Linux Compared To Windows
linux compared to windows
Related Articles: linux compared to windows
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to linux compared to windows. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Linux vs. Windows: A Comprehensive Comparison in 2023
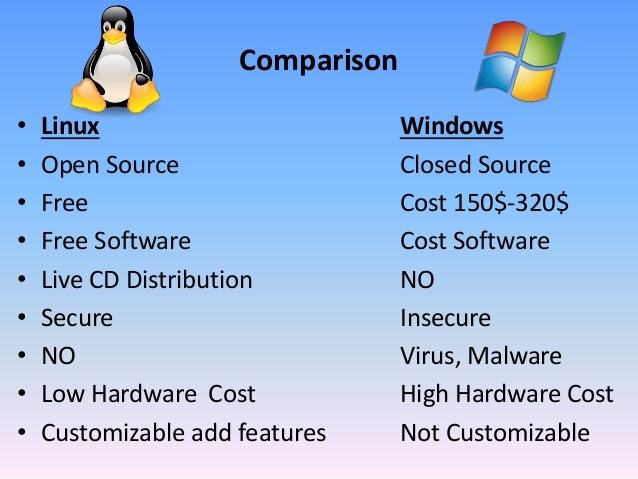
The choice between Linux and Windows operating systems is a constant debate, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. This comprehensive comparison delves into the intricacies of both systems, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and use cases, providing a clear understanding for users seeking the best fit for their needs.
Core Differences: The Philosophical Divide
At their core, Linux and Windows represent contrasting philosophies. Linux, a Unix-like operating system, is built on the principles of open-source development, community collaboration, and user freedom. Windows, a proprietary system developed by Microsoft, emphasizes ease of use, commercial software compatibility, and a streamlined user experience.
1. Open Source vs. Proprietary: The Freedom Factor
Linux’s open-source nature grants users the freedom to access, modify, and distribute the source code. This transparency fosters a vibrant community of developers who contribute to its constant improvement. Windows, on the other hand, is a closed-source system, meaning its source code is not publicly available, limiting customization and user control.
2. Cost: A Matter of Dollars and Cents
Linux distributions are generally free of charge, offering a cost-effective alternative to Windows. While some commercial distributions exist, the majority are readily available for download and use without any licensing fees. Windows, however, requires a purchase license for each user, making it a more expensive option, especially for businesses and large organizations.
3. Security: A Battleground for Vulnerability
The open-source nature of Linux allows for rapid security updates and bug fixes. The community-driven approach ensures constant scrutiny of the codebase, making it more resistant to malware and exploits. Windows, due to its closed-source nature, relies heavily on Microsoft for security updates, which can sometimes be slower, leading to potential vulnerabilities.
4. Performance: Speed and Efficiency
Linux is known for its efficient resource management and lean design, resulting in faster boot times and smoother performance, particularly on older or less powerful hardware. Windows, with its more resource-intensive graphical interface and numerous background processes, can be slower, especially on systems with limited resources.
5. Stability: A Matter of Reliability
Linux systems are renowned for their stability and reliability, with fewer crashes and system errors. Their modular design allows for easier troubleshooting and recovery, reducing downtime. Windows, while generally stable, can be prone to occasional crashes and updates that may cause system instability.
6. Customization: Tailoring the Experience
Linux offers unparalleled customization options. Users can tailor their system’s appearance, functionality, and configuration to suit their specific needs. Windows, while offering some customization, is more limited in its options, adhering to a more standardized user experience.
7. Software Availability: The Ecosystem
While Linux boasts a vast and growing software ecosystem, it still lags behind Windows in terms of commercial software availability. Many popular games and productivity suites are primarily designed for Windows, limiting Linux users’ options. However, with the rise of cross-platform software and the growing Linux gaming community, this gap is gradually closing.
8. Hardware Compatibility: The Hardware Landscape
Windows typically offers wider hardware compatibility, especially for newer devices and peripherals. Linux, while supporting a wide range of hardware, may require additional drivers or configuration for certain devices. However, the Linux community actively develops drivers for new hardware, constantly expanding its compatibility.
Use Cases: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
The choice between Linux and Windows depends on the specific use case and individual needs.
