Navigating Administrative Privileges In Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Administrative Privileges
- 3.2 Standard User Accounts vs. Administrator Accounts
- 3.3 The Importance of Elevated Privileges
- 3.4 Accessing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home
- 3.5 Best Practices for Managing Administrative Privileges
- 3.6 FAQs:
- 3.7 Tips:
- 3.8 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide

Windows 10 Home, while offering a user-friendly environment for everyday tasks, presents limitations when it comes to system-level modifications. This is due to the inherent security measures built into the operating system, which restrict certain actions to prevent accidental or malicious changes. However, situations may arise where elevated privileges are required, such as installing specific software, configuring network settings, or troubleshooting system issues. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of administrative privileges in Windows 10 Home, outlining the available options, their implications, and best practices for navigating these permissions.
Understanding Administrative Privileges
Administrative privileges, often referred to as "administrator rights," grant users the authority to make significant changes to the operating system. These changes can range from installing and removing software to altering system settings, modifying user accounts, and accessing sensitive files. While these privileges offer immense power, they also come with a responsibility to exercise caution, as any mistakes can have serious consequences.
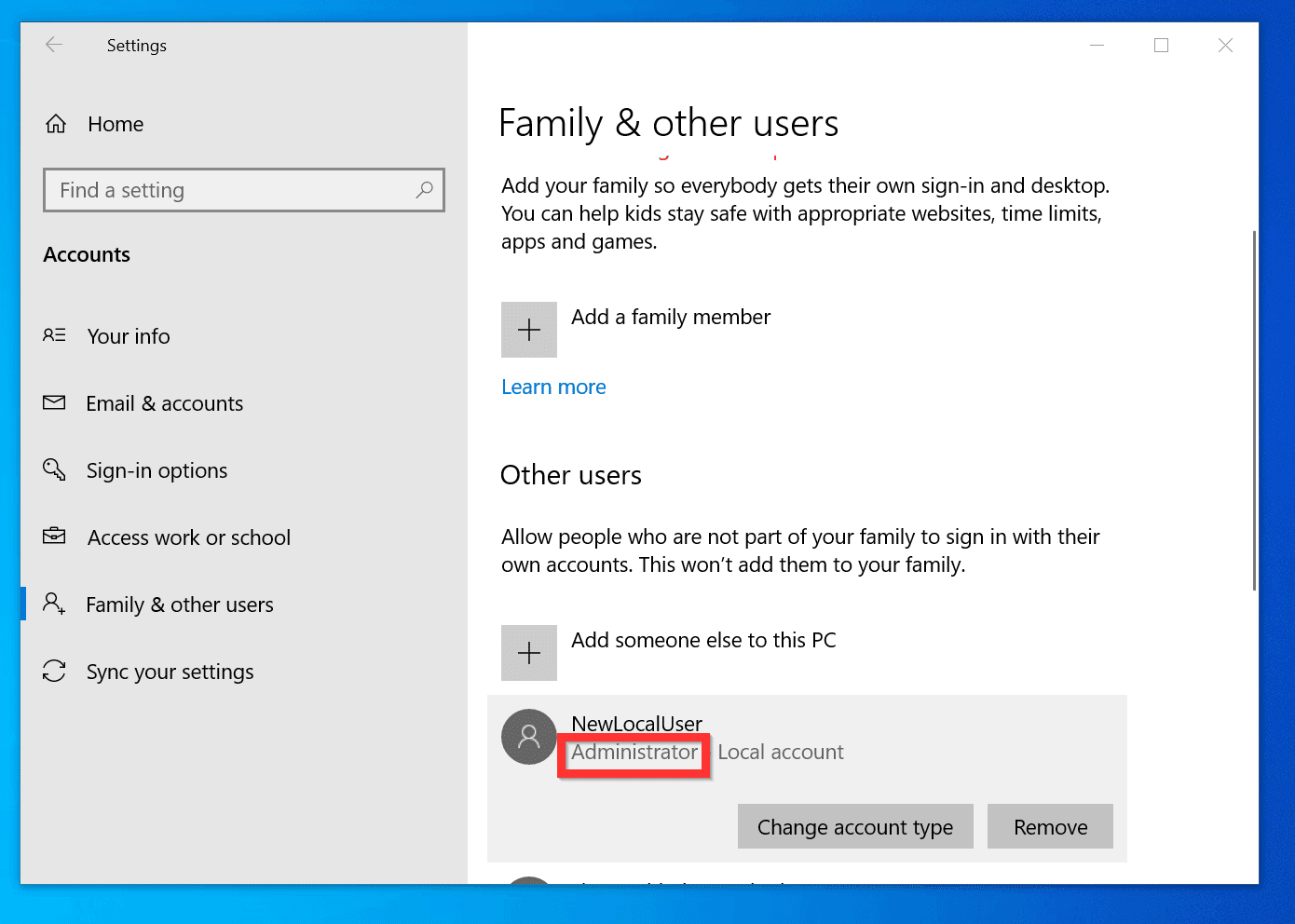
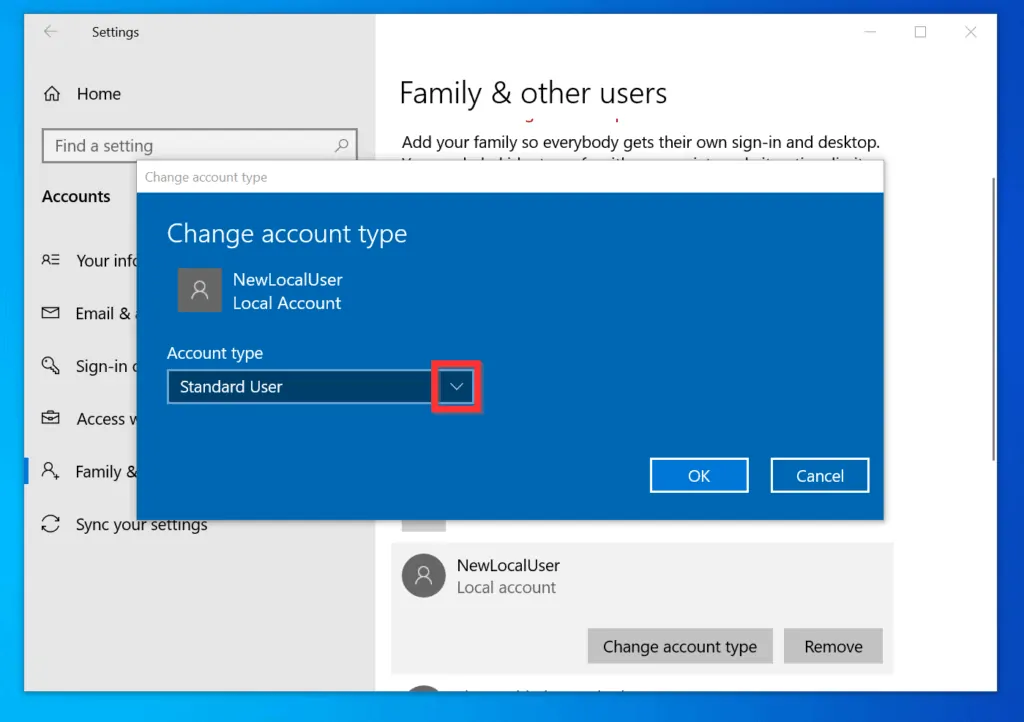
Standard User Accounts vs. Administrator Accounts
Windows 10 Home typically creates two types of user accounts: Standard User accounts and Administrator accounts.
- Standard User Accounts are designed for everyday tasks and offer limited access to system resources. Users with Standard accounts cannot install software, modify system settings, or make changes to other user accounts.
- Administrator Accounts provide full control over the system, allowing users to perform all actions, including those that require elevated privileges.
