Merging Disk Partitions In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Merging Disk Partitions in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Merging Disk Partitions in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Merging Disk Partitions in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Merging Disk Partitions in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of computer storage management, disk partitioning plays a crucial role in organizing data and optimizing performance. Windows 11, with its advanced storage capabilities, offers a versatile approach to managing disk partitions. One particularly useful technique is merging partitions, a process that combines two or more partitions into a single, larger partition. This can be a valuable tool for various purposes, including:
1. Consolidating Storage Space: Merging partitions allows users to combine smaller, fragmented partitions into a larger, contiguous space, effectively eliminating wasted storage space and providing a more organized storage structure. This can be particularly beneficial for users who have a limited amount of disk space or who have accumulated a large number of files over time.
2. Simplifying Disk Management: By reducing the number of partitions, merging simplifies disk management. Instead of navigating multiple partitions, users can access all their data from a single, unified partition, making data organization and retrieval more efficient.
3. Optimizing Performance: In some cases, merging partitions can improve performance by eliminating the need for the system to access data from multiple partitions, which can lead to delays and fragmentation.
Understanding the Process
Merging partitions involves two main steps:
1. Shrinking the Source Partition: The first step involves shrinking the source partition, the partition that will be merged into the destination partition. This frees up space within the source partition, making it possible to merge it into the destination partition.
2. Expanding the Destination Partition: The second step involves expanding the destination partition, the partition that will absorb the source partition. This process uses the freed-up space from the source partition to increase the size of the destination partition.
Methods for Merging Partitions
Windows 11 offers two primary methods for merging partitions:
1. Using Disk Management: Windows 11’s built-in Disk Management tool provides a user-friendly interface for managing disk partitions, including merging. This method is suitable for most users and offers a straightforward approach to merging partitions.
2. Using Third-Party Partition Managers: Several third-party partition management tools offer more advanced features and flexibility compared to Disk Management. These tools can be particularly helpful for users who require more control over the merging process or who need to perform complex partition operations.
Prerequisites for Merging Partitions
Before attempting to merge partitions, it is essential to consider the following prerequisites:
1. Backup Data: Merging partitions can potentially lead to data loss if not performed carefully. Therefore, it is crucial to create a complete backup of all data on the partitions involved in the merging process before proceeding.
2. Free Space: The source partition must have sufficient free space to accommodate the data from the destination partition. If the source partition does not have enough free space, it will need to be shrunk further before the merging process can be initiated.
3. Partition Type: Not all partitions can be merged. System partitions, boot partitions, and partitions containing critical system files should not be merged, as doing so can lead to system instability or data loss.
Step-by-Step Guide: Merging Partitions using Disk Management
-
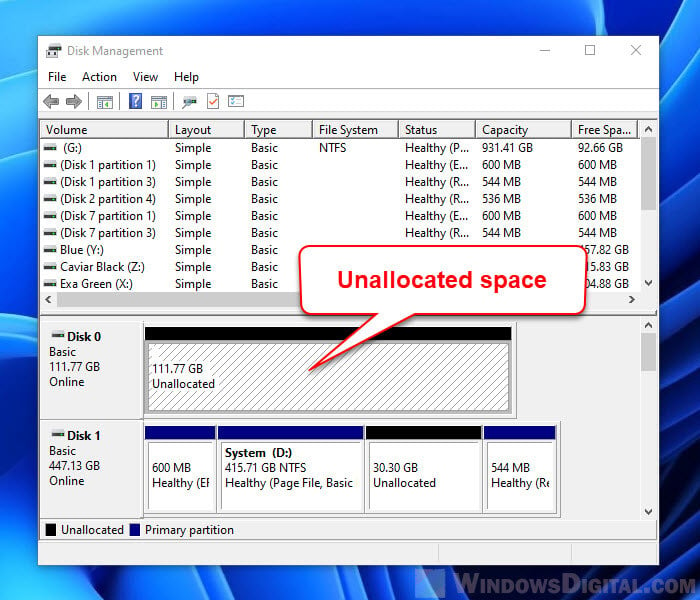
Open Disk Management: Open the Start menu and search for "Disk Management." Select the "Disk Management" option from the results.
