Managing Administrative Privileges In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers a robust system for managing administrative privileges. This system is crucial for maintaining system security, preventing unauthorized modifications, and ensuring smooth operation. This article explores the various aspects of administrative access control in Windows 11, providing a comprehensive understanding of its functionalities, benefits, and best practices.
Understanding the Concept of Administrative Privileges
In Windows 11, user accounts are categorized into two primary groups: Standard Users and Administrators. Administrators possess the highest level of privileges, allowing them to perform actions that can significantly impact the operating system’s functionality, including:
- Installing and Uninstalling Software: Administrators can install or remove any software on the system, including applications and system drivers.
- Making System-Wide Changes: They can modify system settings, configure network connections, and manage user accounts.
- Accessing and Modifying System Files: Administrators have complete read and write access to all system files, including those critical for the operating system’s stability.
- Running Programs with Elevated Privileges: Administrators can execute programs and processes that require administrative permissions, such as system maintenance tools or security software.
The Importance of Limited Administrative Access
While administrative privileges are essential for system management, granting them indiscriminately poses significant security risks. A user with administrator privileges can inadvertently or intentionally install malicious software, modify system configurations, or delete critical data, potentially jeopardizing the entire system.
Limiting administrative access is crucial for several reasons:
- Enhanced Security: By restricting administrative privileges, the system becomes less vulnerable to malware and other security threats. Malicious software often requires administrative rights to execute and spread.
- Reduced Risk of Accidental Damage: Standard users with limited access cannot make system-wide changes that could cause instability or data loss.
- Improved System Stability: Unnecessary administrative actions can sometimes lead to system instability or unexpected behavior. Limiting access to administrators helps maintain a more stable system.
- Compliance with Security Policies: Many organizations have strict security policies that mandate the use of limited administrative access to ensure data integrity and compliance with industry regulations.
Strategies for Implementing Limited Administrative Access
Windows 11 offers various mechanisms to implement limited administrative access, each catering to specific needs and scenarios.
1. Standard User Accounts:
- Purpose: Standard user accounts are designed for everyday tasks like browsing the internet, using applications, and accessing personal files. They lack the ability to make system-wide changes or install software.
- Implementation: When setting up a new Windows 11 installation, it is recommended to create a standard user account for everyday use and a separate administrator account for system management. This approach minimizes the risk of accidental damage or security breaches.
- Benefits: Standard user accounts offer a significant layer of protection against malicious software and accidental system modifications.
2. Run as Administrator:
- Purpose: This feature allows a standard user to temporarily elevate their privileges for specific tasks that require administrative access.
- Implementation: Right-clicking an application or program and selecting "Run as administrator" prompts the user to provide administrative credentials. This grants elevated privileges only for that specific instance of the program.
- Benefits: This method provides a controlled and temporary elevation of privileges, minimizing the risk of unauthorized actions.
3. User Account Control (UAC):
- Purpose: UAC acts as a security mechanism that prompts users to confirm administrative actions. It helps prevent malicious software from executing without explicit user consent.
- Implementation: UAC is enabled by default in Windows 11 and can be configured to different levels of sensitivity.
- Benefits: UAC adds an extra layer of security by requiring user confirmation before granting administrative privileges, making it more difficult for malware to execute without user awareness.
4. Local Group Policy Editor:
- Purpose: This advanced tool allows administrators to define specific access permissions for users and groups. It provides fine-grained control over system resources and applications.
- Implementation: The Local Group Policy Editor is accessible through the "gpedit.msc" command in the Run dialog box.
- Benefits: The Local Group Policy Editor offers granular control over administrative privileges, enabling administrators to customize access based on specific needs and security requirements.
5. Windows Security:
- Purpose: Windows Security, previously known as Windows Defender Security Center, provides a comprehensive security platform that includes features like application control and device security.
- Implementation: The Windows Security app offers various options for managing administrative access, including blocking unauthorized software execution and setting specific access permissions for applications.
- Benefits: Windows Security provides a centralized platform for managing administrative access and other security features, streamlining the process and offering a holistic approach to system security.
6. Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune):
- Purpose: Intune is a cloud-based service that allows administrators to manage and secure devices and applications in a large organization.