The Importance of Elevated Privileges
While Standard User accounts offer a secure and stable environment for most users, there are specific situations where elevated privileges are necessary. These include:
- Installing Software: Many software applications require administrative privileges for installation. This ensures that the software can be integrated properly into the system and access necessary resources.
- Modifying System Settings: Advanced system configurations, such as network settings, firewall settings, and power options, often require administrative rights.
- Troubleshooting System Issues: Diagnosing and resolving system errors may require administrative access to system files and processes.
- Managing User Accounts: Creating, deleting, or modifying user accounts, including setting passwords and permissions, necessitates administrative privileges.
Accessing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home
While Windows 10 Home does not offer a dedicated "Administrator" account, there are alternative methods to gain elevated privileges:
1. Using the "Run as Administrator" Option:
This method allows you to temporarily elevate the privileges of a specific application. To use this option:
- Right-click the application shortcut or executable file.
- Select "Run as administrator" from the context menu.
- Confirm your action by providing administrator credentials if prompted.
2. Utilizing the Command Prompt with Administrative Privileges:
The Command Prompt, a powerful tool for interacting with the operating system, can be launched with administrative privileges:
- Search for "cmd" in the Start menu.
- Right-click the "Command Prompt" result and select "Run as administrator".
- Confirm your action by providing administrator credentials if prompted.
3. Utilizing PowerShell with Administrative Privileges:
PowerShell, a more advanced command-line interface, can also be launched with elevated privileges:
- Search for "powershell" in the Start menu.
- Right-click the "Windows PowerShell" result and select "Run as administrator".
- Confirm your action by providing administrator credentials if prompted.