-
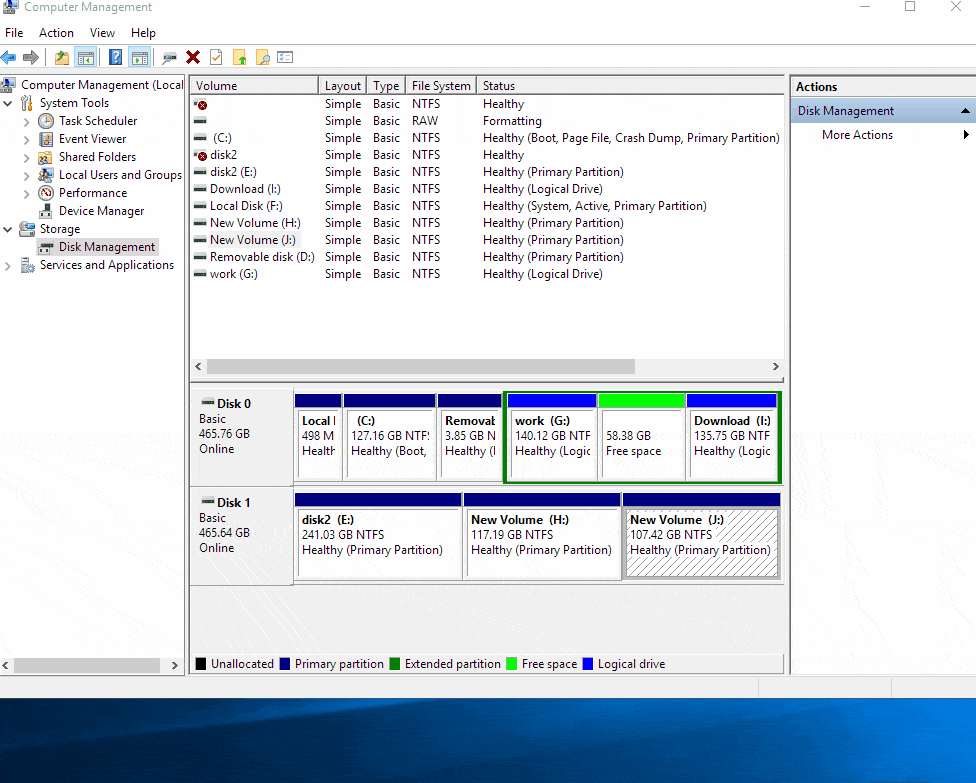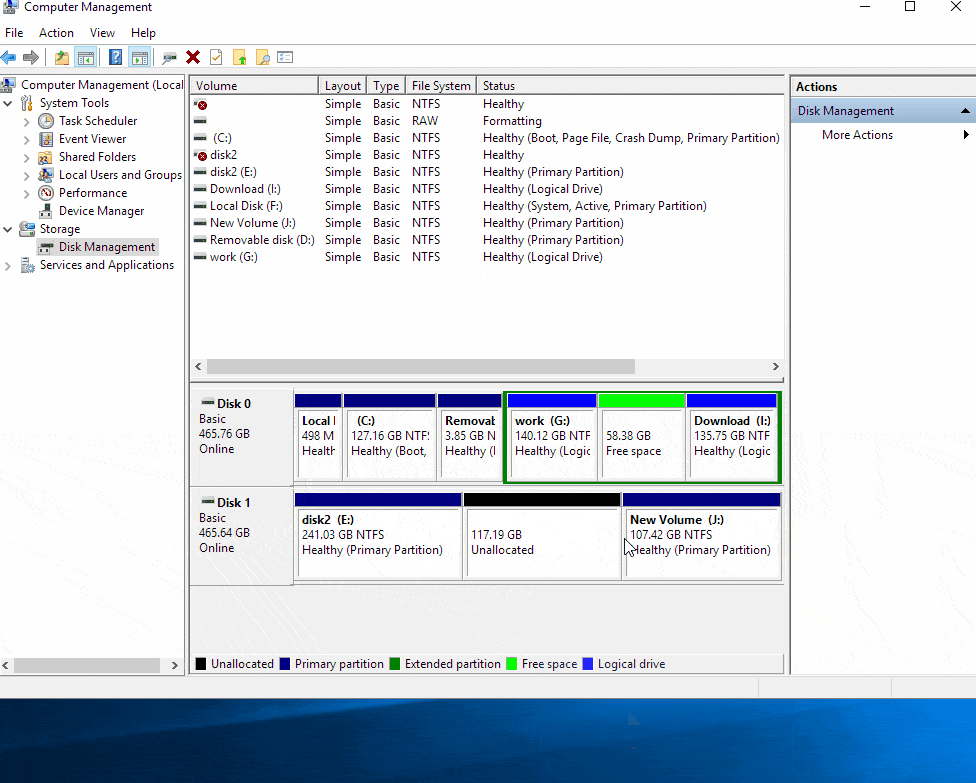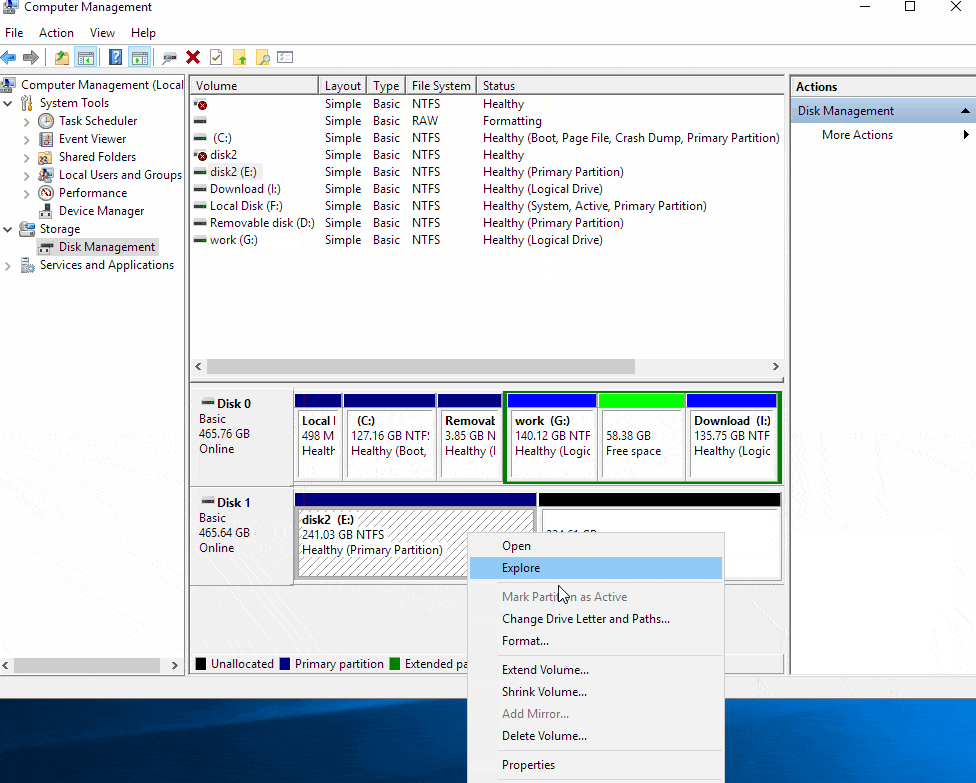