Merging Disks In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Disk Management in Windows 11
- 3.2 The Concept of Disk Merging
- 3.3 Advantages of Disk Merging
- 3.4 Types of Disk Merging
- 3.5 Considerations Before Merging Disks
- 3.6 Steps for Merging Disks in Windows 11
- 3.7 FAQs about Merging Disks in Windows 11
- 3.8 Tips for Merging Disks in Windows 11
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

Merging disks in Windows 11 is a powerful technique that allows users to combine multiple physical drives into a single, larger logical drive. This process, often referred to as "disk spanning" or "disk striping," offers several benefits, including increased storage space, improved performance, and enhanced data redundancy. However, it’s crucial to understand the intricacies of disk merging before embarking on this operation. This article provides a detailed explanation of the process, its advantages, potential pitfalls, and essential considerations for users considering merging disks in Windows 11.
Understanding Disk Management in Windows 11
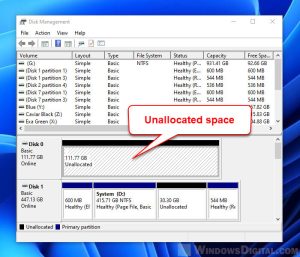
Before diving into disk merging, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of disk management in Windows 11. The operating system utilizes a disk management system that allows users to view, manage, and manipulate physical storage devices connected to the computer. This system provides tools for formatting disks, creating partitions, assigning drive letters, and performing other essential disk-related operations.