- Implementation: Intune offers features like application control, device restrictions, and user account management, providing comprehensive control over administrative access in a corporate environment.
- Benefits: Intune streamlines administrative access management across multiple devices and users, simplifying the process and enhancing security in enterprise settings.
FAQs
1. How do I create a standard user account in Windows 11?
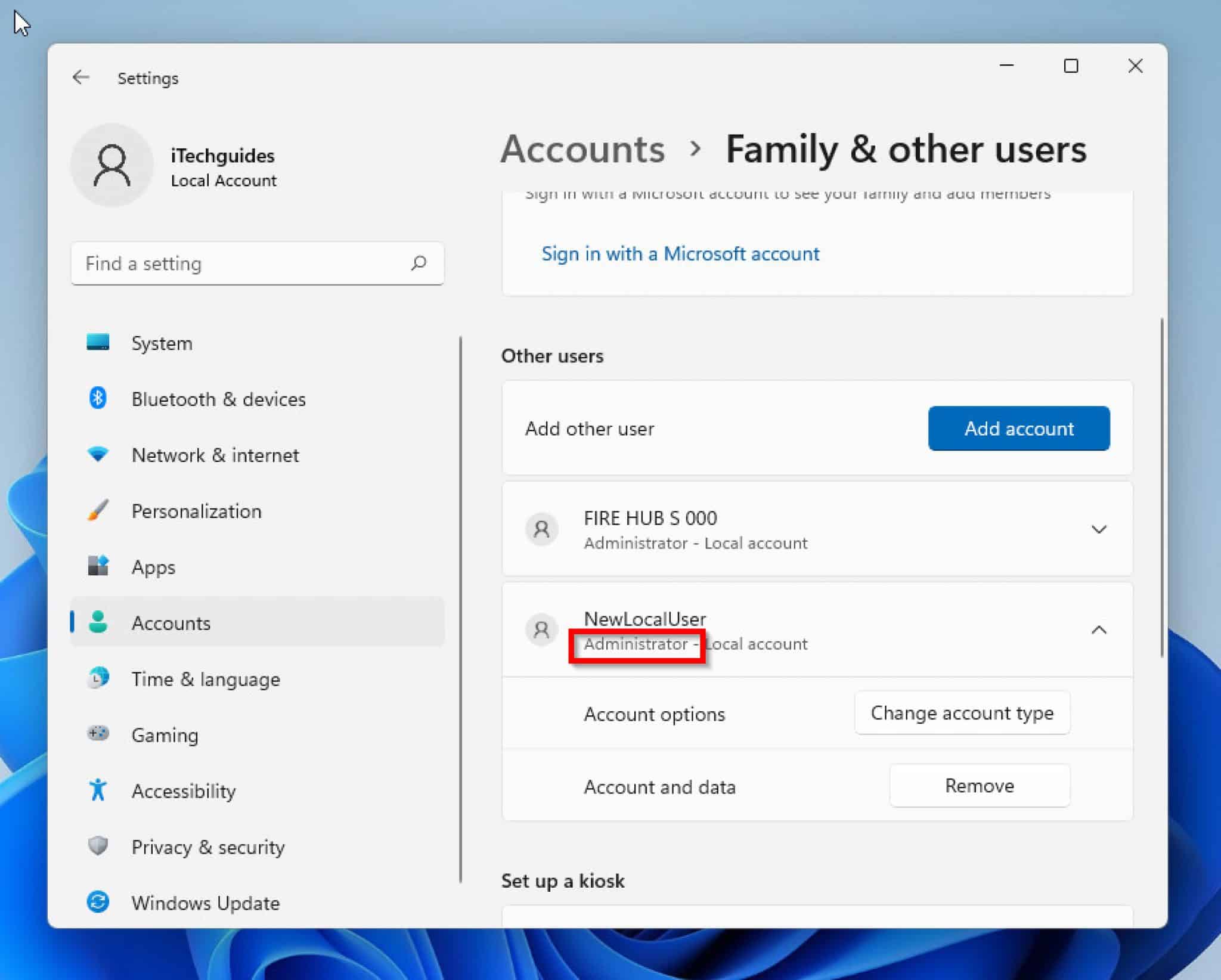