Best Practices for Managing Administrative Privileges
While gaining temporary administrative privileges is often necessary, it’s crucial to maintain a secure and stable system by following best practices:
- Minimize the Use of Elevated Privileges: Only use administrative privileges when absolutely necessary. Avoid running applications or performing tasks with elevated privileges unless explicitly required.
- Be Mindful of Software Installations: Carefully review the permissions requested by software during installation. Avoid granting unnecessary privileges to applications.
- Use Strong Passwords: Protect your administrator account with a robust password that is difficult to guess. Avoid using common or easily accessible information.
- Keep Your System Updated: Regularly update your Windows operating system and software applications to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security.
- Be Cautious with Downloaded Software: Only download software from trusted sources and be wary of suspicious links or downloads.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus program to protect your system from malware and other threats.
FAQs:
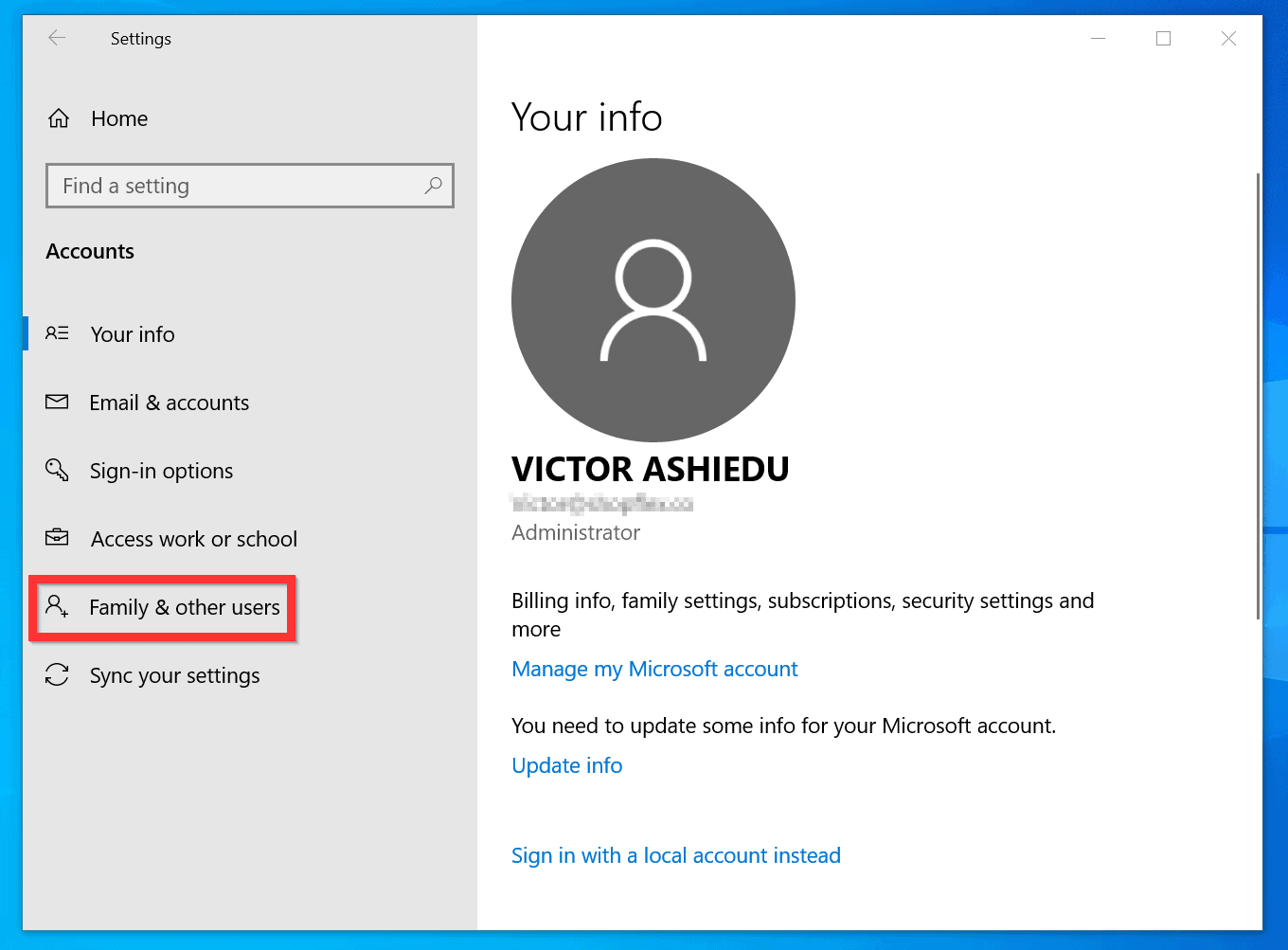
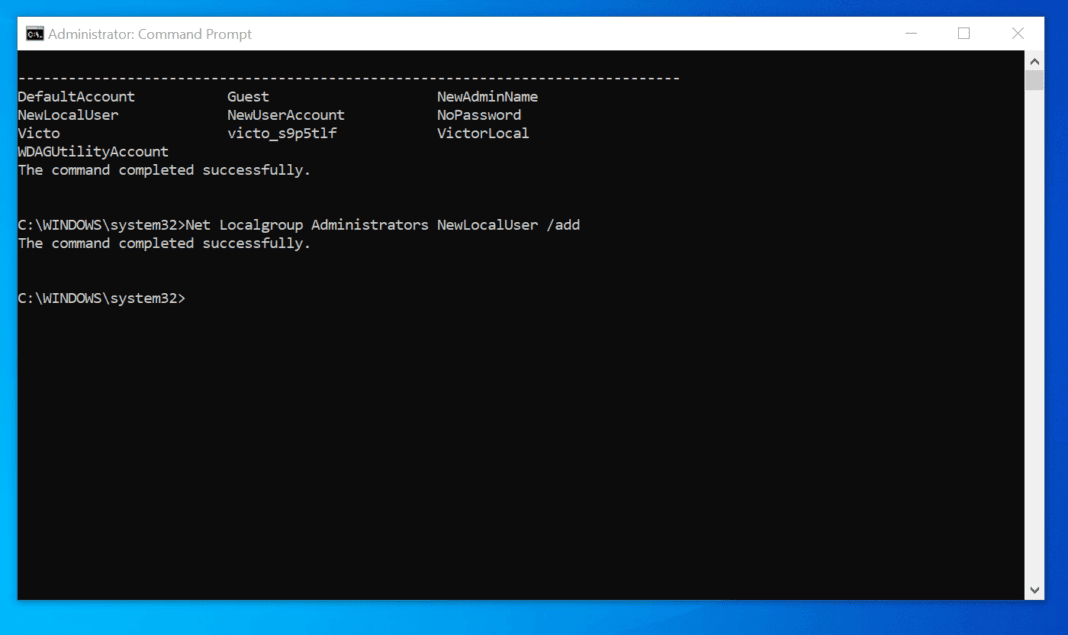
1. Can I permanently create an Administrator account in Windows 10 Home?
Unfortunately, Windows 10 Home does not offer the option to create a dedicated Administrator account. However, you can use the "Local Administrator" account, which is typically hidden by default. To access this account, you can use the "net user" command in the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
2. Is it safe to use the "Run as Administrator" option frequently?
While using "Run as Administrator" is necessary for specific tasks, it’s not recommended to use it for everyday activities. This is because elevated privileges can expose your system to security risks, as malicious software could potentially exploit these permissions.
3. What are the potential consequences of running software with elevated privileges without proper authorization?
Running software with elevated privileges without proper authorization can lead to several issues, including:
- Security Risks: Malicious software can potentially exploit these privileges to gain unauthorized access to your system and steal sensitive data.
