Exploiting Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive Into Metasploit And Windows 7
Exploiting Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Metasploit and Windows 7
Related Articles: Exploiting Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Metasploit and Windows 7
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Exploiting Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Metasploit and Windows 7. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploiting Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Metasploit and Windows 7
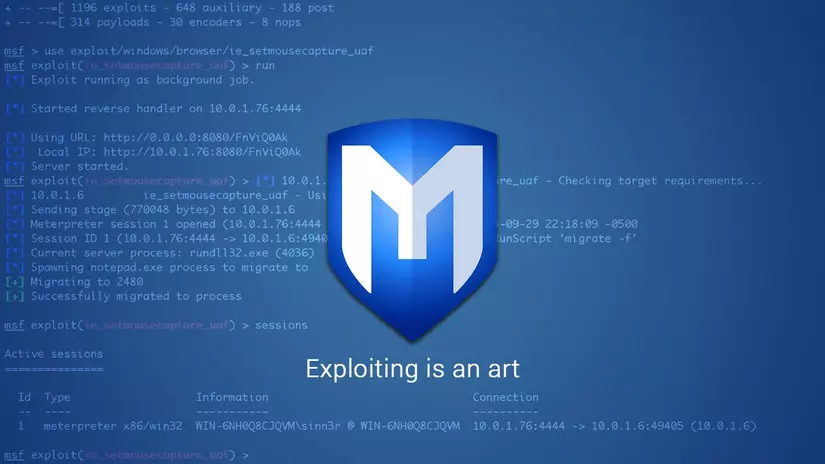
Windows 7, once a ubiquitous operating system, has transitioned into the realm of legacy software. While its support ended in 2020, its presence persists in various environments, making it a potential target for malicious actors. This article delves into the world of Metasploit, a powerful penetration testing framework, and its role in uncovering and exploiting vulnerabilities within Windows 7 systems.
Understanding Metasploit: A Framework for Ethical Hacking
Metasploit, developed by Rapid7, is a widely recognized and respected toolset used for penetration testing and security research. It provides a comprehensive platform for identifying, exploiting, and analyzing vulnerabilities in various operating systems, including Windows 7.
Metasploit operates through a modular approach, offering a vast library of exploits, payloads, and auxiliary modules. These components work in tandem to facilitate a multifaceted attack process.
- Exploits: These modules target specific vulnerabilities in software or operating systems. When successfully executed, they exploit the weakness, granting access to the system.
- Payloads: These modules are delivered after a successful exploit and establish a foothold within the compromised system. They can range from simple reverse shells, allowing remote control, to more complex tools for data exfiltration or persistence.
- Auxiliary Modules: These modules augment the attack process by providing additional functionality, such as network scanning, port enumeration, or credential harvesting.
The Significance of Metasploit in Windows 7 Exploitation
Windows 7’s end-of-life status has rendered it particularly vulnerable to exploits. Without security updates and patches, previously unknown vulnerabilities can remain unaddressed, providing an entry point for attackers. Metasploit’s arsenal of exploits, specifically designed for Windows 7, empowers penetration testers and security researchers to:
- Identify and Assess Vulnerabilities: By leveraging Metasploit’s extensive database of exploits, security professionals can simulate real-world attacks and pinpoint potential weaknesses in Windows 7 systems. This proactive approach allows organizations to prioritize patching and mitigation efforts before malicious actors exploit them.
- Demonstrate the Impact of Exploits: Metasploit facilitates practical demonstrations of vulnerabilities. By showcasing the consequences of successful exploits, security teams can effectively communicate the risks associated with unpatched systems to stakeholders, fostering a sense of urgency for remediation.
- Develop and Test Mitigation Strategies: Metasploit’s tools can be used to test the effectiveness of security measures implemented to protect against known vulnerabilities. This iterative process allows security teams to fine-tune their defenses, ensuring robust protection against potential attacks.
Common Metasploit Exploits Targeting Windows 7
Several notable Metasploit exploits have historically targeted Windows 7, exploiting specific vulnerabilities in its core components or applications:
- MS17-010 EternalBlue: This exploit targets a vulnerability in the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, a fundamental networking protocol used for file sharing. Successful exploitation allows attackers to remotely execute code on vulnerable systems, granting them complete control.
- MS14-068: This exploit targets a vulnerability in the Windows kernel, the core of the operating system. Successful exploitation allows attackers to gain elevated privileges, enabling them to execute code with administrative rights.
- MS08-067: This exploit targets a vulnerability in the Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), a protocol used for remote access. Successful exploitation allows attackers to gain control of the remote system, potentially stealing sensitive data or installing malware.
Understanding the Importance of Responsible Exploitation
While Metasploit is a powerful tool for ethical hacking and security research, it is crucial to use it responsibly. Exploiting vulnerabilities without proper authorization is illegal and unethical. Metasploit should only be used in authorized environments for legitimate purposes, such as penetration testing, vulnerability research, and security training.
FAQs Regarding Metasploit and Windows 7 Exploits
1. Is Metasploit Legal to Use?
Metasploit itself is a legitimate tool used for ethical hacking and security research. However, its use for unauthorized activities, such as exploiting vulnerabilities without permission, is illegal and unethical.
2. How Can I Protect My Windows 7 System From Exploits?
While Windows 7 is no longer supported, organizations can still mitigate risks by:
- Applying Available Patches: Although no new security updates are released for Windows 7, organizations can implement the latest patches available at the time of its end-of-life.
- Implementing Network Segmentation: Isolating Windows 7 systems from critical infrastructure can limit the impact of a successful exploit.
- Utilizing Security Software: Antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can help identify and mitigate malicious activity targeting Windows 7 systems.
- Considering Migration: Transitioning to a supported operating system, such as Windows 10 or 11, offers the most comprehensive protection against vulnerabilities.
3. What are the Potential Consequences of Exploiting Windows 7 Systems?
Exploiting Windows 7 systems can lead to various consequences, including:
- Data Theft: Sensitive data, such as financial records, personal information, or intellectual property, can be stolen and misused.
- System Compromise: Attackers can gain control of the system, installing malware, stealing credentials, or launching further attacks.
- Denial of Service: Attackers can disrupt system functionality, rendering it unusable for legitimate purposes.
- Reputation Damage: A successful attack can damage an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of trust and customer confidence.
Tips for Responsible Use of Metasploit
- Always Obtain Proper Authorization: Before using Metasploit to test systems, secure explicit permission from the system owner.
- Respect Privacy and Confidentiality: Avoid targeting systems or individuals without their consent.
- Focus on Ethical Hacking: Use Metasploit for legitimate security research and penetration testing, not for malicious activities.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest security vulnerabilities and exploit techniques.
- Contribute to Security: Share your findings responsibly with the security community to help improve overall security.
Conclusion
Metasploit plays a crucial role in uncovering and exploiting vulnerabilities within Windows 7 systems. While the operating system is no longer supported, its presence in various environments necessitates a proactive approach to security. By understanding the capabilities of Metasploit and its potential impact, organizations can effectively address vulnerabilities, protect sensitive data, and mitigate risks associated with legacy systems. Responsible use of Metasploit for ethical hacking and security research empowers individuals and organizations to build a safer and more secure digital landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploiting Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Metasploit and Windows 7. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!