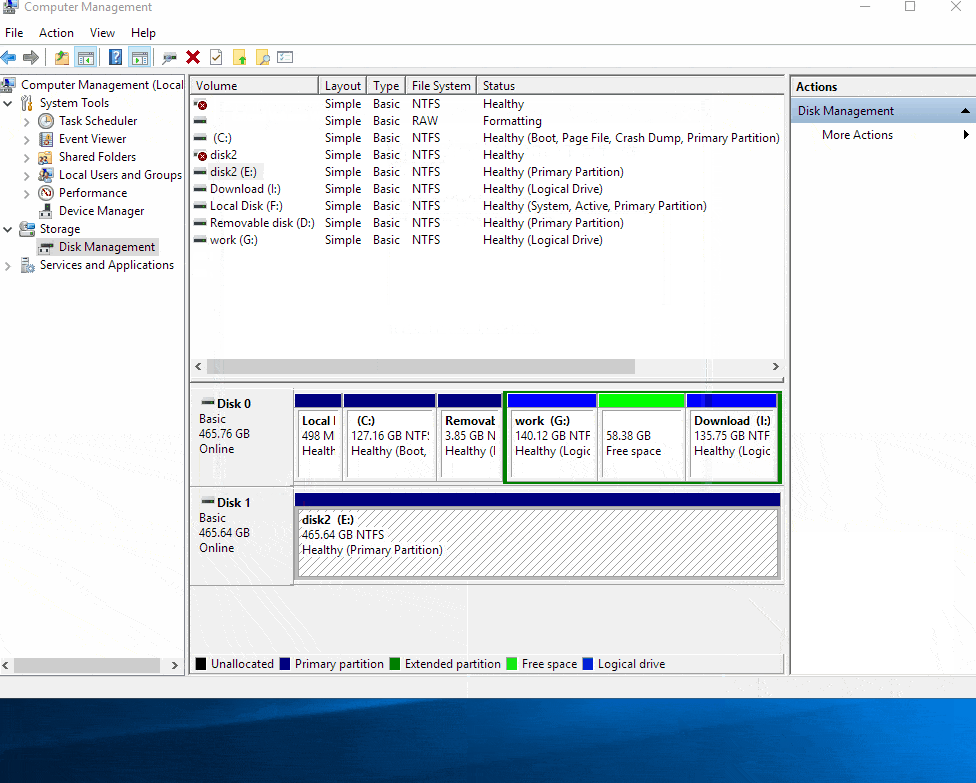
Locate the Partitions: Identify the source partition and the destination partition that you want to merge.
