A Legacy Of Innovation: Exploring The Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System
A Legacy of Innovation: Exploring the Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System
Related Articles: A Legacy of Innovation: Exploring the Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Legacy of Innovation: Exploring the Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Legacy of Innovation: Exploring the Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System

The landscape of mobile computing has undergone a dramatic transformation, with smartphones and tablets becoming ubiquitous. While Android and iOS dominate the market today, there was a time when Microsoft’s Windows Mobile held a significant presence, shaping the early stages of mobile operating systems. This article delves into the history, evolution, and impact of Windows Mobile, exploring its key features, successes, and eventual decline.
The Genesis of Windows Mobile: A Response to the Mobile Revolution
The late 1990s witnessed the rise of mobile devices, primarily in the form of cellular phones. Recognizing the potential of this emerging market, Microsoft embarked on a journey to create a mobile operating system that could rival the growing popularity of Palm OS and Symbian.
In 2000, Microsoft unveiled its first foray into the mobile space: Windows CE (Compact Edition). Designed for devices with limited resources, Windows CE offered a stripped-down version of the familiar Windows desktop experience. This initial release paved the way for the development of Windows Mobile, a more comprehensive platform aimed at the burgeoning mobile market.
Windows Mobile: A Platform for Pocket PCs and Smartphones
Windows Mobile officially debuted in 2002, building upon the foundation of Windows CE. It was designed specifically for handheld devices, primarily targeting the then-popular "Pocket PC" category, which featured devices with touchscreens and stylus input. Windows Mobile offered a user interface that resembled the Windows desktop, featuring a Start menu, taskbar, and a familiar folder-based file system.
Key features of Windows Mobile included:
- Integration with Microsoft Office: Users could seamlessly view and edit Microsoft Office documents, enhancing productivity on the go.
- ActiveSync: This technology enabled seamless synchronization of data between mobile devices and desktop computers, ensuring data consistency across platforms.
- Windows Media Player: Windows Mobile included a built-in media player, allowing users to enjoy music, videos, and podcasts on their devices.
- Internet Explorer: Users could access the web through a dedicated browser, providing access to online content and services.
- Support for various applications: Windows Mobile supported a wide range of applications, including productivity tools, games, and utilities, expanding the functionality of mobile devices.
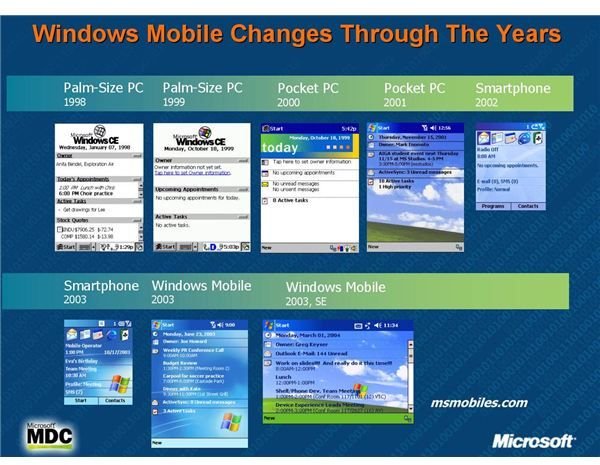
Evolution of Windows Mobile: From Pocket PCs to Smartphones
Over the years, Windows Mobile underwent several iterations, incorporating new features and technologies to keep pace with the evolving mobile landscape. Key milestones in the evolution of Windows Mobile include:
- Windows Mobile 2003: This release introduced improvements to the user interface, enhanced multimedia support, and introduced the "Today" screen, providing quick access to essential information.
- Windows Mobile 5.0: This version brought a significant redesign to the user interface, simplifying navigation and enhancing touch-based interactions. It also introduced support for Wi-Fi connectivity, expanding mobile internet access.
- Windows Mobile 6.0: This release further refined the user interface, introduced new features like GPS navigation and improved multimedia capabilities, and offered enhanced security features.
- Windows Mobile 6.5: This version focused on improving the user experience with a new "Today" screen, streamlined navigation, and enhanced multitasking capabilities.
The Rise and Fall of Windows Mobile: A Tale of Two Eras
Windows Mobile achieved significant success in its early years, particularly in the Pocket PC market. Devices like the HP iPAQ and the Dell Axim were popular choices for professionals and mobile enthusiasts. However, the rise of touchscreen-based smartphones, led by the iPhone and Android devices, marked a turning point for Windows Mobile.