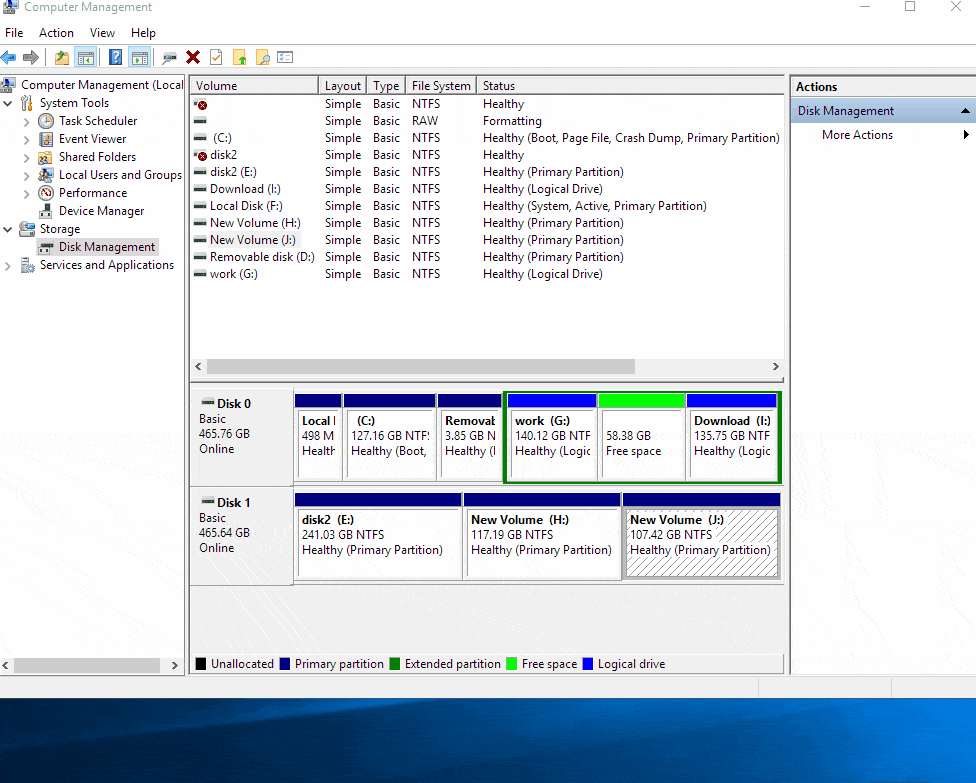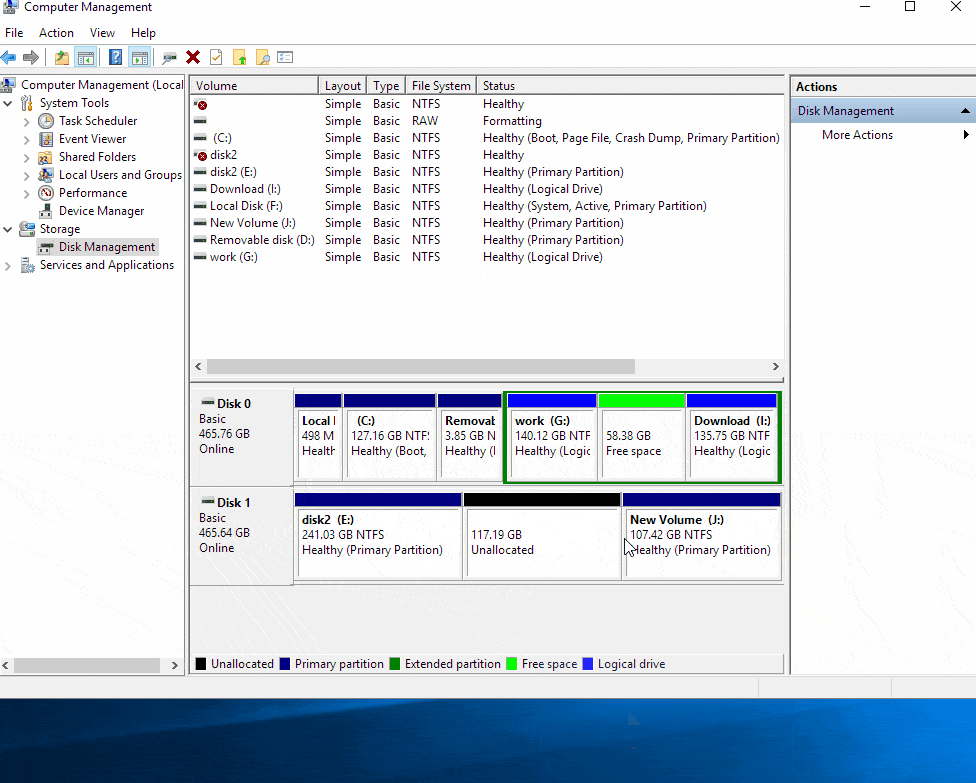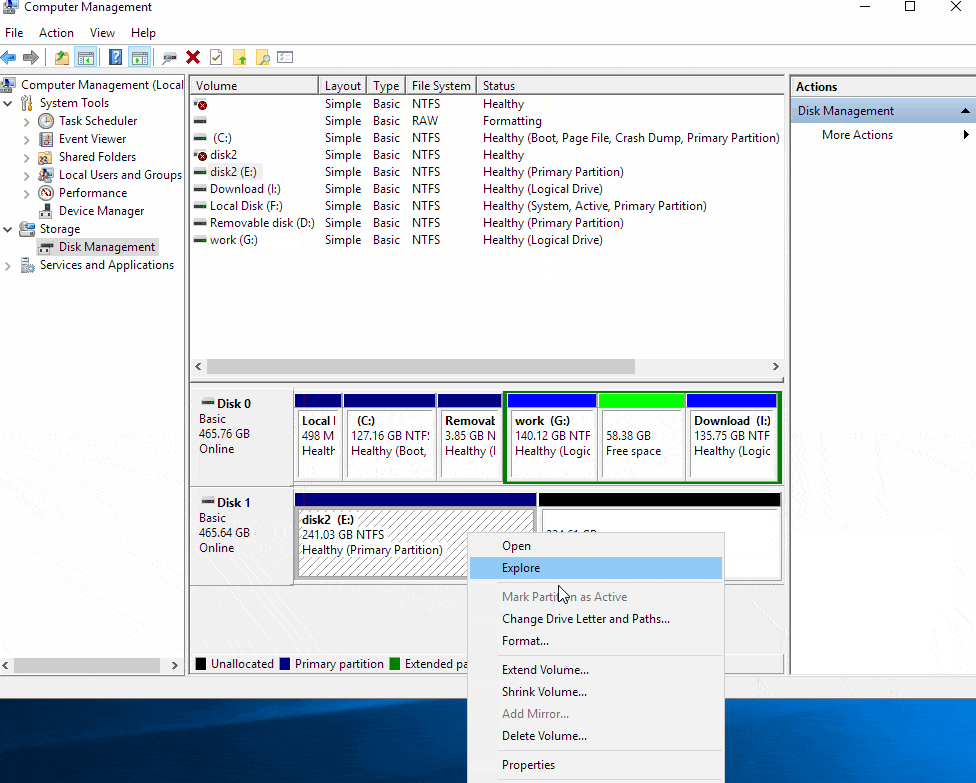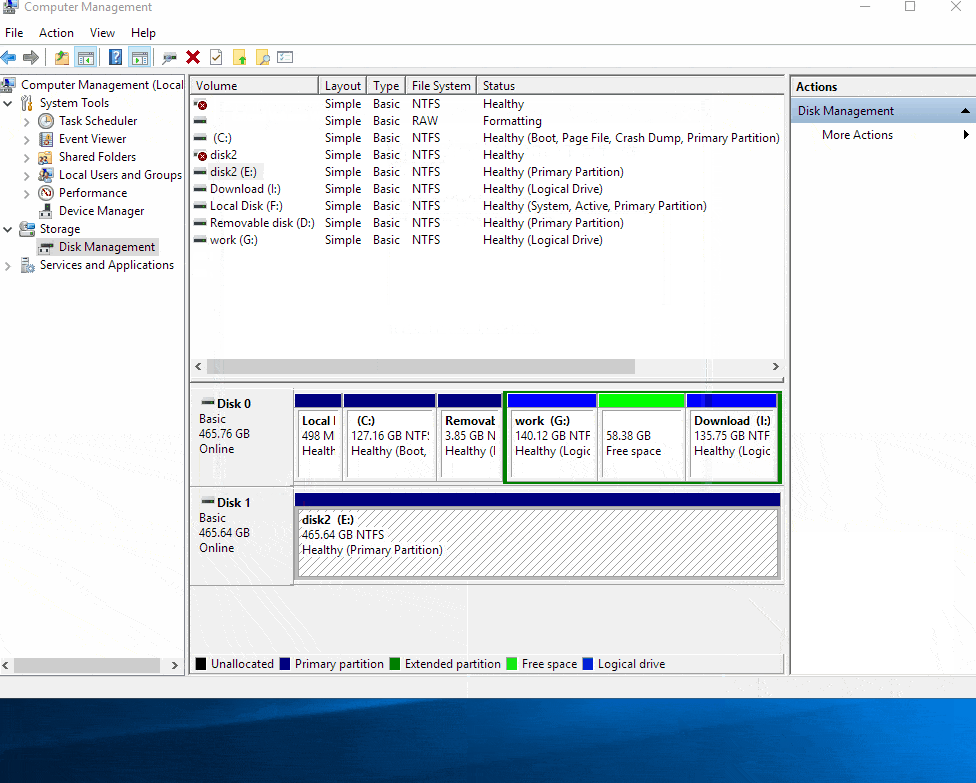
Windows 11 offers a dedicated Disk Management tool accessible through the Control Panel or by searching for "Disk Management" in the Start menu. This tool visually represents all connected physical drives and their partitions, providing a graphical interface for managing them.
The Concept of Disk Merging
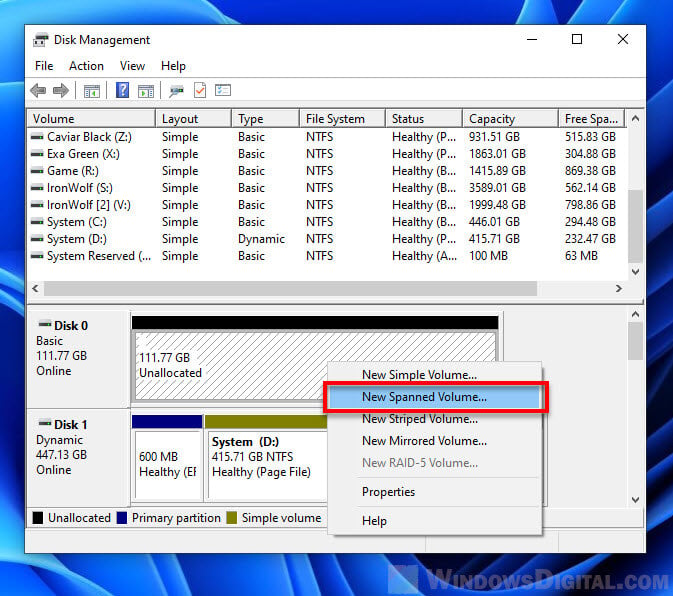
Disk merging, in the context of Windows 11, involves combining two or more physical drives into a single logical drive. This process essentially treats multiple physical drives as one, allowing the operating system to access them as a unified storage space. This approach offers several benefits, primarily increased storage capacity and enhanced performance.
