Connecting Computers To A Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Network Fundamentals
- 3.2 Types of Networks
- 3.3 Connecting Computers to a Network
- 3.4 Benefits of Connecting Computers to a Network
- 3.5 Common Network Connectivity Issues and Solutions
- 3.6 Network Security Considerations
- 3.7 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.8 Tips for Connecting Computers to a Network
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide

The ability to connect computers to a network has become an indispensable aspect of modern life, revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, and access information. Whether it’s a small home network or a large enterprise network, connecting computers enables seamless sharing of resources, data, and applications, fostering collaboration and efficiency. This article delves into the intricacies of connecting computers to a network, exploring the underlying concepts, essential components, and practical considerations.
Understanding Network Fundamentals
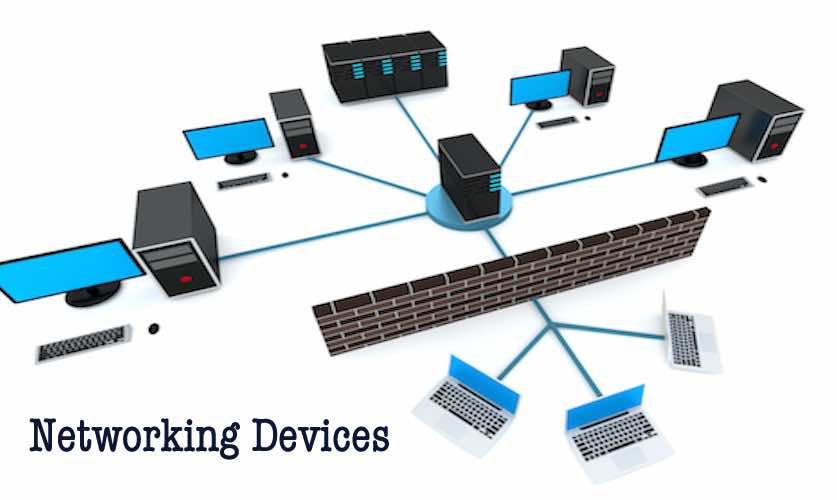
A network, at its core, is a system of interconnected devices that can communicate with each other. This communication is facilitated through a shared medium, often cables or wireless signals, allowing for the transmission of data between devices. The fundamental building blocks of a network include:
- Network Interface Card (NIC): This hardware component, typically integrated into the motherboard, enables a computer to connect to the network. Each NIC has a unique identifier, known as a MAC address, which distinguishes it from other devices on the network.
- Network Cables: These physical connections, commonly Ethernet cables, transmit data between devices, connecting them to a central point like a router or switch.
- Router: This device acts as a gateway, connecting multiple networks or devices together and directing traffic between them. It assigns IP addresses to devices, enabling them to communicate across different networks.
- Switch: This device facilitates communication between connected devices, forwarding data packets to their intended destinations. Unlike routers, switches operate at a lower level, primarily focusing on the physical layer of the network.
- Wireless Access Point (WAP): This device allows wireless devices, such as laptops and smartphones, to connect to the network using radio waves.
Types of Networks
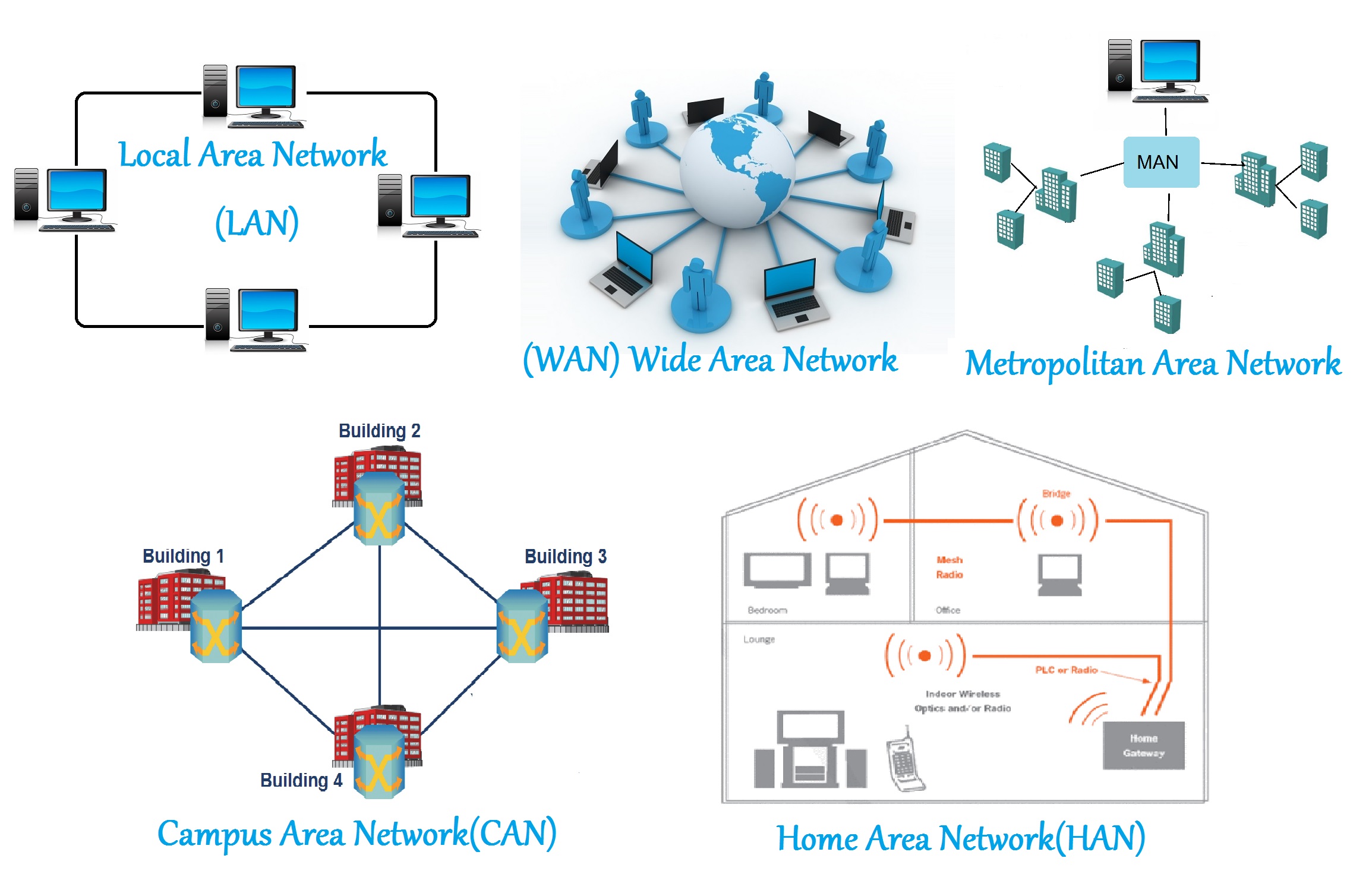
Networks can be classified based on their size, scope, and purpose. Some common types include:
- Local Area Network (LAN): A network that connects devices within a limited geographical area, typically a home, office, or building.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): A network that connects devices across geographically dispersed areas, often using public communication lines.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A network that covers a city or a large metropolitan area, typically used by businesses and organizations.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): A secure connection that allows devices to communicate over a public network, encrypting data to protect privacy and security.
Connecting Computers to a Network
The process of connecting a computer to a network involves several steps, depending on the network type and configuration:
- Identifying the Network Type: Determine whether the network is wired or wireless. Wired networks use physical cables, while wireless networks rely on radio waves.
- Configuring the Network Interface Card (NIC): Ensure the NIC is enabled and properly configured to match the network settings. This may involve setting the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Connecting to the Network: If using a wired network, connect the computer to the network using an Ethernet cable. For wireless networks, connect to the network using the SSID (network name) and password.
- Testing the Connection: Once connected, test the network connection by browsing the internet or accessing shared resources.
Benefits of Connecting Computers to a Network
Connecting computers to a network offers numerous advantages, including:
- Shared Resources: Networks allow devices to access and share resources such as printers, scanners, and storage devices.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Networks facilitate collaboration by enabling users to share files, documents, and applications, promoting teamwork and efficiency.