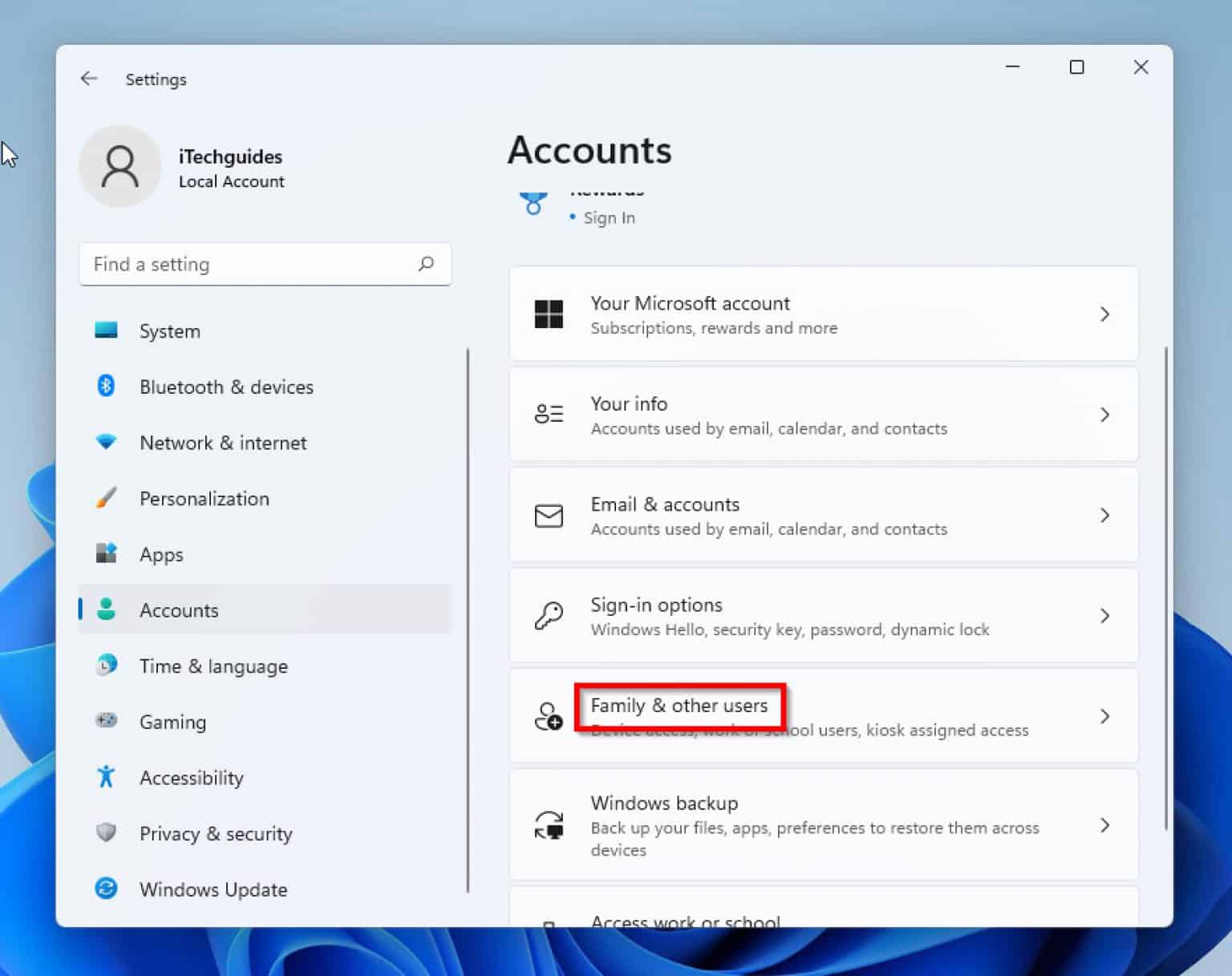
To create a standard user account, navigate to "Settings" > "Accounts" > "Family & other users." Click on "Add someone else to this PC" and follow the on-screen instructions. Select "I don’t have this person’s sign-in information" and choose "Add a user without a Microsoft account." Provide a username and password for the new account, ensuring you choose "Standard account" during the setup process.