Advantages of Disk Merging
1. Increased Storage Capacity: Disk merging effectively expands the available storage space by combining the capacity of multiple drives. This is particularly advantageous for users facing storage constraints on their primary drive.
2. Enhanced Performance: By spreading data across multiple drives, disk merging can significantly improve read and write speeds, especially when performing large file transfers or accessing data-intensive applications.
3. Data Redundancy: While not the primary purpose of disk merging, it can offer a degree of data redundancy. By mirroring data across multiple drives, users can mitigate the risk of data loss if one drive fails. However, this requires specific configurations and is not a full-fledged backup solution.
Types of Disk Merging
There are two main types of disk merging techniques commonly employed in Windows 11:
1. RAID 0 (Striping): RAID 0, or striping, involves dividing data into smaller blocks and distributing them across multiple drives. This method enhances performance by allowing simultaneous read/write operations on multiple drives, effectively increasing data transfer speeds. However, RAID 0 offers no redundancy, meaning data loss occurs if one drive fails.
2. RAID 1 (Mirroring): RAID 1, or mirroring, duplicates data across multiple drives, creating an exact copy on each drive. This approach provides high data redundancy, ensuring data remains accessible even if one drive fails. However, RAID 1 requires twice the storage space as the original drive, making it less efficient in terms of storage utilization.
Considerations Before Merging Disks
1. Data Backup: Before merging disks, it’s crucial to back up all data on the drives involved. This ensures data recovery in case of errors or unforeseen issues during the merging process.
2. Drive Compatibility: Ensure the drives to be merged are compatible in terms of size, speed, and interface (e.g., SATA, NVMe). Incompatible drives can lead to performance bottlenecks or other issues.
3. Operating System Support: Verify that the operating system supports the chosen disk merging technique. Windows 11 supports both RAID 0 and RAID 1 configurations.
4. Data Loss Risk: Disk merging can potentially lead to data loss if not performed correctly. It’s essential to follow the correct steps and ensure data integrity throughout the process.
Steps for Merging Disks in Windows 11
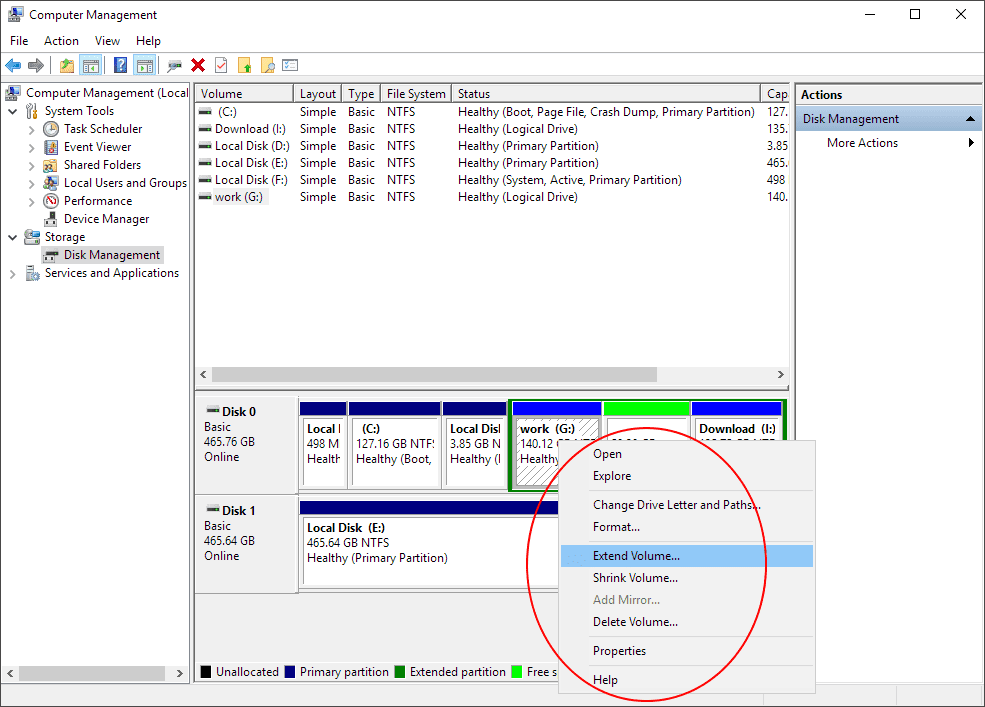
Merging disks in Windows 11 can be accomplished using the built-in Disk Management tool or through third-party software. Here’s a step-by-step guide for merging disks using the Disk Management tool:
-
Open Disk Management: Access the Disk Management tool through the Control Panel or by searching for "Disk Management" in the Start menu.