- System Instability: Unnecessary use of elevated privileges can interfere with system processes and cause instability or crashes.
- Data Loss: Incorrectly modifying system settings or files with elevated privileges can lead to data loss or corruption.
4. How can I revert changes made with administrative privileges?
Depending on the specific changes made, you can revert them through various methods:
- System Restore: Use the built-in System Restore feature to restore your system to a previous point in time.
- Uninstall Software: If you installed software with elevated privileges, you can uninstall it using the Control Panel or the application’s uninstaller.
- Reversing Settings: If you modified system settings with elevated privileges, you can revert them to their default values through the relevant settings menus.
Tips:
- Use Virtual Machines: Consider using virtual machines to test software or perform tasks that require elevated privileges without affecting your main system.
- Utilize Third-Party Tools: Explore third-party tools designed to manage administrative privileges and simplify the process of granting or revoking permissions.
- Document Your Actions: Keep a record of any changes you make using administrative privileges, including the specific applications, settings, or files modified. This can be helpful for troubleshooting or reverting changes if necessary.
Conclusion:
While Windows 10 Home prioritizes security by limiting access to system-level functions, situations may arise where elevated privileges are necessary. By understanding the importance of administrative privileges and utilizing the available methods for accessing them responsibly, users can effectively manage their system and perform critical tasks without compromising security. Remember to always prioritize safety and exercise caution when working with administrative privileges, ensuring that you only grant elevated access when absolutely required.
![[Guide] How To Get Administrator Privileges On Windows 10](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/05/get-admin-rights-on-windows-10.png)
![[Guide] Windows 10 Administrator Privileges Usage Guide](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/04/A-Guide-on-Windows-10-Administrator-Privileges.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Administrative Privileges in Windows 10 Home: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!