1. Servers and Data Centers: Linux reigns supreme in the server environment due to its stability, security, and cost-effectiveness. Its open-source nature allows for customization and automation, making it ideal for managing large-scale infrastructure.
2. Desktop Computing: Windows remains dominant in the desktop space, particularly for users who prioritize ease of use, commercial software compatibility, and a familiar user experience. However, Linux distributions like Ubuntu and Fedora offer a user-friendly interface and a growing selection of desktop applications, making them viable alternatives for everyday tasks.
3. Web Development and Programming: Linux is widely favored among developers due to its command-line interface, open-source tools, and compatibility with various programming languages. Its flexibility and control make it an ideal environment for building and deploying web applications.
4. Education and Research: Linux’s cost-effectiveness and powerful scientific computing tools make it a popular choice in academic settings. Its open-source nature allows researchers to collaborate and share code, fostering innovation and knowledge exchange.
5. Embedded Systems and IoT: Linux’s lightweight and resource-efficient nature makes it ideal for embedded systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). Its flexibility and customization options allow developers to tailor it to specific hardware and applications.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can I switch from Windows to Linux?
A: Yes, switching from Windows to Linux is possible and relatively straightforward. Many Linux distributions offer tools and guides to assist with the transition. However, some users may need to adjust to a different interface and workflow.
Q: Is Linux secure?
A: Linux is generally considered more secure than Windows due to its open-source nature and robust security features. However, it’s crucial to stay up-to-date with security updates and practice safe computing habits to minimize risks.
Q: Can I play games on Linux?
A: While Linux gaming is growing, it still lags behind Windows in terms of game availability. However, many popular games are now available through platforms like Steam, and the Linux gaming community is actively developing and porting games to the platform.
Q: Is Linux difficult to use?
A: Many Linux distributions offer user-friendly interfaces and intuitive workflows, making them easy to learn and use, even for beginners. However, some users may need to familiarize themselves with the command-line interface for advanced tasks.
Tips: Navigating the Linux Landscape
1. Choose the Right Distribution: Select a Linux distribution that aligns with your needs and experience level. Popular options include Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and Mint.
2. Explore the Command Line: Familiarize yourself with the command line interface, which provides advanced control and flexibility.
3. Utilize Package Managers: Leverage package managers like apt, yum, or pacman to install and manage software.
4. Join the Community: Engage with the vibrant Linux community through forums, chat rooms, and online resources.
5. Experiment and Learn: Linux is highly customizable, so experiment with different settings and configurations to personalize your experience.
Conclusion: A World of Possibilities
Linux and Windows offer distinct advantages and cater to different needs. Linux’s open-source nature, security, stability, and customization options make it a compelling choice for servers, development, and specialized use cases. Windows, with its ease of use, commercial software compatibility, and widespread hardware support, remains dominant in the desktop and gaming space. Ultimately, the best operating system is the one that best meets your individual requirements and preferences. By understanding the key differences and use cases, users can make an informed decision that aligns with their needs and unlocks a world of possibilities.
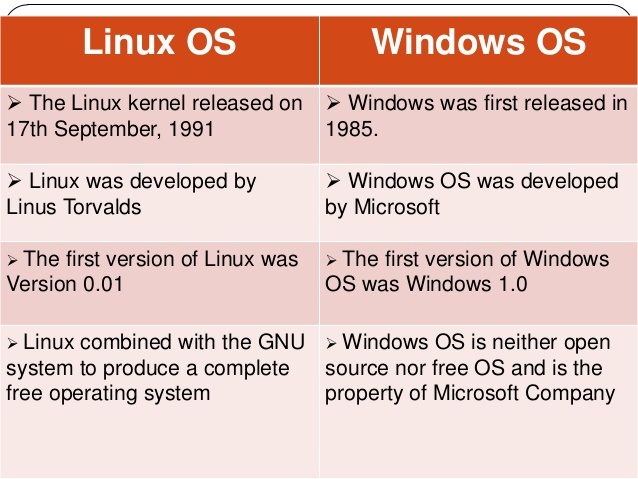






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into linux compared to windows. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!