-
Identify Drives: Identify the physical drives you want to merge. Ensure they are formatted and have sufficient free space.
-
Create a New Volume: Right-click on any of the selected drives and choose "New Simple Volume."
-
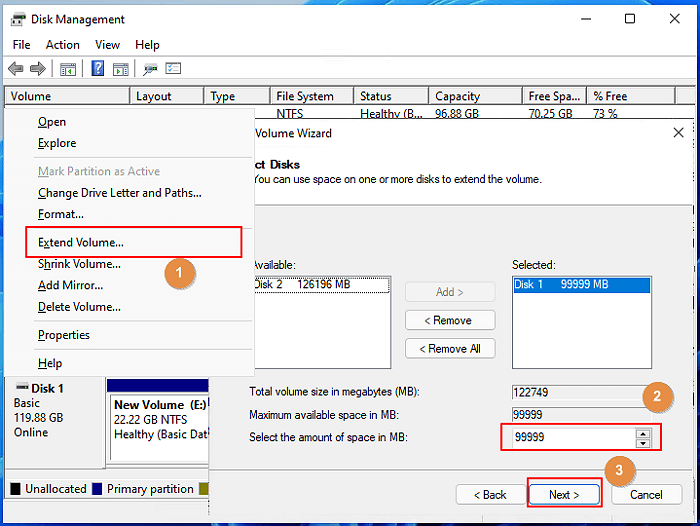
Select Disk Space: Specify the amount of disk space you want to allocate to the new volume. This can be the entire capacity of both drives or a smaller portion.
-
Assign Drive Letter: Assign a drive letter to the new volume.
-
Format Volume: Choose a file system (e.g., NTFS) and format the new volume.
-
Complete Process: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the merging process.
FAQs about Merging Disks in Windows 11
Q: Can I merge different types of drives (e.g., SSD and HDD)?
A: While it’s possible to merge different types of drives, it’s generally not recommended. The performance of the combined volume will be limited by the slower drive.
Q: What happens to my data during the merging process?
A: Data on the drives being merged will be combined into a single volume. It’s essential to back up data beforehand to prevent accidental loss.
Q: Can I unmerge disks after merging them?
A: Yes, you can unmerge disks. However, this requires deleting the merged volume and formatting the individual drives separately.
Q: Is disk merging a good option for all users?
A: Disk merging is not always the best solution. It’s beneficial for users seeking increased storage space, improved performance, or data redundancy. However, it requires careful planning and understanding of the potential risks.
Tips for Merging Disks in Windows 11
1. Use Reliable Software: When using third-party software for disk merging, choose reputable and well-tested options.
2. Test Thoroughly: After merging disks, test the new volume thoroughly to ensure data integrity and performance.
3. Monitor Disk Health: Regularly monitor the health of the drives involved in the merged volume to detect any potential issues early.
4. Consider Backup Strategies: Implement comprehensive backup strategies to protect data against potential data loss.
Conclusion
Merging disks in Windows 11 can be a powerful technique for increasing storage space, enhancing performance, and improving data redundancy. However, it’s a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. By understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and potential risks, users can make informed decisions about whether disk merging is the right solution for their specific needs. Remember, data backup is paramount before embarking on any disk merging operation, and thorough testing is crucial to ensure data integrity and performance after the process is complete.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Merging Disks in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!