Consolidating Data: The Art And Science Of Combining Disks
Consolidating Data: The Art and Science of Combining Disks
Related Articles: Consolidating Data: The Art and Science of Combining Disks
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Consolidating Data: The Art and Science of Combining Disks. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Consolidating Data: The Art and Science of Combining Disks

The digital age has ushered in an era of data abundance. As we generate, store, and manage vast amounts of information, the need for efficient and effective data management becomes paramount. One common challenge arises when data is scattered across multiple storage devices, leading to inefficiencies in access, organization, and overall utilization. This is where the concept of combining data from multiple disks into a single, unified storage space comes into play.
This process, often referred to as "disk merging," offers numerous advantages, including:
1. Enhanced Data Accessibility: Consolidating data from multiple disks into a single location simplifies data retrieval and management. Users can easily access and navigate all their information from a central point, eliminating the need to search across multiple drives.
2. Improved Data Organization: Merging disks allows for a more structured and organized data environment. By combining data from different sources, it becomes possible to establish a unified directory structure, facilitating efficient data organization and search capabilities.
3. Increased Storage Capacity: Combining multiple disks can create a larger, unified storage space, effectively increasing the overall storage capacity. This is particularly beneficial for users facing storage limitations on individual drives.
4. Simplified Backup and Recovery: Merging disks can simplify data backup and recovery processes. By consolidating data into a single location, backups can be performed more efficiently, and recovery operations can be streamlined.
5. Enhanced Data Security: Combining disks can enhance data security by centralizing data storage and enabling the implementation of comprehensive security measures, such as encryption and access controls, across the entire consolidated storage space.
6. Improved Performance: In some cases, merging disks can improve overall system performance. By consolidating data onto a single drive with faster read and write speeds, data access times can be reduced, leading to a more responsive system.
Methods for Combining Disks:
There are various methods for combining disks, each with its own set of considerations and advantages:
1. Disk Cloning: This method involves creating an exact copy of one disk onto another. While this approach maintains the original disk’s structure and data integrity, it requires sufficient space on the target disk to accommodate the entire source disk.
2. Disk Imaging: Similar to cloning, disk imaging creates a complete image of the source disk, which can be stored on a different disk or another storage medium. This method allows for easy restoration of the original disk’s contents if necessary.
3. Data Transfer: This method involves manually transferring data from one disk to another. While this approach offers flexibility in terms of selecting specific files and folders for transfer, it requires more time and effort than other methods.
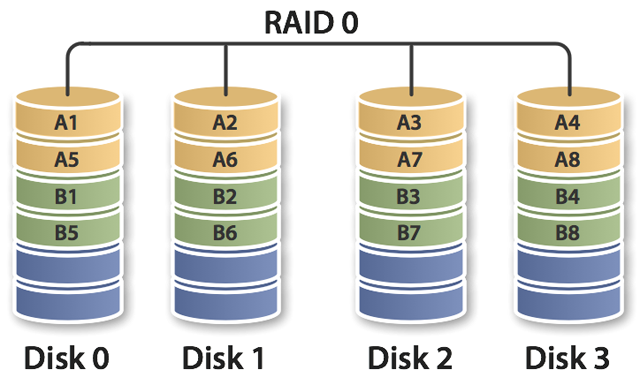
4. RAID Configuration: RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations combine multiple physical disks into a logical unit, providing features such as data redundancy, increased performance, or a combination of both. RAID configurations require specialized hardware or software and can be complex to implement.
5. Software-Based Merging Tools: Various software tools are available that facilitate disk merging. These tools typically offer a user-friendly interface and automate the process of combining data from multiple disks into a single destination.
Considerations for Combining Disks:
1. Data Integrity: It is crucial to ensure data integrity during the merging process. Using reliable tools and techniques is essential to prevent data loss or corruption.
2. Disk Space Requirements: The target disk must have sufficient space to accommodate the combined data from all source disks.
3. Data Organization: Carefully plan the organization of data on the merged disk to ensure easy access and navigation.
4. Backup and Recovery: Create backups of all source disks before initiating the merging process to ensure data recovery in case of errors or unforeseen circumstances.
5. Compatibility: Ensure that the source and target disks are compatible with the chosen merging method and the operating system.
6. Security: Implement appropriate security measures to protect the merged data from unauthorized access or malicious attacks.
FAQs about Combining Disks:
1. Can I combine disks of different sizes?
Yes, you can combine disks of different sizes, but the total storage capacity of the merged disk will be limited to the size of the smallest disk.
2. Can I combine disks with different file systems?
It is generally not recommended to combine disks with different file systems. Different file systems have different structures and formats, and combining them can lead to compatibility issues.
3. Can I combine disks with different data types?
Yes, you can combine disks with different data types, such as documents, images, videos, and applications.
4. What are the risks associated with combining disks?
The primary risk associated with combining disks is data loss or corruption. It is essential to use reliable tools and techniques and to create backups before initiating the process.
5. What are the best practices for combining disks?
- Plan the process carefully, considering data integrity, disk space requirements, and data organization.
- Use reliable tools and techniques to minimize the risk of data loss or corruption.
- Create backups of all source disks before initiating the merging process.
- Ensure compatibility between source and target disks.
- Implement appropriate security measures to protect the merged data.
Tips for Combining Disks:
- Use a dedicated tool: Employ specialized software designed for merging disks to ensure a smooth and reliable process.
- Check disk space: Verify that the target disk has enough space to accommodate the combined data.
- Plan data organization: Consider how you want to organize data on the merged disk for efficient access.
- Create backups: Back up all source disks before initiating the merging process.
- Test the merged disk: After merging disks, thoroughly test the merged disk to ensure data integrity and functionality.
Conclusion:
Combining disks offers numerous benefits, including enhanced data accessibility, improved data organization, increased storage capacity, simplified backup and recovery, enhanced data security, and potentially improved system performance. By carefully planning and implementing the merging process, users can effectively consolidate their data into a unified storage space, streamlining data management and maximizing the utilization of their storage resources.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Consolidating Data: The Art and Science of Combining Disks. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!