The user interface of Windows Mobile, while familiar to Windows users, struggled to adapt to the touch-centric approach embraced by competitors. Additionally, the platform faced challenges in terms of app availability and developer support, as developers increasingly focused on the rapidly growing Android and iOS ecosystems.
Windows Phone: A New Beginning, But Ultimately a Short-Lived Hope
In 2010, Microsoft launched Windows Phone, a complete overhaul of its mobile operating system. This new platform featured a tile-based user interface, a focus on social integration, and a streamlined app ecosystem. Windows Phone aimed to differentiate itself from the competition with its unique design and user experience.
Despite initial positive reception, Windows Phone faced an uphill battle against the established dominance of Android and iOS. While it gained some traction in specific markets, it struggled to achieve widespread adoption. Microsoft’s acquisition of Nokia in 2013 brought a renewed push for Windows Phone, but ultimately, it failed to capture a significant share of the market.
The Legacy of Windows Mobile: A Vital Stepping Stone in Mobile Innovation
While Windows Mobile’s reign in the mobile world was ultimately short-lived, its impact on the evolution of mobile operating systems cannot be ignored. It introduced several key features that became commonplace in later platforms, including:
- Integration with desktop software: The seamless synchronization of data between mobile devices and desktop computers, pioneered by ActiveSync, laid the groundwork for cloud-based data management and cross-platform compatibility.
- Touchscreen interaction: While not the first to embrace touchscreens, Windows Mobile’s evolution towards a more touch-friendly interface paved the way for the touchscreen-centric approach that defines mobile devices today.
- Multimedia capabilities: Windows Mobile’s focus on multimedia features, including music playback and video support, contributed to the development of mobile devices as entertainment hubs.
FAQs about Microsoft Windows Mobile
1. What is the latest version of Windows Mobile?
Windows Mobile 6.5 was the final major release of the operating system. Microsoft discontinued support for Windows Mobile in 2014, focusing its efforts on Windows Phone and later, Windows 10 Mobile.
2. What are some popular devices that ran Windows Mobile?
Popular Windows Mobile devices included the HP iPAQ, Dell Axim, HTC Touch, and various models from Samsung, LG, and others.
3. What were the main reasons for the decline of Windows Mobile?
The decline of Windows Mobile was attributed to several factors, including:
- Lack of app availability and developer support: The platform faced a significant gap in app availability compared to Android and iOS, making it less appealing to users.
- Outdated user interface: The user interface of Windows Mobile struggled to adapt to the touch-centric approach adopted by competitors.
- Limited hardware options: The number of devices running Windows Mobile was significantly less than those running Android and iOS, limiting user choice.
4. Is Windows Mobile still used today?
Windows Mobile is no longer supported or actively used. Devices running Windows Mobile are considered legacy devices, and software updates or security patches are no longer available.
5. What is the difference between Windows Mobile and Windows Phone?
Windows Mobile and Windows Phone are distinct operating systems. Windows Mobile was designed for Pocket PCs and early smartphones, while Windows Phone was a complete overhaul of the mobile platform, introducing a new tile-based user interface and a focus on touch-based interactions.
Tips for Using Windows Mobile Devices
While Windows Mobile is no longer supported, users who still rely on legacy devices can consider the following tips:
- Back up data regularly: Ensure that important data is backed up to a computer or cloud storage service to prevent data loss.
- Use compatible applications: Only use applications designed for Windows Mobile to avoid compatibility issues.
- Avoid connecting to unsecured networks: Be cautious when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, as Windows Mobile devices may not have the latest security updates.
- Keep the operating system updated: If any updates are available for the specific version of Windows Mobile, ensure the device is updated to improve security and performance.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation and a Lesson in Adaptation
The story of Microsoft Windows Mobile is a testament to the dynamic nature of the technology industry. While it failed to achieve the widespread success of its competitors, it played a crucial role in shaping the early stages of mobile computing. Windows Mobile introduced key concepts and features that became integral to modern mobile operating systems, demonstrating the importance of adaptation and innovation in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. While its legacy may be primarily historical, the lessons learned from its rise and fall continue to influence the development of mobile operating systems today.

![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Legacy of Innovation: Exploring the Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!