2. What happens if I disable UAC?
Disabling UAC weakens the security of your Windows 11 system. It allows applications to execute with administrative privileges without user consent, making it easier for malware to compromise your system. It is strongly recommended to keep UAC enabled for enhanced security.
3. Can I temporarily disable administrative access for specific applications?
Yes, you can use the Local Group Policy Editor or Windows Security to restrict specific applications from accessing administrative privileges. This can be useful for applications that do not require administrative access for their core functionalities but might pose a potential security risk if granted elevated privileges.
4. How can I determine which applications have administrative access?
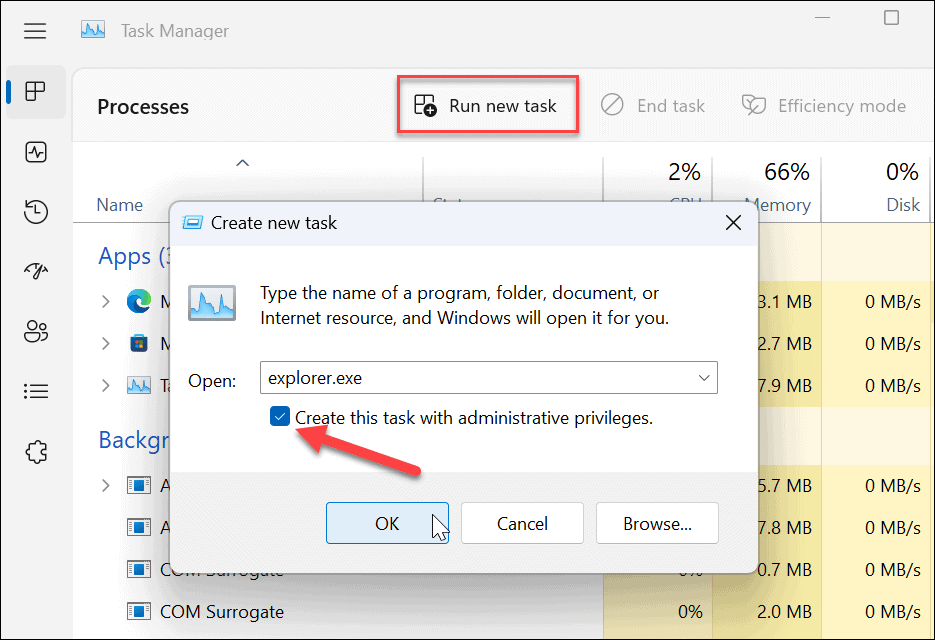
You can use the Task Manager to view running processes and identify those that are running with administrator privileges. Right-click on the taskbar, select "Task Manager," and then click on the "Details" tab. Look for processes marked with "Administrator" in the "User Name" column.
5. Is it possible to use a standard user account for system administration?
While it is possible to use a standard user account for some system administration tasks, it is generally not recommended for everyday system management. This approach can lead to security vulnerabilities and make it challenging to perform essential system maintenance tasks.
Tips
- Use Strong Passwords: Always use strong and unique passwords for both administrator and standard user accounts.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and security software to patch vulnerabilities and strengthen security.
- Be Cautious of Downloads: Only download software from trusted sources and be wary of suspicious links or attachments.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: For additional security, enable two-factor authentication for your Microsoft account and other online services.
- Regularly Review System Permissions: Periodically review the permissions granted to users and applications to ensure they align with your security policies.
- Educate Users: Train users on best security practices, including the importance of limiting administrative access and recognizing potential security threats.
Conclusion
Managing administrative privileges in Windows 11 is crucial for maintaining system security and stability. By implementing strategies like standard user accounts, UAC, and robust security tools, users and administrators can effectively restrict access to sensitive system resources, reducing the risk of malicious software, accidental damage, and unauthorized modifications. A comprehensive understanding of these mechanisms and their proper implementation is essential for ensuring a secure and reliable computing environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!