- Centralized Management: Networks allow administrators to manage and control devices, software, and security settings from a central location.
- Improved Communication: Networks provide a platform for seamless communication through email, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Access to Information: Networks connect users to vast sources of information, including the internet, databases, and online services.
Common Network Connectivity Issues and Solutions
While connecting computers to a network is generally straightforward, issues can arise. Some common problems and their solutions include:
- No Internet Connection: Verify cable connections, check network settings, restart the router, and contact your internet service provider.
- Slow Network Performance: Check for network congestion, update drivers, optimize network settings, and scan for malware.
- Connection Dropping: Check for faulty cables, interference from other devices, and update network drivers.
- Limited Access to Network Resources: Verify access permissions, check firewall settings, and ensure the network service is running.
Network Security Considerations
Connecting computers to a network introduces security risks, as data can be vulnerable to unauthorized access or attacks. Essential security measures include:
- Strong Passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for network accounts and devices.
- Firewall: Enable and configure a firewall to block unauthorized access to the network.
- Antivirus Software: Install and maintain antivirus software to protect against malware and viruses.
- Network Segmentation: Divide the network into smaller segments to limit the impact of security breaches.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep operating systems, software, and firmware up-to-date to patch vulnerabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between a router and a switch?
A: A router connects multiple networks or devices and directs traffic between them, while a switch facilitates communication between connected devices within the same network.
Q: What is an IP address?
A: An IP address is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network, allowing them to communicate with each other.
Q: What is a subnet mask?
A: A subnet mask defines the network portion of an IP address, distinguishing it from the host portion.
Q: What is a default gateway?
A: A default gateway is the IP address of the router, which directs traffic to other networks.
Q: How do I configure my network interface card (NIC)?
A: You can configure your NIC through the operating system’s network settings, typically accessed through the control panel.
Q: What are the different types of network cables?
A: Common network cables include Ethernet cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables.
Q: What is a wireless access point (WAP)?
A: A WAP allows wireless devices to connect to the network using radio waves.
Q: How can I improve my network security?
A: Implement strong passwords, enable a firewall, install antivirus software, segment the network, and keep devices up-to-date.
Tips for Connecting Computers to a Network
- Choose the Right Network Type: Select a wired or wireless network based on your needs and environment.
- Use High-Quality Cables: Invest in high-quality Ethernet cables for reliable wired connections.
- Secure Your Network: Implement strong security measures to protect your network and devices.
- Optimize Network Settings: Adjust network settings to improve performance and stability.
- Monitor Network Activity: Regularly monitor network activity for any unusual behavior.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on network security threats and best practices.
Conclusion
Connecting computers to a network has become an essential aspect of modern technology, enabling seamless communication, resource sharing, and access to information. By understanding the fundamentals of network connectivity, choosing the right network type, and implementing appropriate security measures, individuals and organizations can leverage the benefits of networking to enhance productivity, collaboration, and overall efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of network connectivity will only continue to grow, shaping the way we interact with each other and the world around us.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WirelessNetwork-5994852003f4020011db5333.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Connecting Computers to a Network: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!