store: Discovering and Installing Applications:
The Microsoft Store serves as a central hub for discovering and installing applications. Users can browse a wide range of free and paid applications, including productivity tools, games, and entertainment apps.
c) File Explorer: Managing Files and Folders:
File Explorer allows users to browse, organize, and manage files and folders. Utilize features like search, sorting, and filtering to efficiently locate and organize files.
7. Staying Secure: Understanding Windows Security Features
Windows 11 prioritizes user security with robust features designed to protect against malware, phishing attacks, and other online threats.
a) Windows Defender: Built-in Antivirus Protection:
Windows Defender, the built-in antivirus solution, provides real-time protection against malware and other threats. It automatically scans files and programs, protecting your device from malicious software.
b) Firewall: Protecting Your Device from Unauthorized Access:
The Windows Firewall acts as a barrier, blocking unauthorized access to your device. It helps prevent hackers and malicious programs from accessing your personal information.
c) SmartScreen: Preventing Phishing and Malicious Websites:
SmartScreen helps prevent users from visiting malicious websites or downloading harmful files. It warns users about potentially dangerous websites and downloads, helping to protect against phishing attacks.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues: A Beginner’s Guide
Even with its robust features, users may occasionally encounter technical issues. This section provides solutions for common problems encountered by beginners.
a) Slow Performance: Optimizing System Resources:
If the system is running slowly, consider closing unnecessary applications, managing startup programs, and running a system scan to identify and remove any malware.
b) Network Connectivity Issues: Troubleshooting Internet Access:
If experiencing network connectivity issues, check the Wi-Fi router, restart the modem and router, and ensure the network driver is up to date.
c) Application Errors: Reinstalling or Updating Applications:
For application errors, try reinstalling the application or updating to the latest version. If the error persists, contact the application developer for support.
9. FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How do I update Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 automatically checks for updates and installs them when available. To manually check for updates, go to "Settings" -> "Windows Update" and click "Check for updates."
Q: How do I create a new user account?
A: To create a new user account, go to "Settings" -> "Accounts" -> "Family & other users." Click "Add someone else to this PC" and follow the instructions.
Q: How do I change the language settings?
A: To change the language settings, go to "Settings" -> "Time & language" -> "Language." Click "Add a language" and select the desired language.
Q: How do I customize the Start Menu?
A: To customize the Start Menu, right-click on the Start Menu and select "Settings." Here, you can personalize the Start Menu’s appearance, layout, and pinned applications.
Q: How do I recover lost files?
A: Windows 11 offers a built-in file recovery tool. To access it, go to "This PC" and click "Recycle Bin." Right-click on the desired file and select "Restore."
10. Tips for Beginners: Maximizing Your Windows 11 Experience
a) Utilize Keyboard Shortcuts:
Learning keyboard shortcuts can significantly enhance productivity and navigation. Common shortcuts include "Ctrl + C" for copying, "Ctrl + V" for pasting, and "Ctrl + Z" for undoing.
b) Explore the Settings App:
The Settings app provides access to a wide range of configuration options, allowing users to customize various aspects of Windows 11.
c) Regularly Update Windows and Applications:
Updating Windows and applications ensures optimal performance, security, and access to the latest features.
d) Create a System Restore Point:
Creating a system restore point allows users to revert to a previous state if any changes cause problems.
11. Conclusion: Embracing the Modern Desktop
Windows 11 offers a modern and user-friendly interface designed to enhance productivity and user experience. This guide has provided a comprehensive introduction to the operating system, covering essential aspects from basic navigation to utilizing core features. By exploring the interface, understanding navigation methods, and utilizing built-in tools, beginners can confidently navigate the Windows 11 environment and unlock its full potential. Continued exploration and experimentation will further deepen understanding and allow users to personalize their Windows 11 experience.
![How to Create and Use Virtual Desktops on Windows 11 [Detailed Guide] - Tech-Ensive](https://www.mobigyaan.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/How-to-Use-Virtual-Desktops-in-Windows-11.jpg)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_how-to-use-multiple-desktops-in-windows-11-6826109-55612f49039c4e2da5e34aa4701c9d0c.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Modern Desktop: A Beginner’s Guide to Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!