-
Shrink the Source Partition: Right-click on the source partition and select "Shrink Volume." In the "Shrink Volume" window, specify the amount of space you want to shrink from the source partition. Ensure that the remaining space in the source partition is sufficient to accommodate the data from the destination partition. Click "Shrink" to proceed.
-
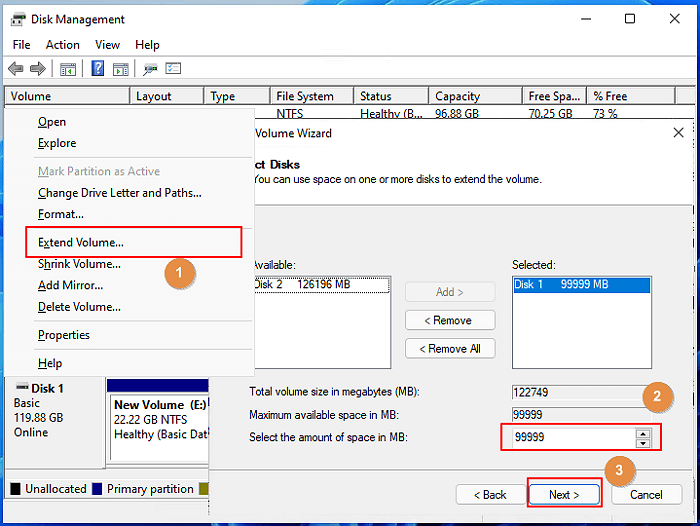
Expand the Destination Partition: Right-click on the destination partition and select "Extend Volume." In the "Extend Volume Wizard," select the unallocated space that was created by shrinking the source partition. Click "Next" to proceed.
-
Complete the Process: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the merging process. Once the process is complete, the source partition will be merged into the destination partition, and the destination partition will have increased in size.
Tips for Merging Partitions
- Choose the Right Destination Partition: Select a destination partition that is large enough to accommodate the data from the source partition.
- Monitor Free Space: Carefully monitor the free space available in the source partition before and during the shrinking process to ensure that there is enough space to accommodate the data from the destination partition.
- Check for Data Integrity: After merging partitions, verify that all data from the source partition is present and accessible within the destination partition.
FAQs: Merging Disk Partitions in Windows 11
Q: Can I merge system partitions?
A: Merging system partitions is not recommended. System partitions contain critical system files, and merging them can lead to system instability or data loss.
Q: Can I merge partitions that are on different disks?
A: No, you cannot merge partitions that are on different disks. Merging partitions requires that the partitions be located on the same physical disk.
Q: What happens to my data after merging partitions?
A: The data from the source partition will be merged into the destination partition. The source partition will be deleted, but its data will be preserved within the destination partition.
Q: Can I undo the merging process?
A: Once partitions are merged, the process cannot be reversed using the Disk Management tool. To undo the merging process, you will need to use a third-party partition management tool or reinstall your operating system.
Conclusion
Merging partitions in Windows 11 offers a valuable tool for optimizing disk space, simplifying storage management, and potentially improving performance. By understanding the process, prerequisites, and available methods, users can effectively merge partitions to streamline their storage structure and enhance their computing experience.




![How to Merge Partitions on SSD in Windows 11/10 [Quick & Easy Methods] - EaseUS](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/merge-partitions-on-ssd-cover.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Merging Disk Partitions in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!